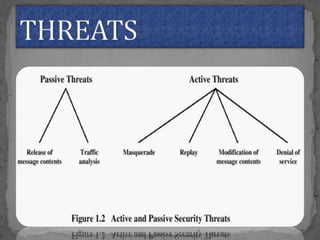
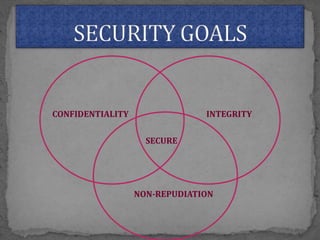
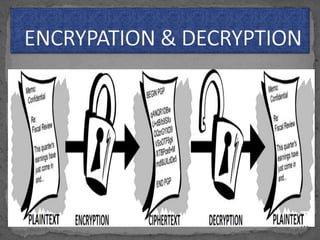
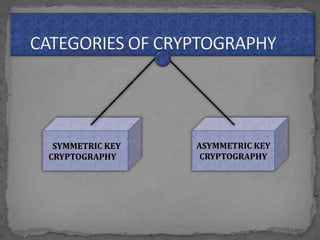
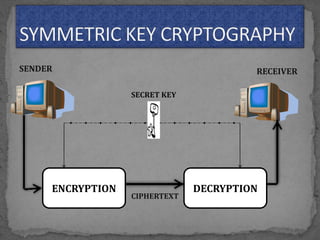
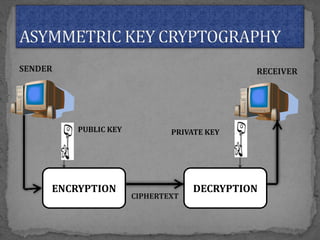
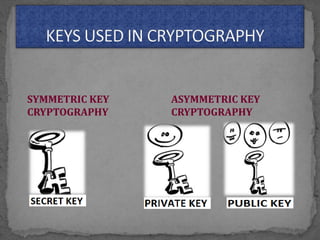
The document discusses various cryptographic concepts and algorithms. It begins with basic terms in cryptography like plain text, cipher text, encryption, decryption, and keys. It then explains symmetric and asymmetric key cryptography. Specific algorithms discussed include MD5, SHA-1, SHA-256, RIPEMD-160, and crypt. Code examples are provided to demonstrate generating hashes using these algorithms.


















![SHA-1 (Secure Hash Algorithm 1) is a set of cryptographic
hash functions designed by the National Security Agency
(NSA).[3] SHA stands for Secure Hash Algorithm.
Cryptographic hash functions are mathematical operations
run on digital data; by comparing the computed "hash" (the
output from execution of the algorithm) to a known and
expected hash value, a person can determine the data's
integrity. For example, computing the hash of a downloaded
file and comparing the result to a previously published hash
result can show whether the download has been modified or
tampered with.[4] A key aspect of cryptographic hash
functions is their collision resistance: nobody should be able
to find two different input values that result in the same hash
output.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cryptography-160630084608/85/Cryptography-28-320.jpg)

![SHA-256 is a variation of SHA-2 (Secure Hash Algorithm
2) which is a set of cryptographic hash functions designed by
the National Security Agency (NSA).[3] SHA stands for Secure
Hash Algorithm. Cryptographic hash functions are
mathematical operations run on digital data; by comparing
the computed "hash" (the output from execution of the
algorithm) to a known and expected hash value, a person can
determine the data's integrity. For example, computing the
hash of a downloaded file and comparing the result to a
previously published hash result can show whether the
download has been modified or tampered with.[4] A key
aspect of cryptographic hash functions is their collision
resistance: nobody should be able to find two different input
values that result in the same hash output.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cryptography-160630084608/85/Cryptography-30-320.jpg)





