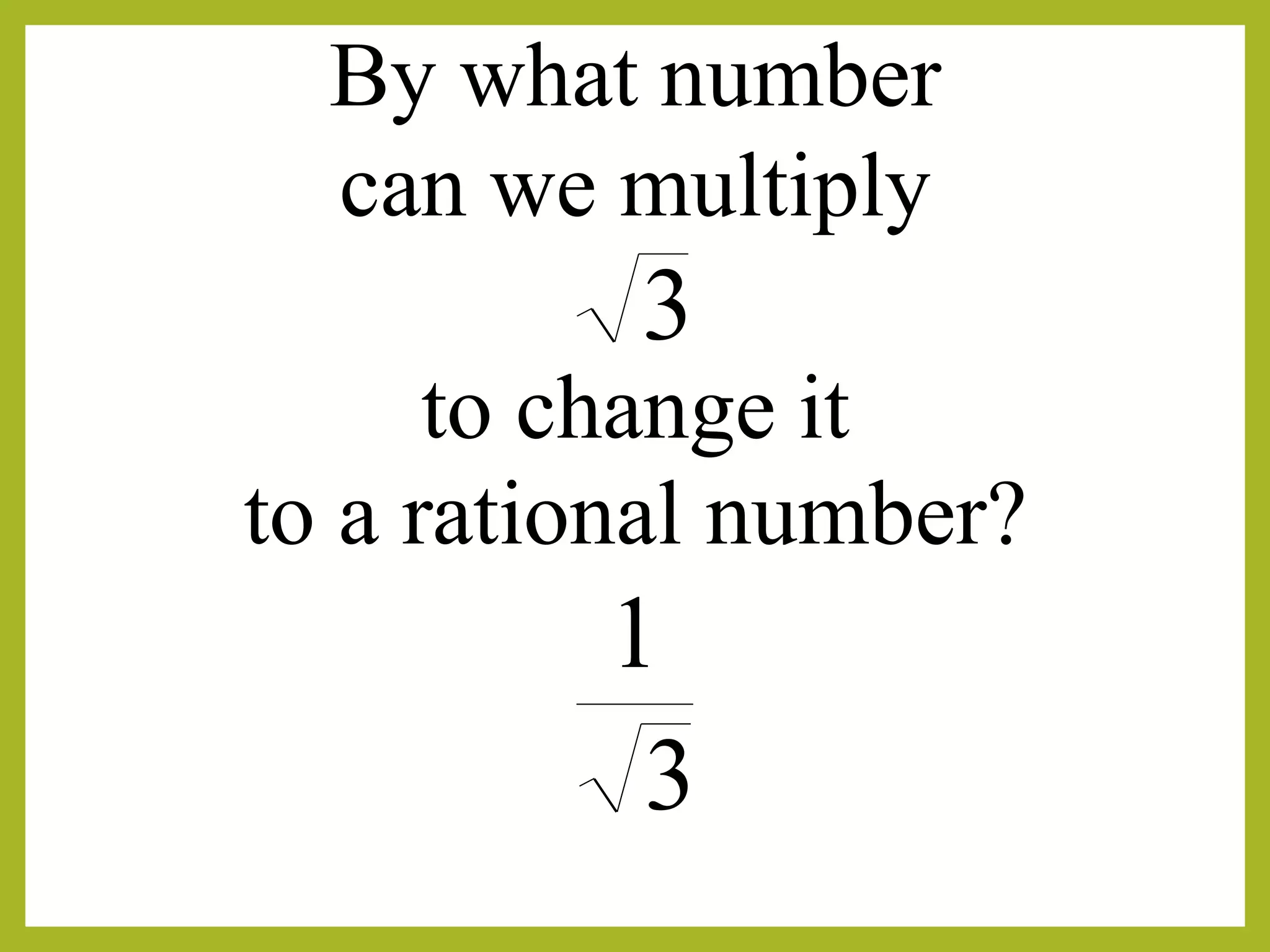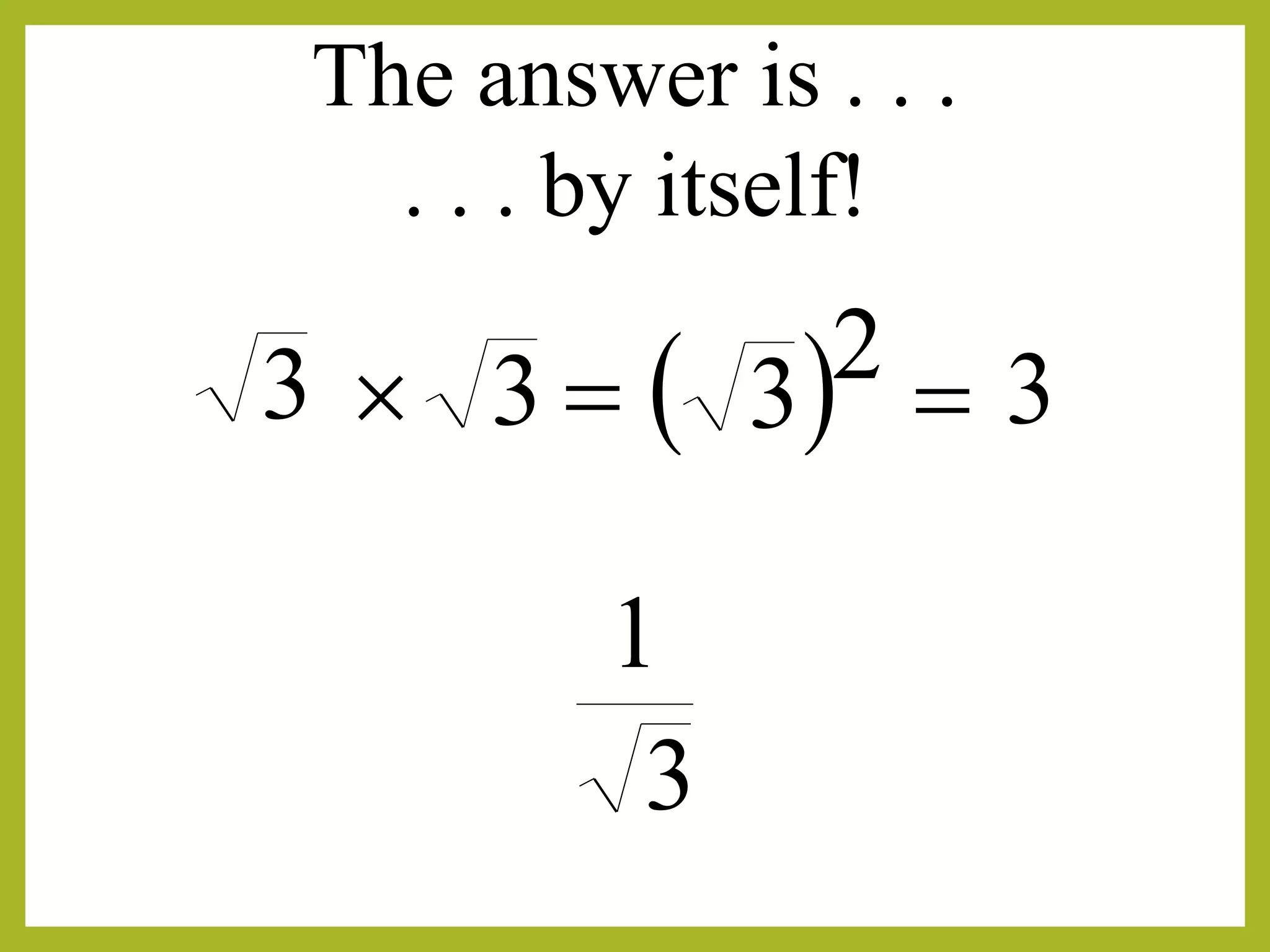Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX




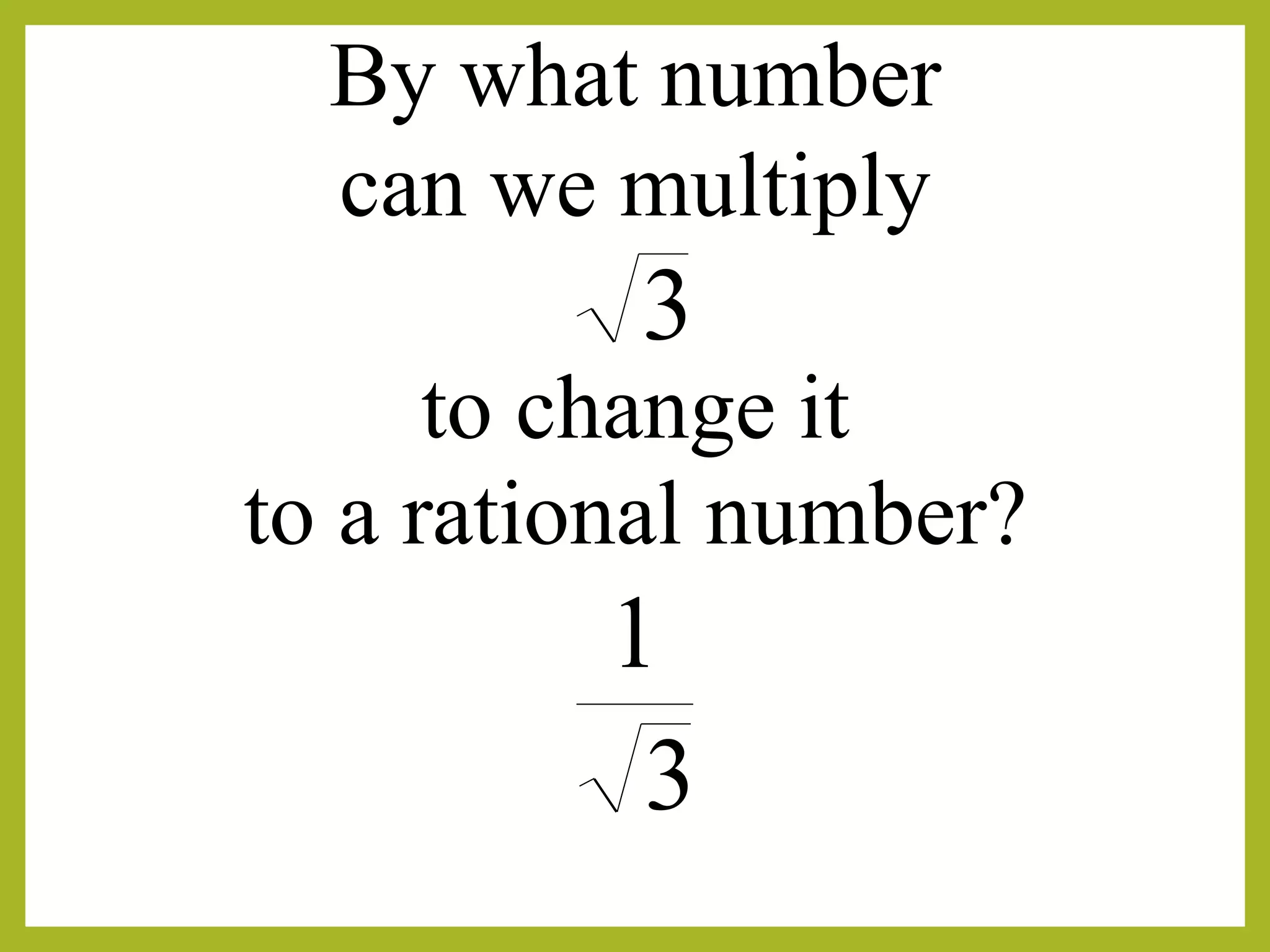
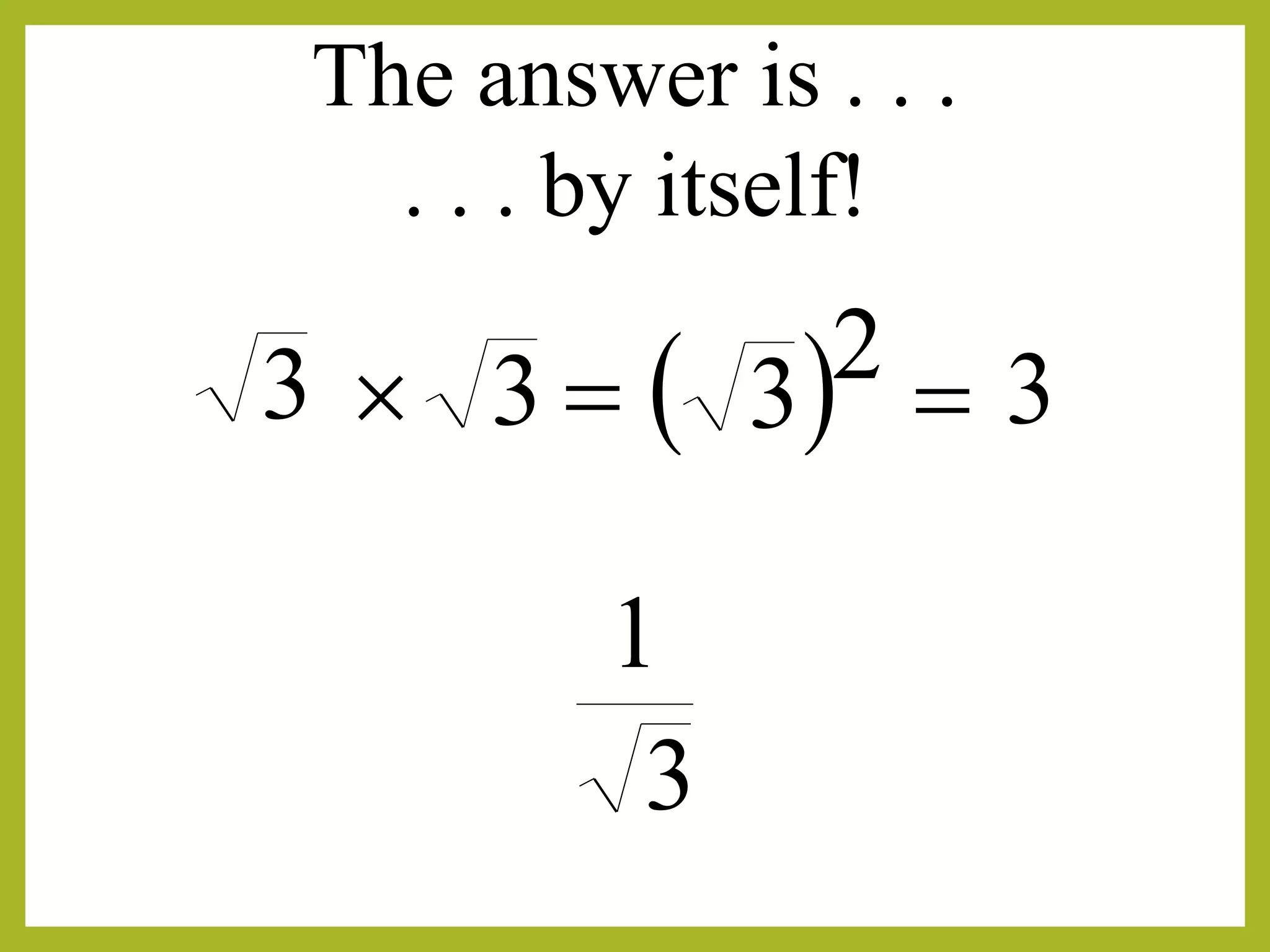

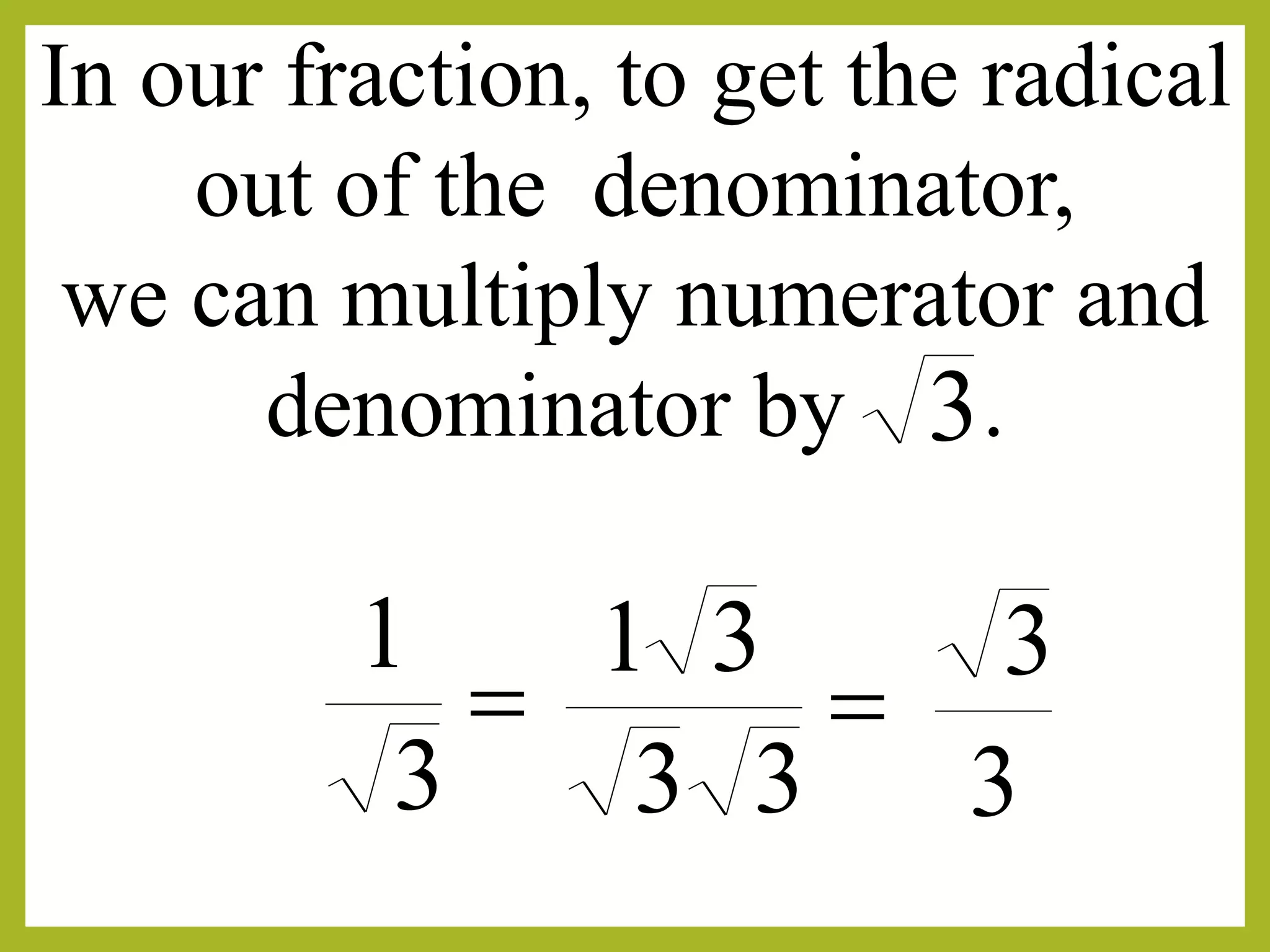
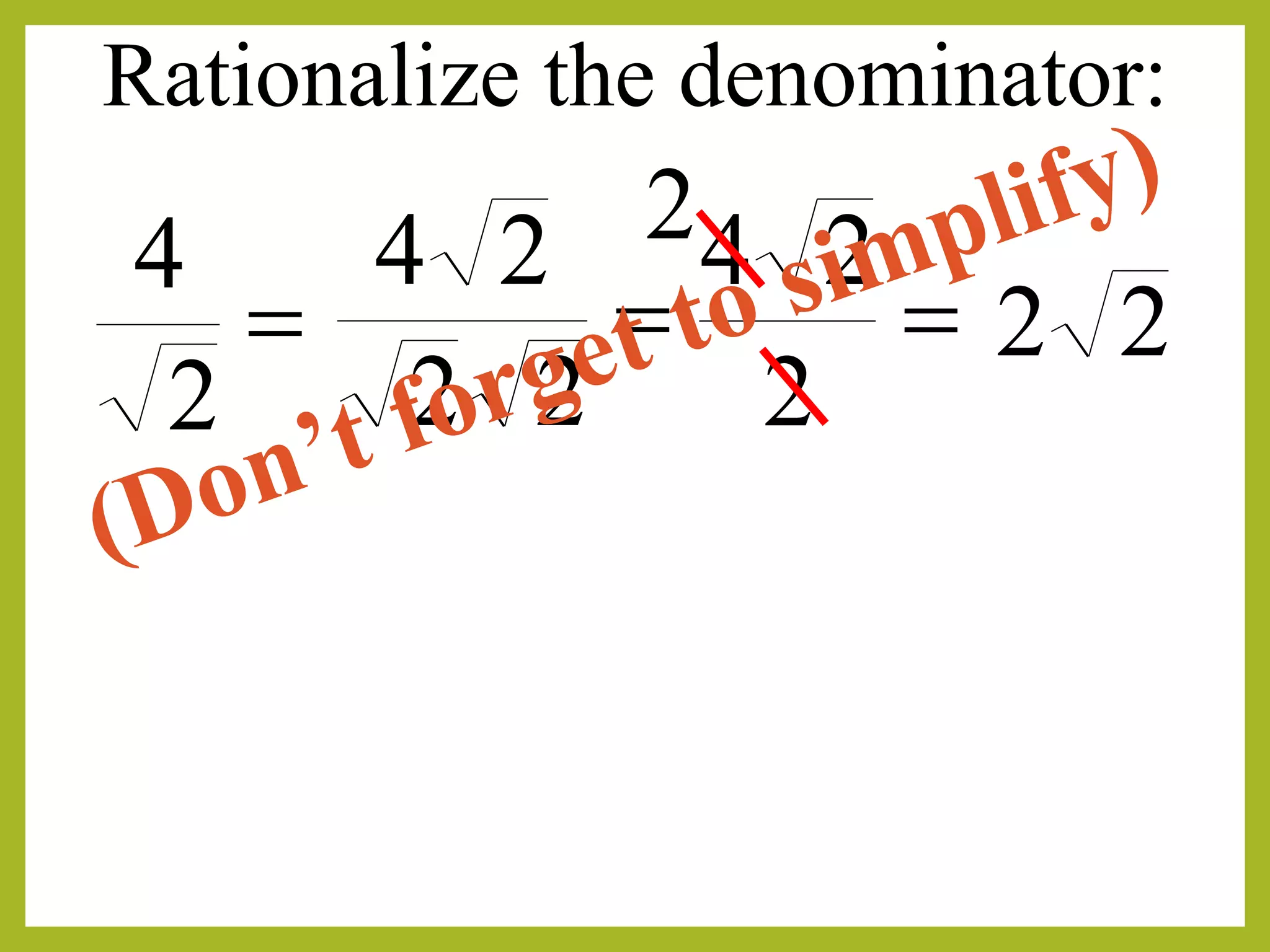
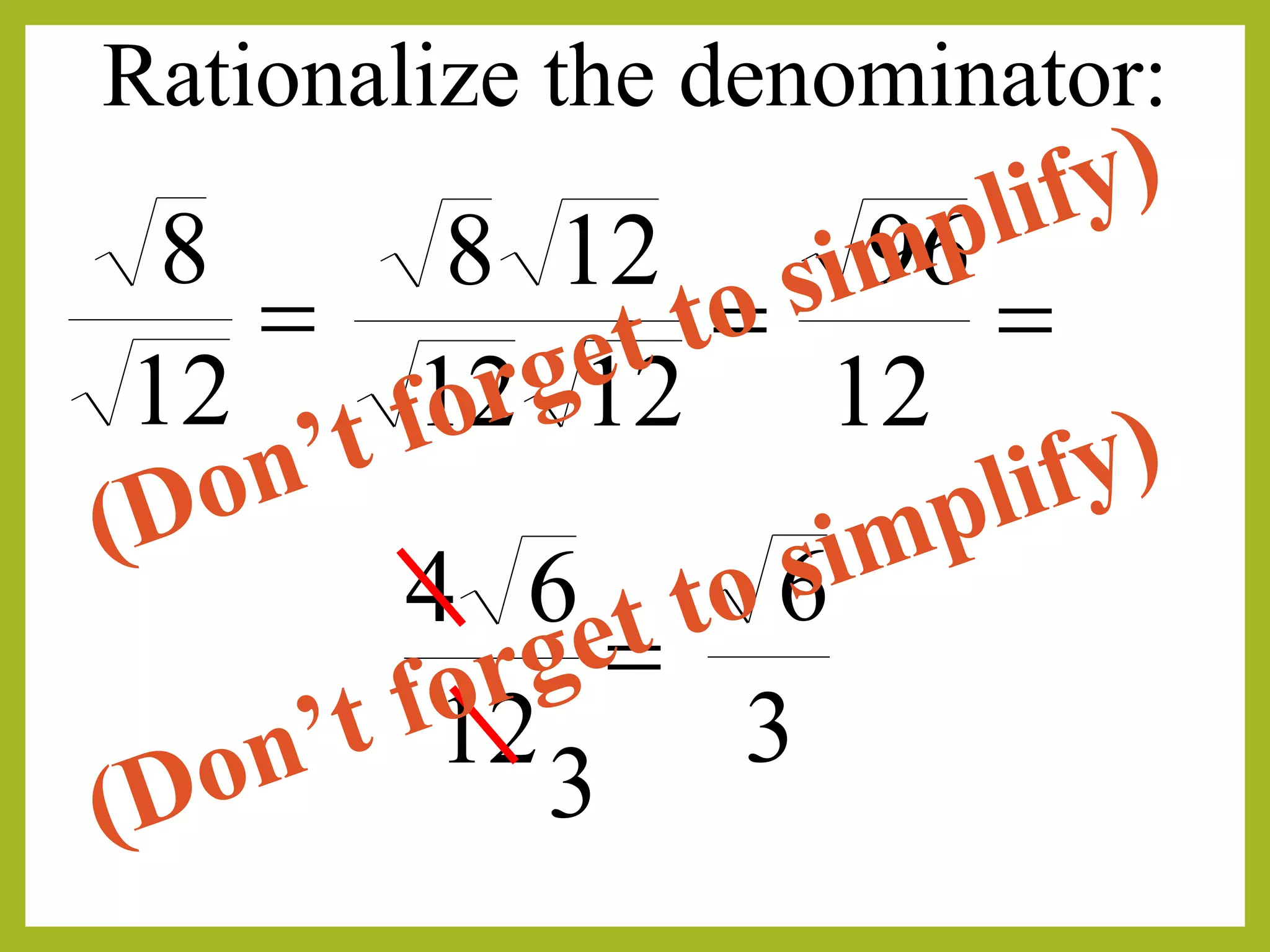

The document discusses rationalizing the denominator of a radical expression. Rationalizing means finding an equivalent expression where the denominator is a perfect square by multiplying the numerator and denominator by the radical in the denominator. This removes the radical from the denominator and makes the expression rational. For example, to rationalize 3/√3, we multiply the numerator and denominator by √3, giving (3√3)/(3) = 1.
The objective is to rationalize the denominator of a radical expression.
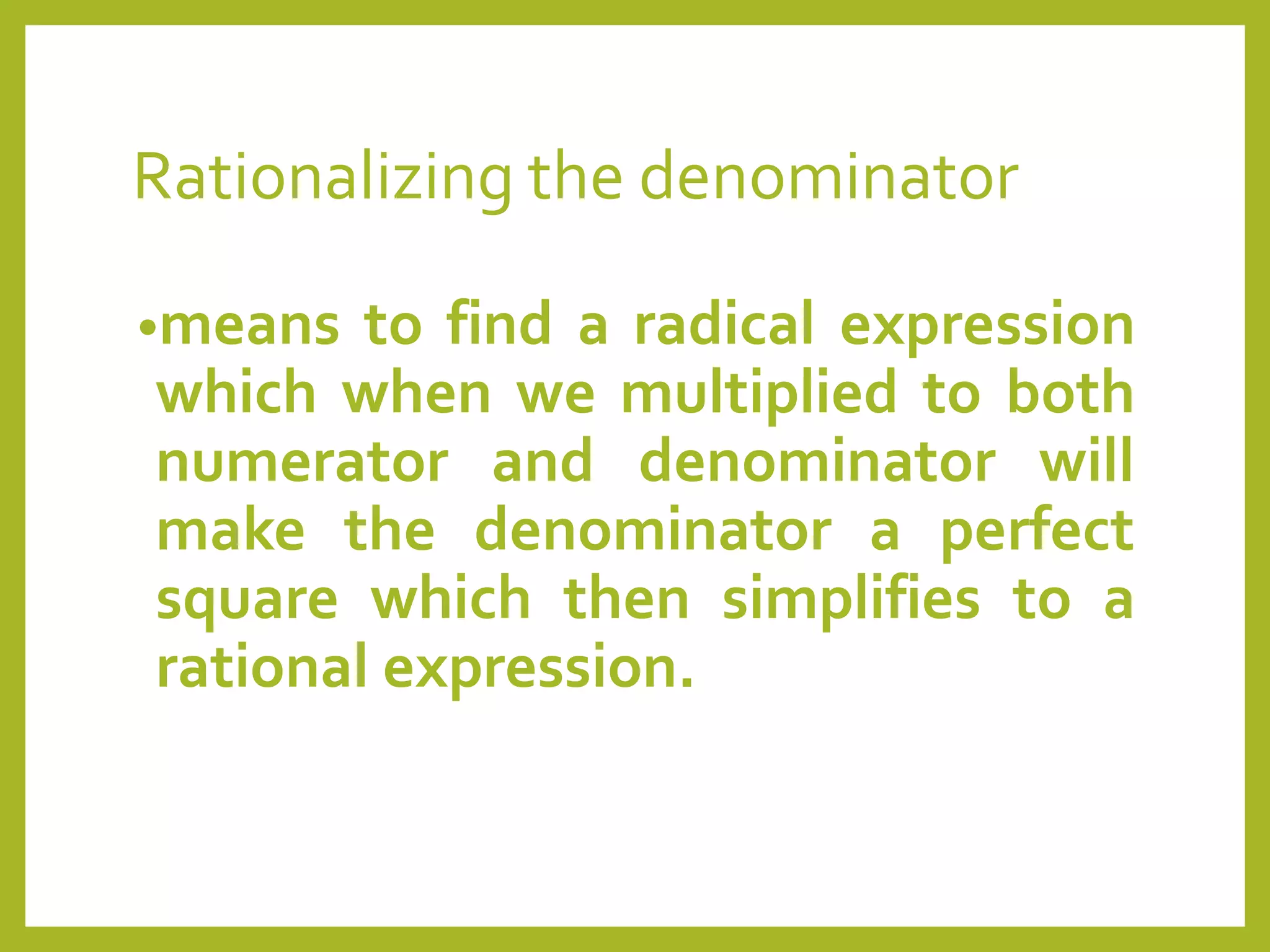
Rationalizing means multiplying by a radical expression to simplify the denominator to a perfect square.
A radical in the denominator is not simplified; rationalization eliminates the radical sign.
In mathematics, it is agreed that radicals should not remain in the denominator of a fraction.
The process to change a fraction's denominator without altering its value is explored.
To change the denominator to a rational number, we multiply it by itself.
To eliminate the radical, multiply both numerator and denominator by the radical.
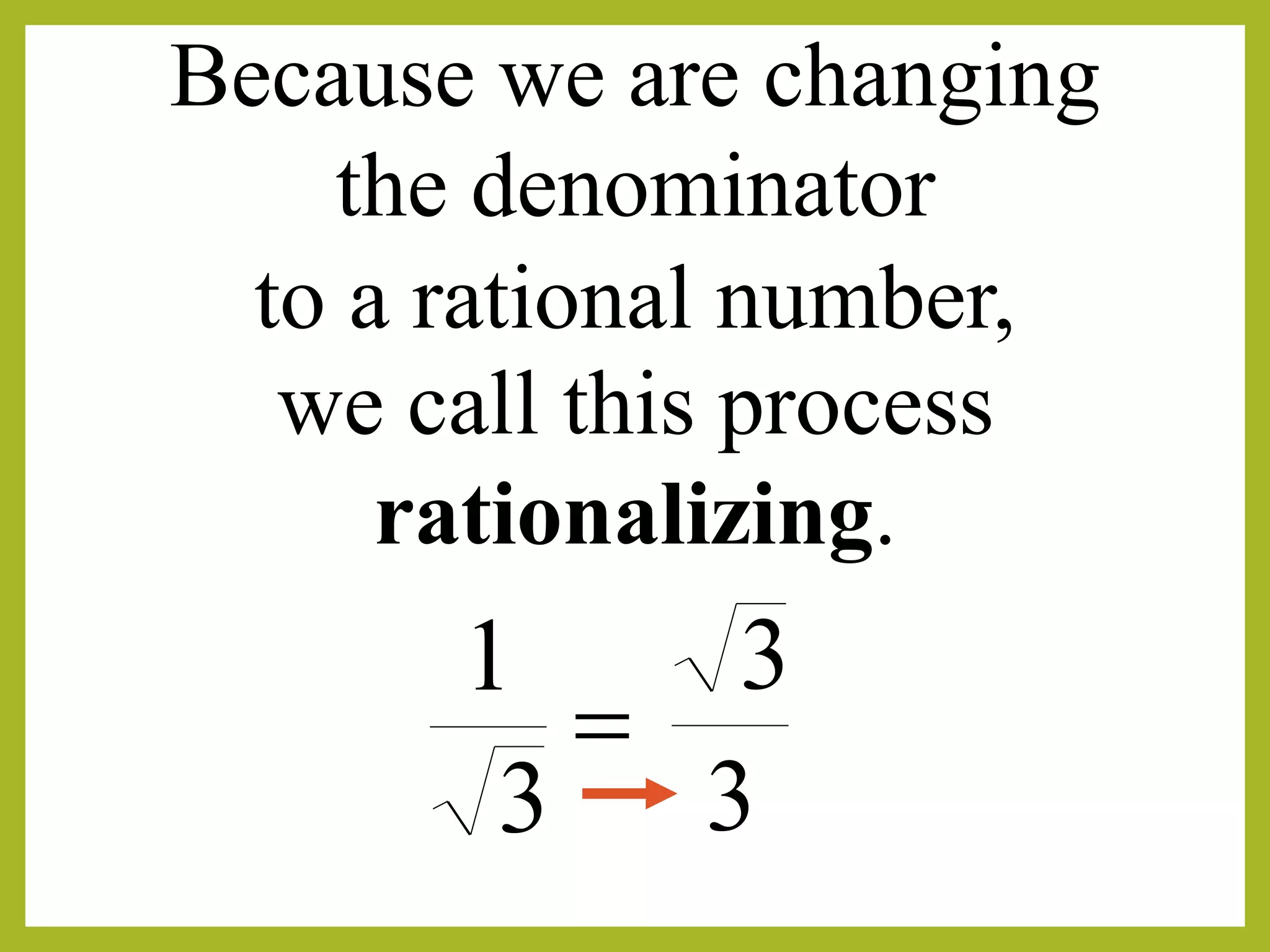
This is called rationalization because we change the denominator to a rational number.
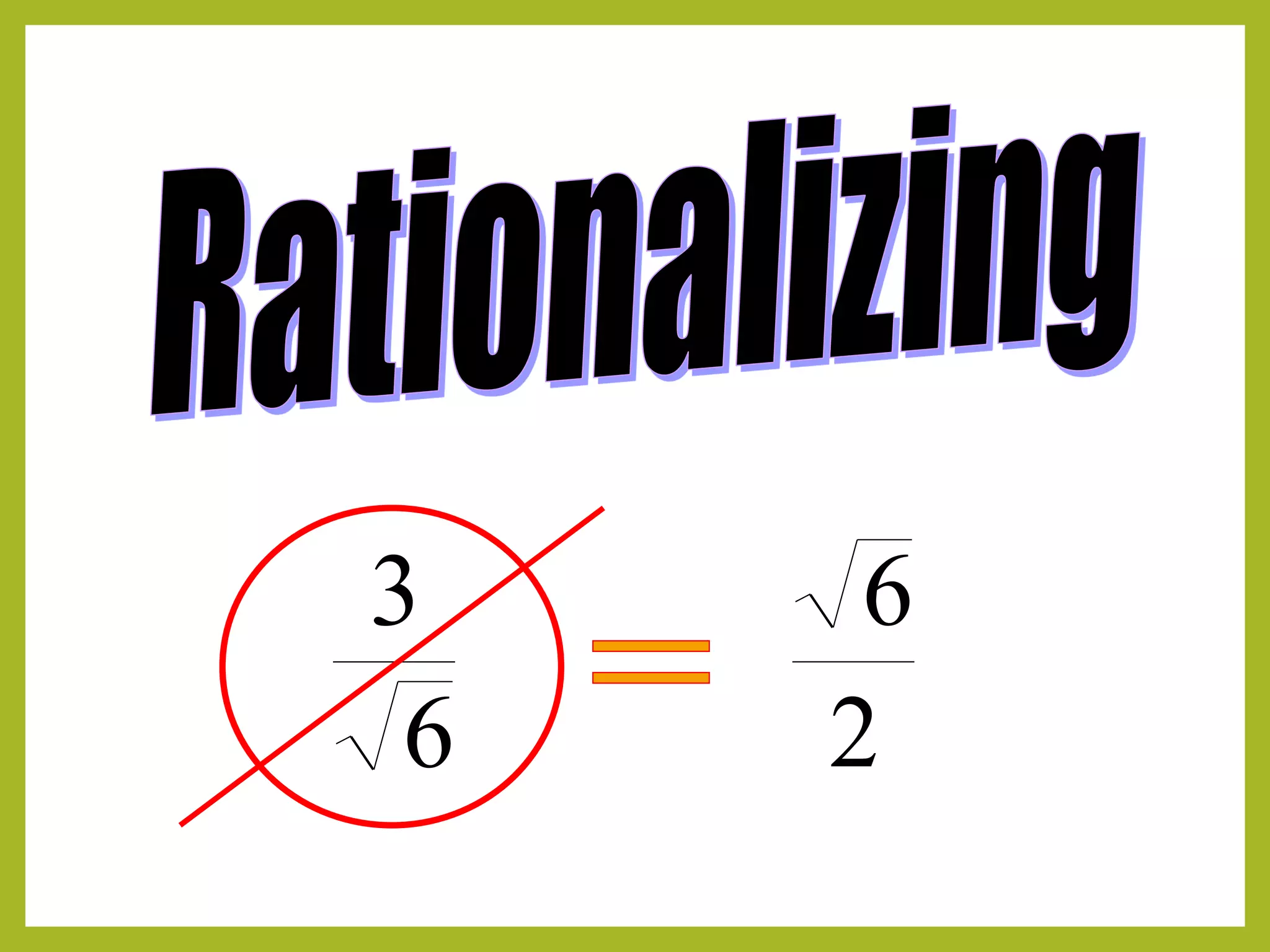
Rationalization example showing how to simplify a fraction with a radical in the denominator.
Another example of rationalizing the denominator ensuring clarity and simplification.
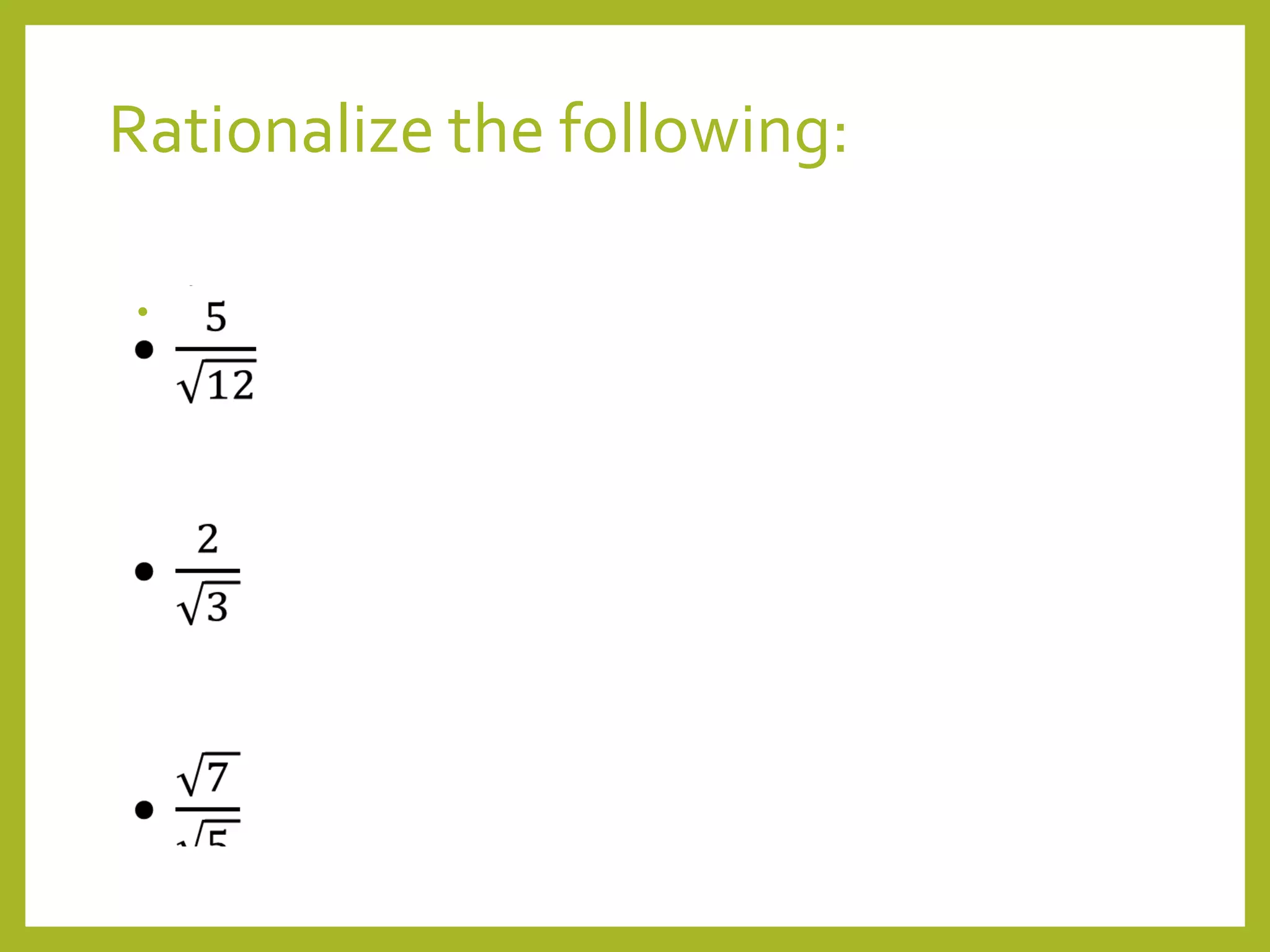
An invitation to rationalize additional expressions as practice.