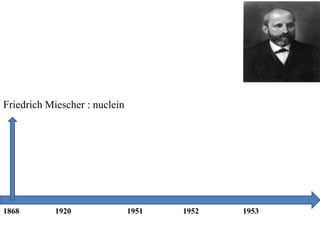
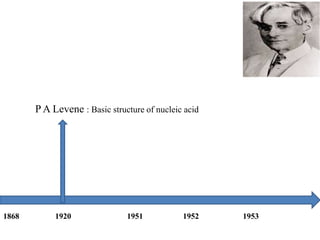
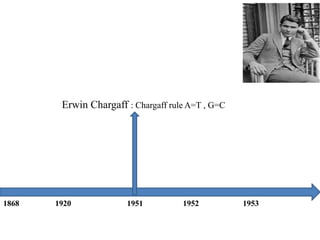
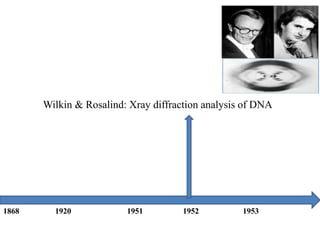
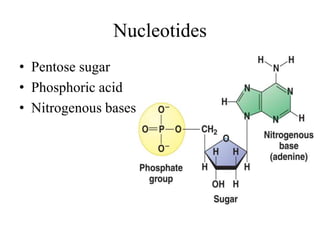
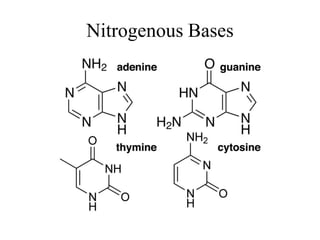
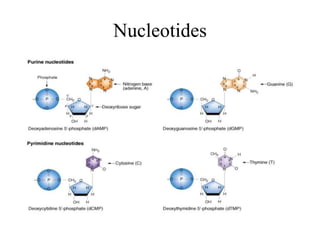
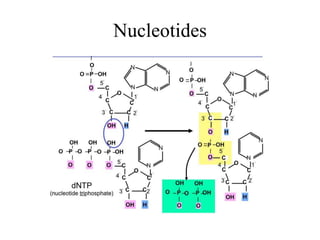
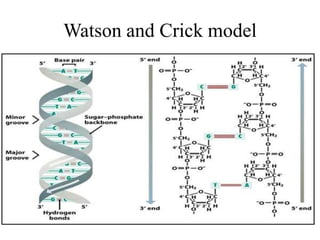
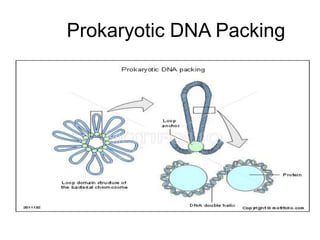
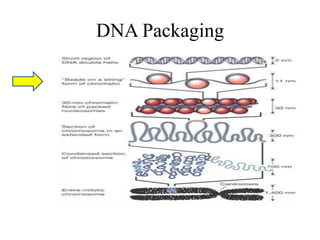
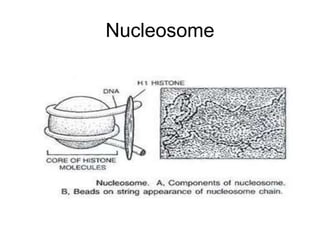
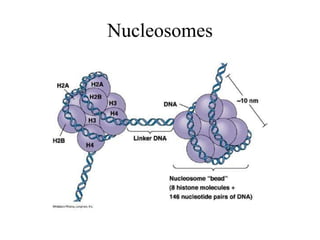
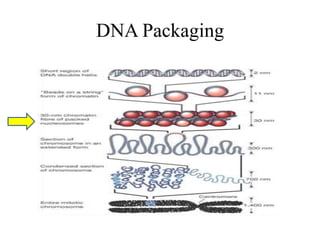
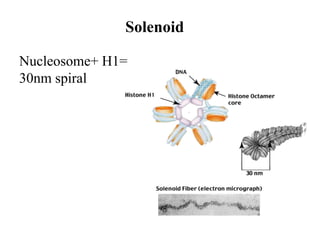
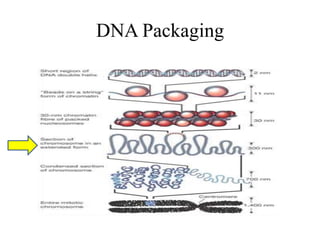
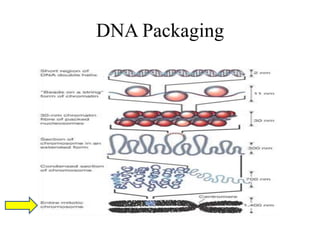
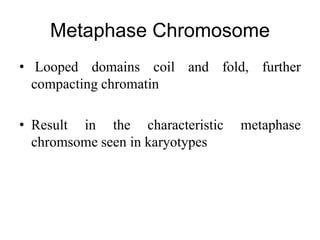
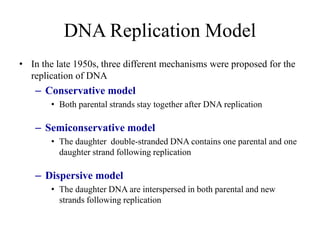
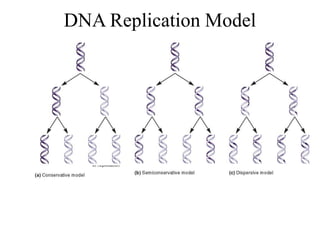
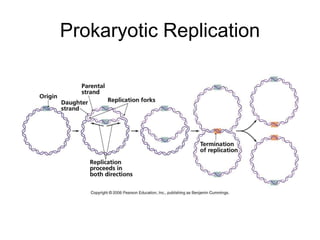
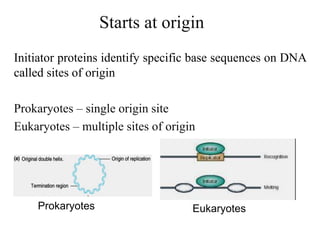
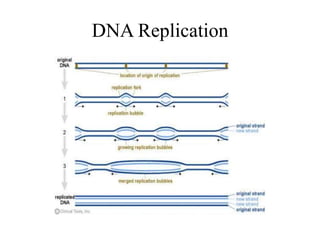
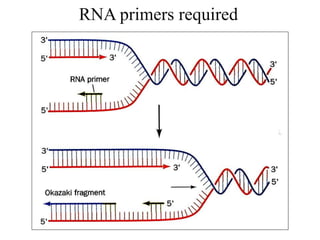
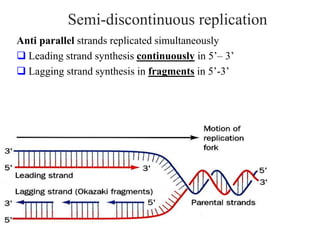
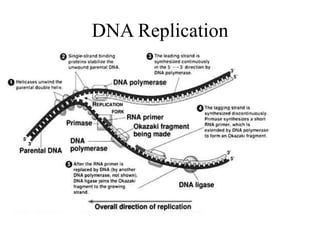
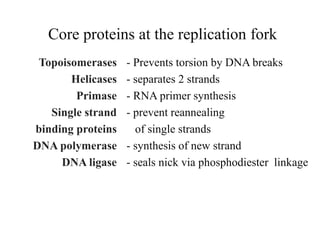
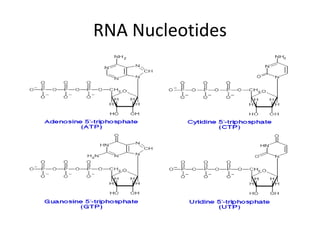
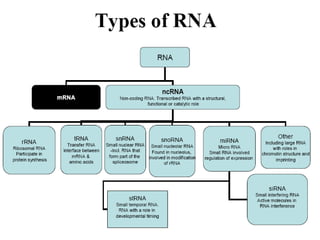
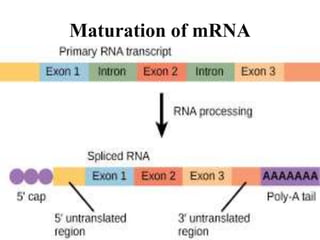
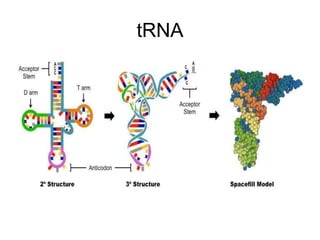
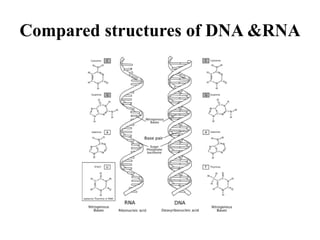
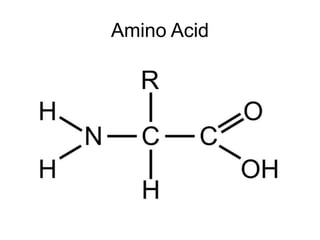
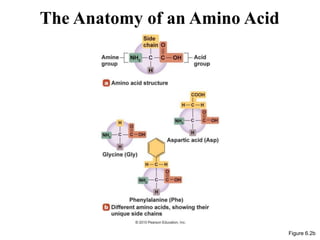
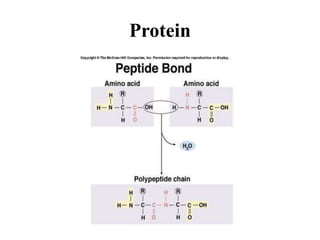
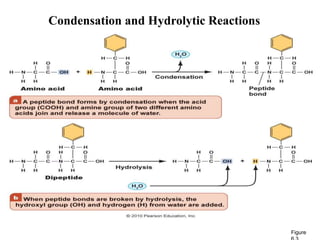
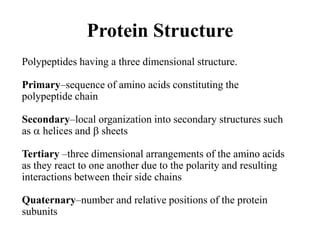
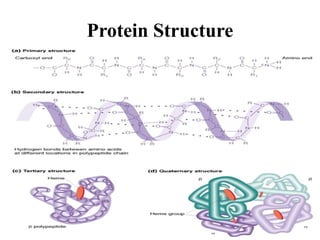
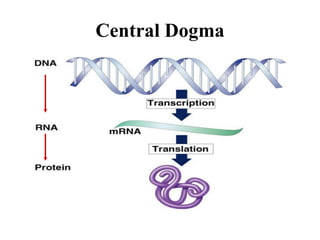
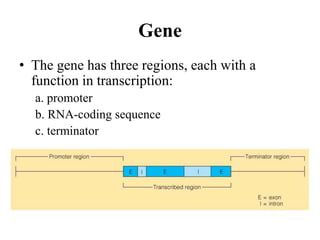
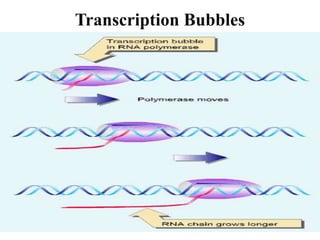
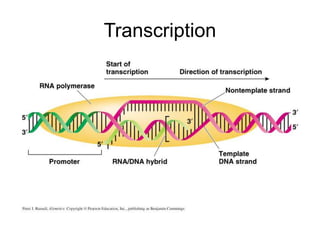
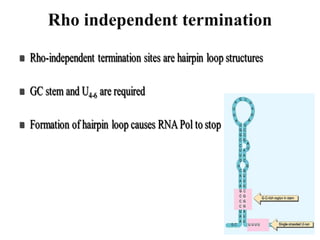
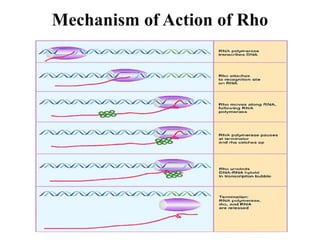
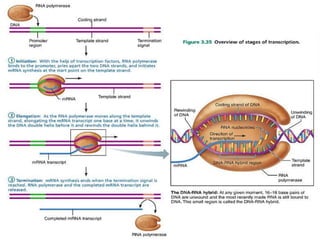
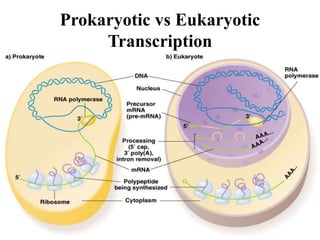
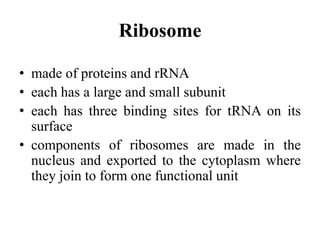
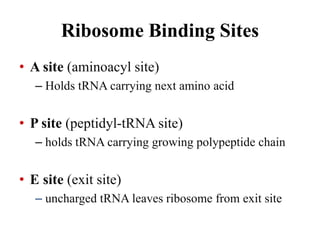
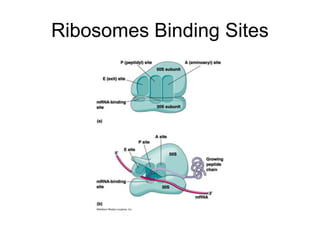
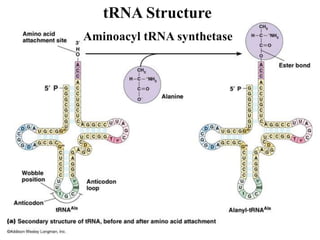
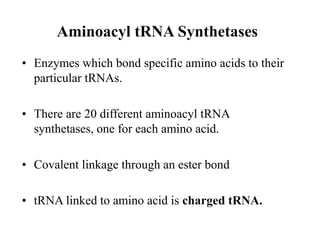
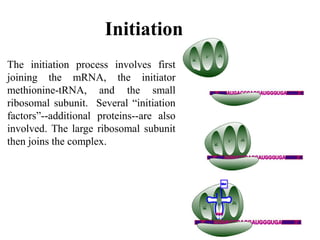
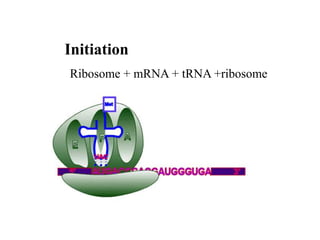
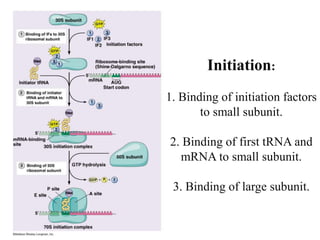
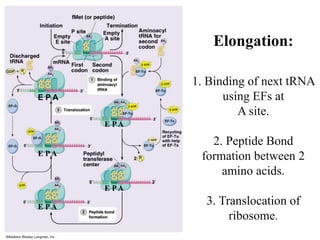
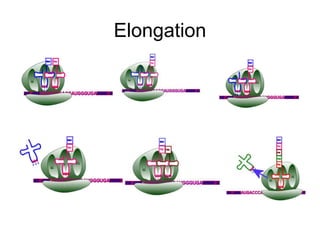
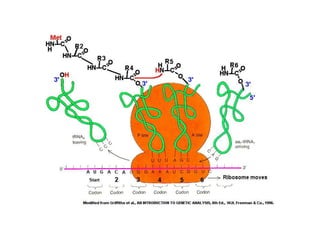
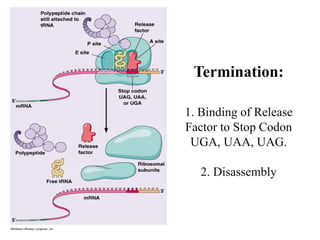
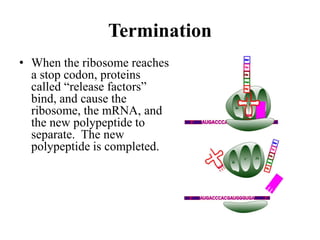
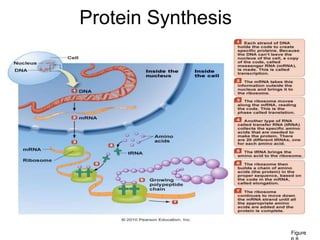
The document discusses the key features and interrelationships between DNA, RNA, and proteins. It covers the central dogma where DNA is transcribed into RNA which is then translated into protein. DNA stores genetic information and its structure was discovered by Watson and Crick. RNA acts as an intermediary between DNA and proteins, and there are three main types - mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA. Proteins are made of amino acids and have complex 3D structures that determine their function. The central dogma flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to protein is described.