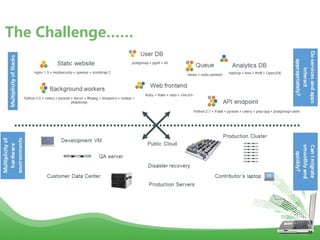
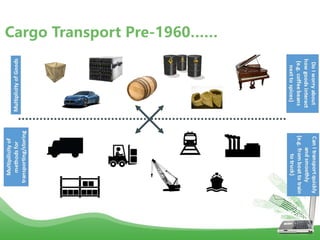
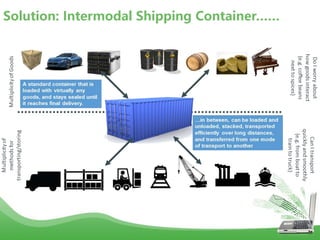
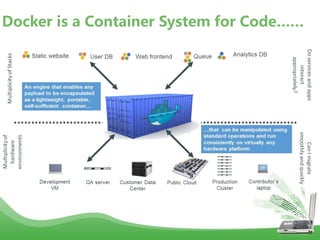
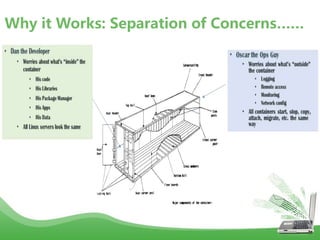
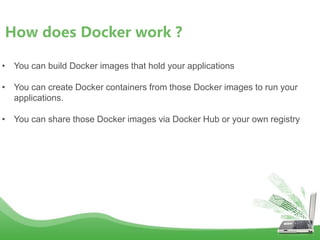
- Docker is an open platform for developers and sysadmins to build, ship, and run distributed applications. It allows applications to run securely isolated in user-defined containers across any infrastructure.
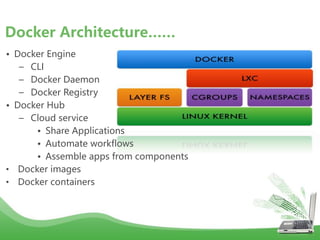
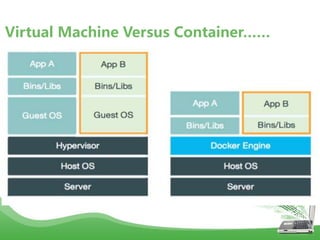
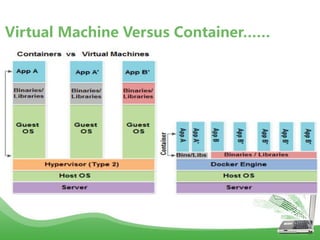
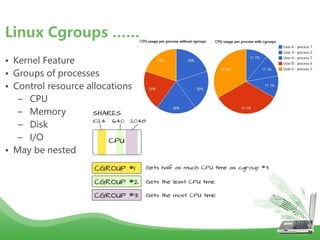
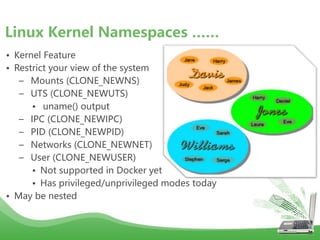
- Docker uses Linux kernel features like cgroups and namespaces to provide isolation and allocate resources only to the containers that "need" them. This makes containers lightweight and efficient.
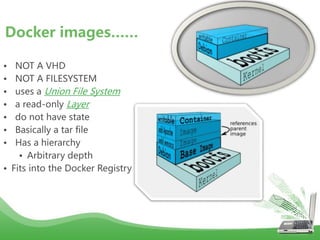
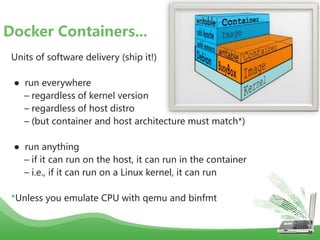
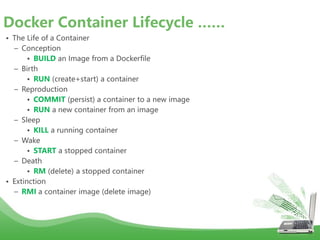
- Docker images are read-only templates that serve as the basis for containers. Images are built from Dockerfiles containing a series of commands to assemble an image. Containers are run from images and are read-write.