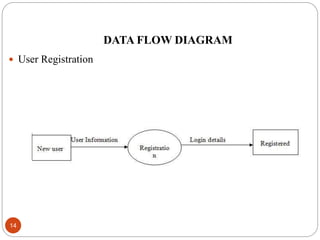
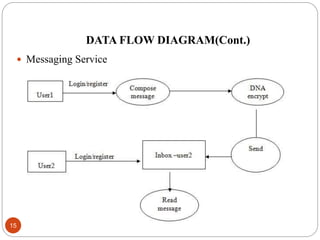
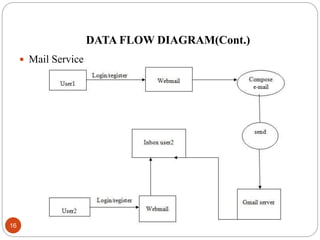
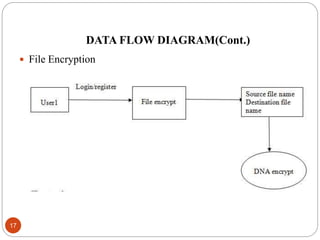
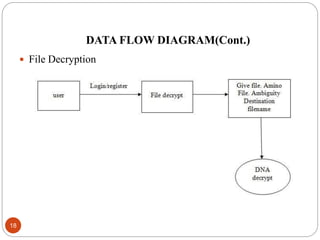
This document describes a proposed DNA-based cryptography and authentication system. The system aims to provide secure data transmission across networks using a novel DNA-based approach. It involves encrypting plaintext messages into DNA sequences using symmetric or asymmetric encryption algorithms. The encrypted DNA sequences can then be transmitted and decrypted back to the original plaintext. The proposed system implements a double layer of encryption using both RSA and DNA-based cryptography for enhanced security. It is intended to securely transmit messages, emails, and files across both local and wide area networks.





![6
SURVEY COMPARISON REPORT
S.
No
METHODS ADVANTAGE DISADVANTAGE
1 DNA based
implementation of
YAEA encryption
algorithm[2006]
•Real message is not
transferred over network.
•Scalable for large digital
information products.
•Size of plain text
increases the
encryption and
decryption time.
2 DNA encryption
based on matrix
manipulation.[2008]
•Always get new cipher
data from same plain text.
•It include only basic
operation and security
only depends on key.
3 Encryption scheme
using DNA
technology.[2008]
•Prevent attack from a
possible word as PCR
primers.
•Cost of encryption is
low.
•Security can depend
only on decryption
key.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f435906d-dcae-48ff-b098-ad5a8bd4481d-150907151826-lva1-app6891/85/DNA-based-Cryptography_Final_Review-6-320.jpg)