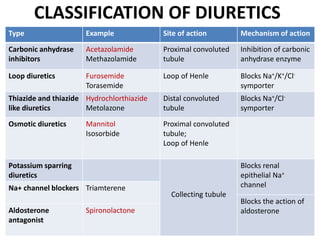
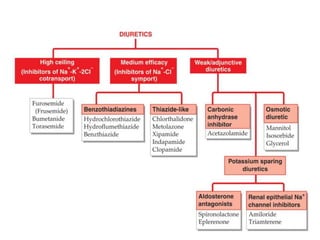
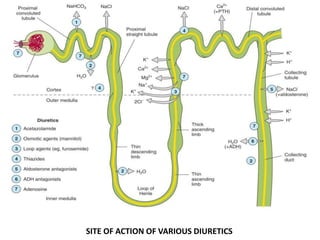
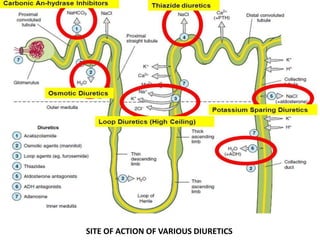
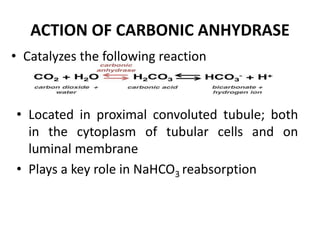
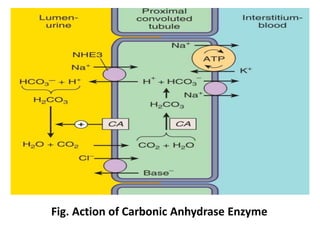
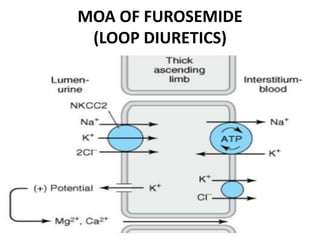
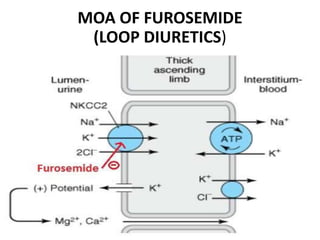
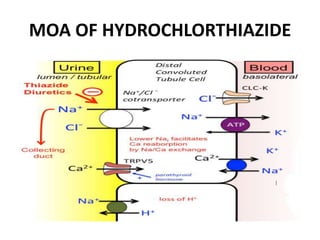
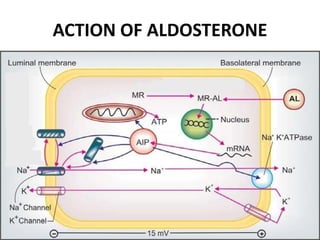
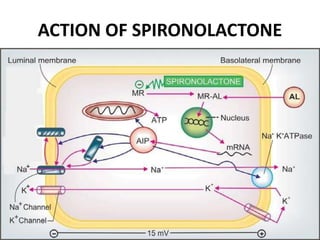
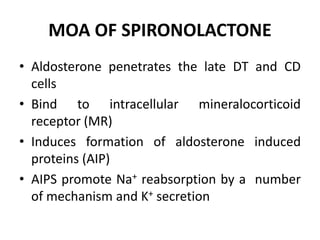
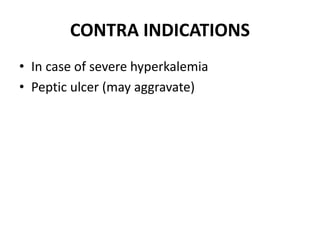
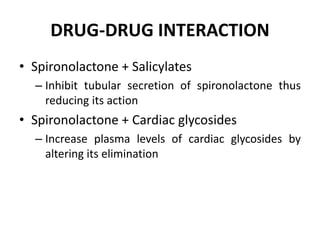
This document discusses different classes of diuretic drugs, including their mechanisms of action and therapeutic uses. It covers carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, loop diuretics, thiazide diuretics, potassium-sparing diuretics like spironolactone, and osmotic diuretics like mannitol. The main points are:
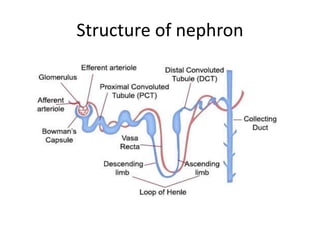
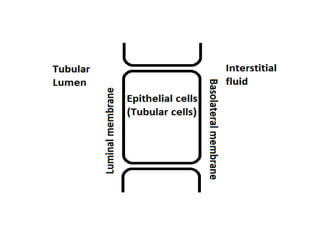
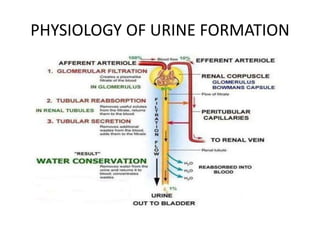
- Diuretics work by inhibiting reabsorption of sodium in different regions of the nephron like the proximal tubule, loop of Henle, or distal tubule.
- Major classes include carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, loop diuretics like furosemide, thiazide diuretics, and potassium-sparing di