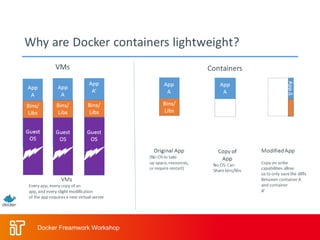
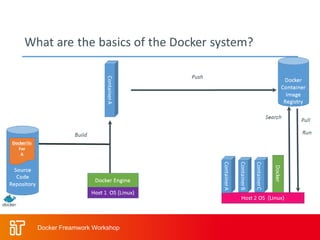
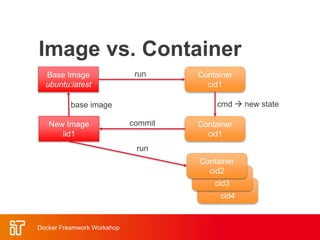
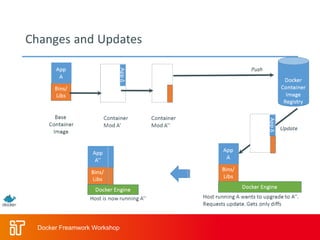
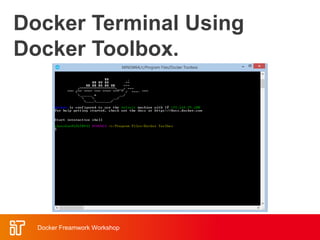
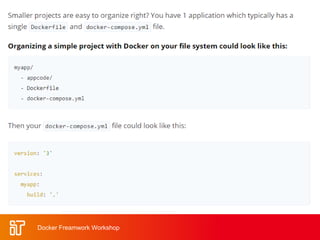
The two-day workshop agenda covers Docker concepts like containers, images, and Dockerfiles. It includes hands-on labs for building Docker images, running containers with resource limits, mounting volumes, publishing ports, and using Docker Compose. Additional topics are Docker Swarm for clustering, Docker registries for storing images, and monitoring Docker systems. The goal is to teach attendees how to use Docker for building, deploying and managing applications across infrastructure.


![Docker: Name
docker [naut.]: der Dockarbeiter, der
Hafenarbeiter
Source: leo.org
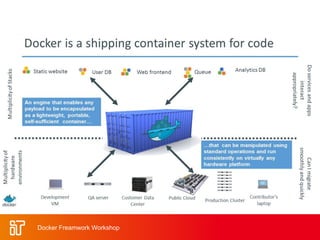
• Provide a uniformed wrapper around a
software package: «Build, Ship and Run Any
App, Anywhere» [www.docker.com]
– Similar to shipping containers: The
container is always the same, regardless
of the contents and thus fits on all trucks,
cranes, ships, ...
[www.docker.com]
Docker Freamwork Workshop](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dockerfreamwork-200213031121/85/Docker-framework-4-320.jpg)

![Docker Technology
• libvirt: Platform Virtualization
• LXC (LinuX Containers): Multiple
isolated Linux systems (containers)
on a single host
• Layered File System
[Source: https://docs.docker.com/terms/layer/]
Docker Freamwork Workshop](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dockerfreamwork-200213031121/85/Docker-framework-9-320.jpg)

![Hello World
Simple Command - Ad-Hoc
Container
• docker run ubuntu echo
Hello World
– docker images [-a]
– docker ps –a
Docker Freamwork Workshop](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dockerfreamwork-200213031121/85/Docker-framework-15-320.jpg)





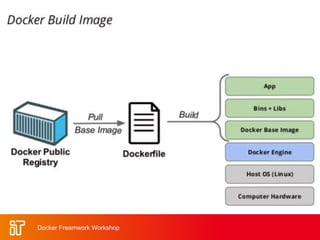
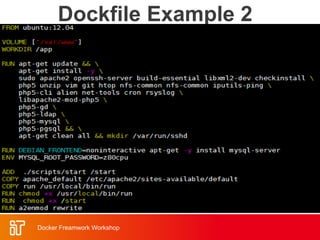
![Dockerfile Example
• Dockerfile:
– FROM ubuntu
ENV DOCK_MESSAGE Hello My World
ADD dir /files
CMD ["bash", "someScript"]
• docker build [DockerFileDir]
• docker inspect [imageId]
Docker Freamwork Workshop](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dockerfreamwork-200213031121/85/Docker-framework-28-320.jpg)





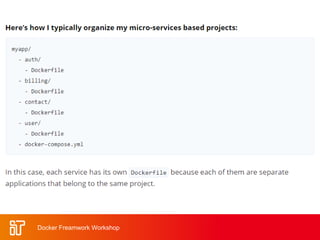
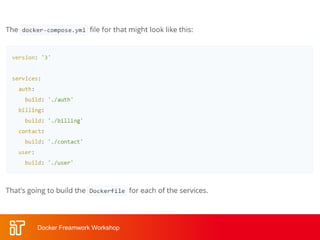


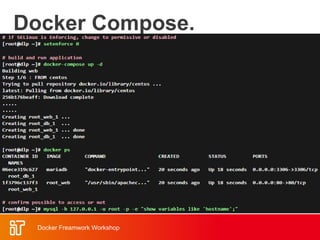

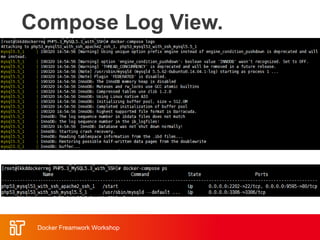



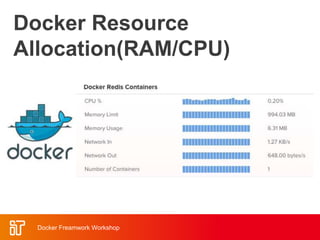
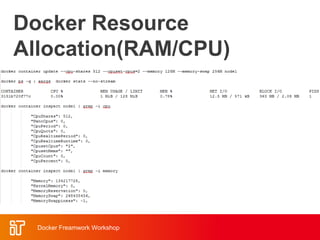
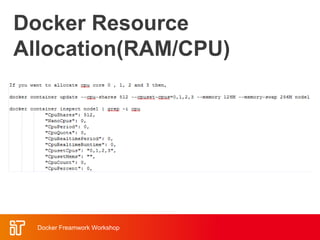
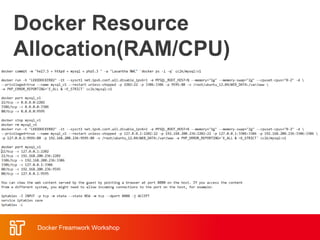

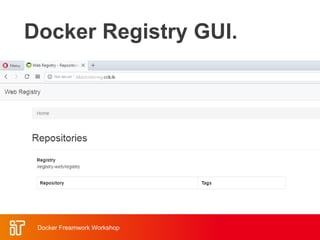


![Docker Hub
• Public repository of Docker images
– https://hub.docker.com/
– docker search [term]
• Automated: Has been
automatically built from Dockerfile
– Source for build is available on
GitHub
Docker Freamwork Workshop](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dockerfreamwork-200213031121/85/Docker-framework-58-320.jpg)