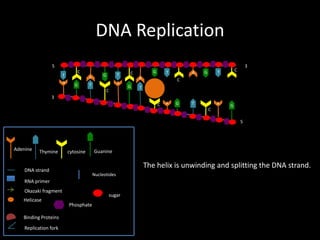
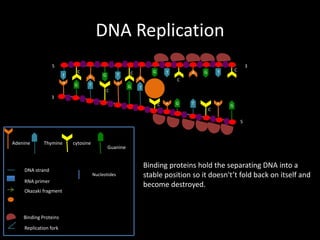
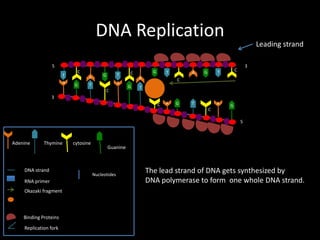
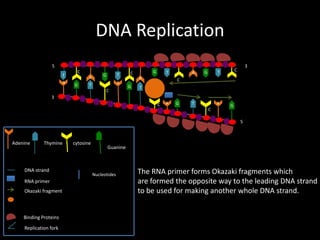
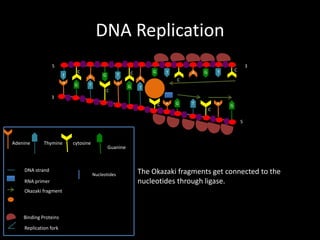
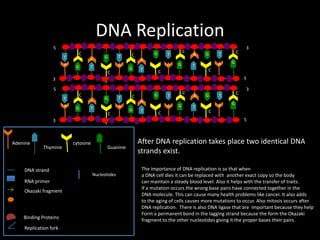
DNA replication produces two identical DNA strands from one original DNA strand. The DNA unwinds and separates, with binding proteins holding the strands apart. As the replication fork moves along the DNA, DNA polymerase synthesizes a new complementary strand. On the leading strand, DNA is synthesized continuously. On the lagging strand, RNA primers initiate short Okazaki fragments that are later joined by DNA ligase to form a continuous strand. After replication, two identical DNA double helices exist to maintain the genetic information during cell division.