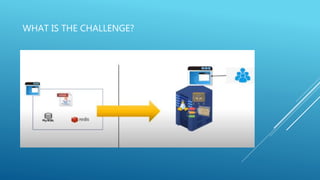
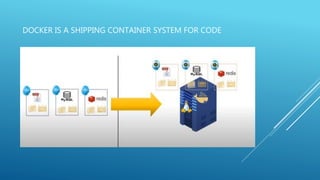
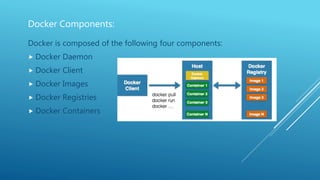
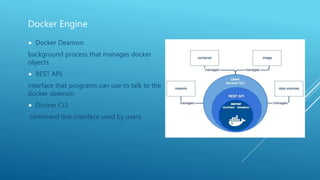
Docker is a containerization platform that allows applications and their dependencies to be packaged into standardized units called containers that can run on any infrastructure regardless of the underlying operating system. The key components of Docker include images which serve as templates for building containers, a daemon that manages the containers, a client to interact with the daemon, and a registry to store and distribute images. Containers offer isolation, portability and scalability compared to virtual machines.