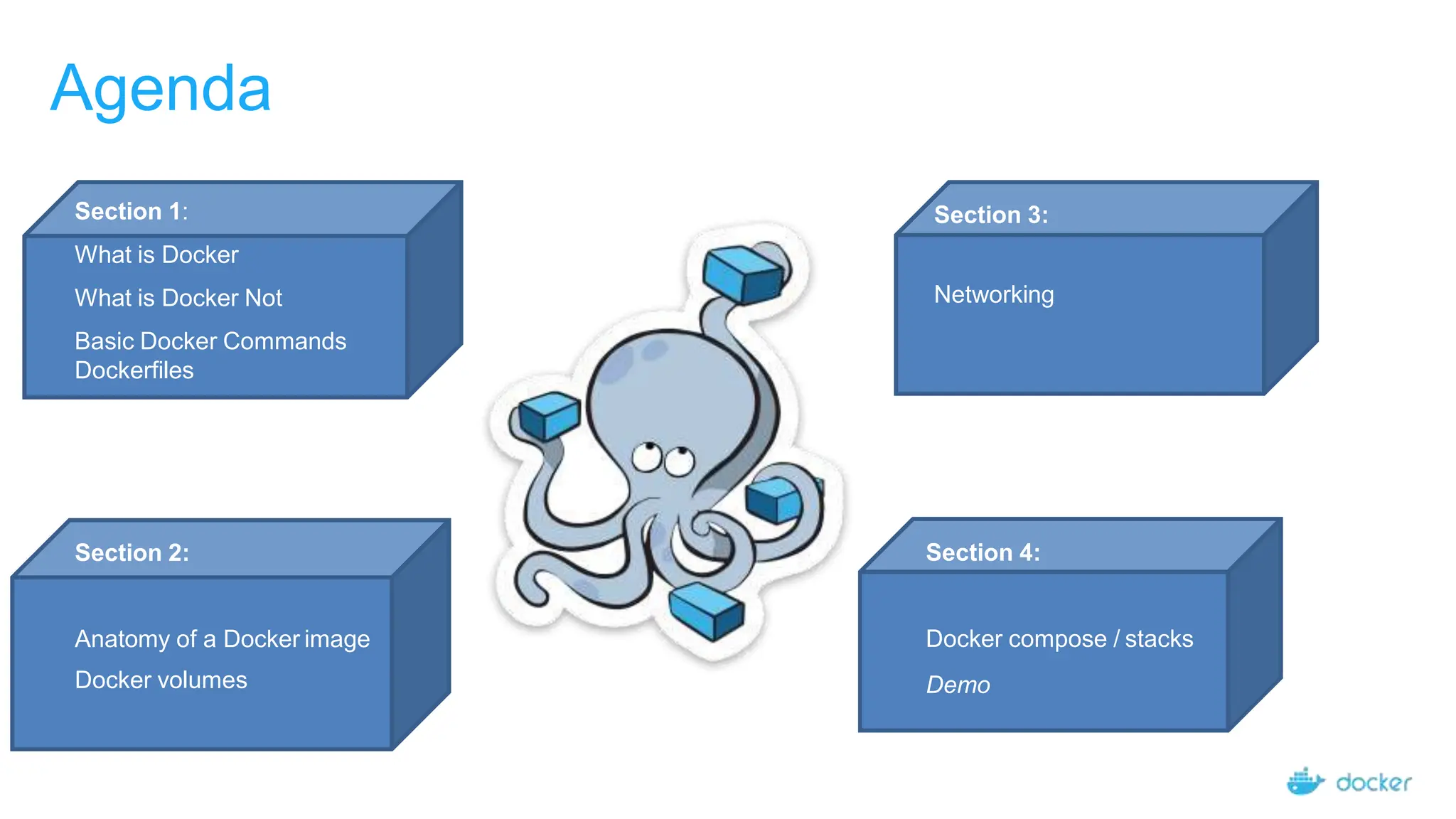
This document provides an introduction and overview of Docker including:
- Docker allows packaging applications with dependencies to create standardized units for software development and deployment called containers.
- Key Docker concepts include images, which are templates for creating containers, and containers which are runtime instances of images that execute applications.
- Basic Docker commands are demonstrated for pulling images, running containers, building images from Dockerfiles, and pushing images to registries.
- Networking, volumes, and Docker Compose/stacks for defining and running multi-container applications are also introduced.