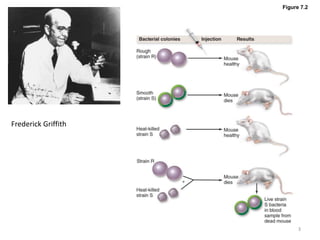
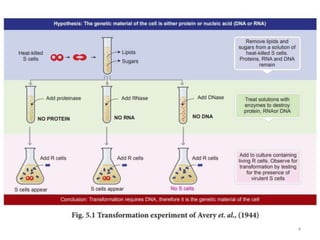
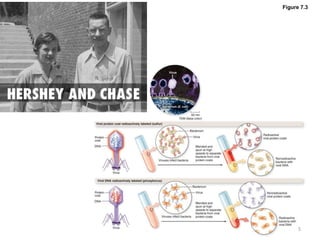
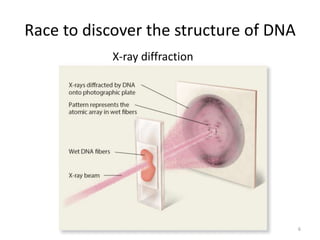
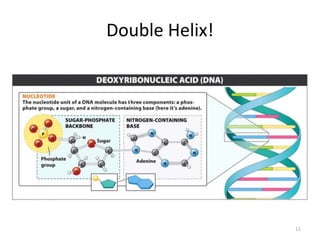
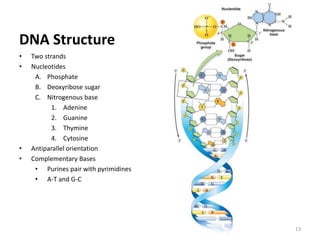
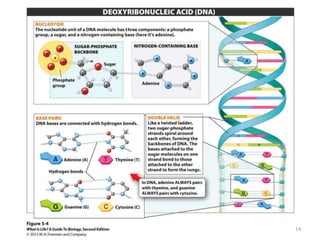
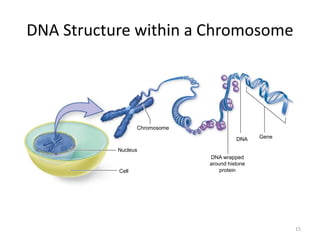
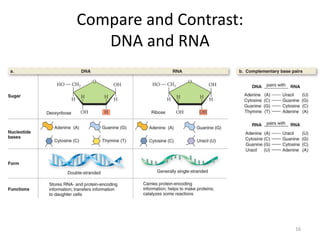
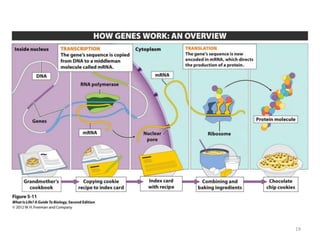
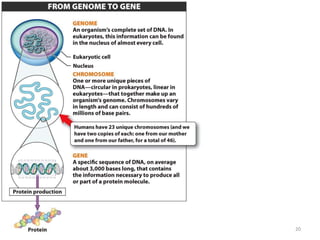
DNA was discovered in 1869, but its structure and role as the genetic material was not understood until later breakthroughs in the 20th century. In 1953, Watson and Crick published their discovery of the double helix structure of DNA, with two strands coiled around each other and connected through complementary base pairing of adenine and thymine and cytosine and guanine. This breakthrough explained DNA's role in inheritance and provided the foundation for modern genetics and molecular biology.