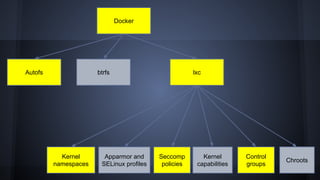
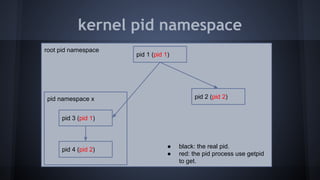
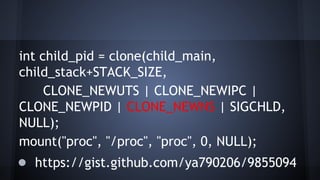
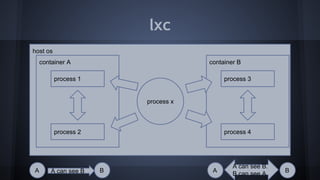
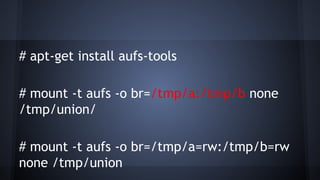
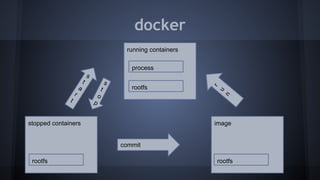
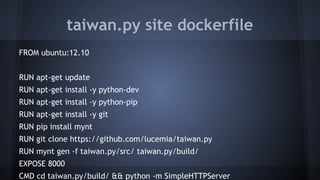
This document discusses Docker concepts and implementation in Chinese. It covers Linux kernel namespaces, seccomp, cgroups, LXC, and Docker. Namespaces isolate processes and resources between containers. Cgroups control resource limits and prioritization. LXC provides containerization tools while Docker builds on these concepts and provides an easy-to-use interface for containers. The document also provides examples of using namespaces, cgroups, LXC, and building Docker images.