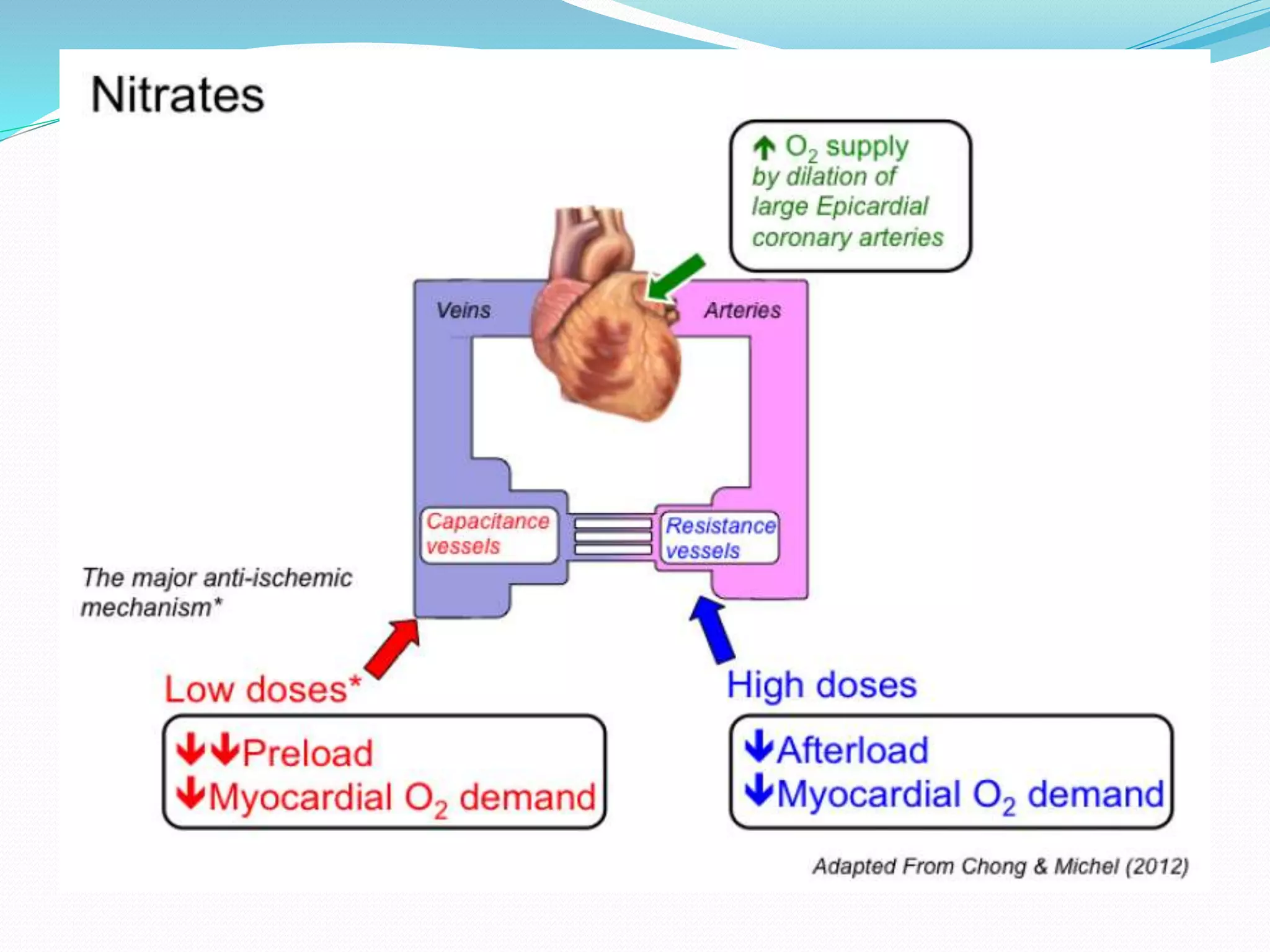
Angina pectoris is a sudden chest pain often radiating to the left arm, neck, or back, treated with antianginal drugs like nitrates that reduce cardiac work by dilating blood vessels. Nitrates come in various forms, including short-acting and long-acting options, each with specific dosages and pharmacokinetic profiles. Side effects include headaches and dizziness, with important drug interactions noted, particularly with erectile dysfunction medications that can cause dangerous hypotension.





![NITROGLYCRIN[short acting]
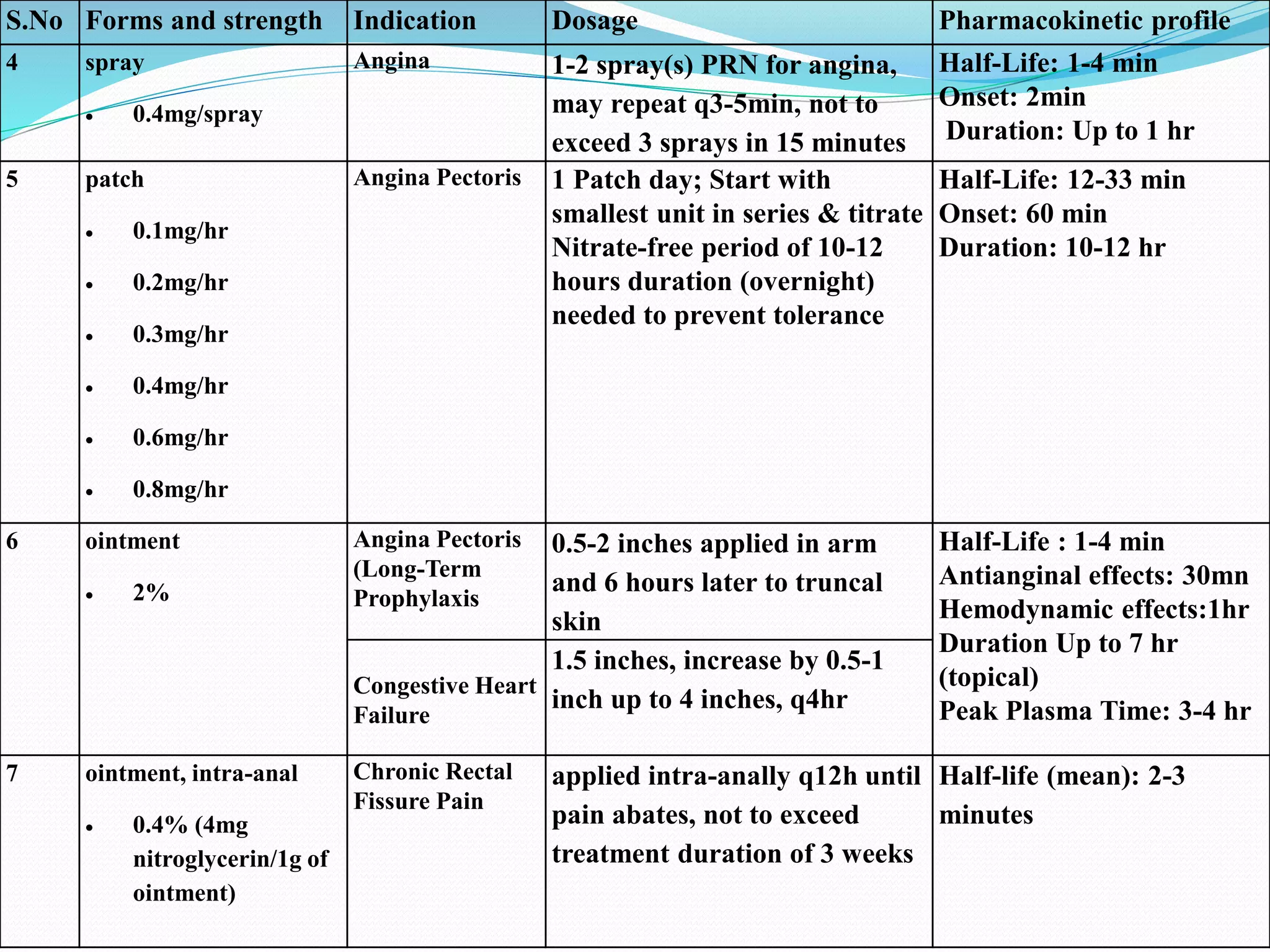
S.No Forms and strength Indication Dosage Pharmacokinetic profile
1 infusion solution
25mg/250mL
50mg/250mL
100mg/250mL
injectable solution
5mg/mL
Angina
Myocardial
Infarction
5 mcg/min continuous IV infusion
via non-absorptive tubing; increase
by 5 mcg/min every 3 to 5 minutes
as needed up to 20 mcg/min, then
by 10 or 20 mcg/min if needed
Half life:1-4 min
DA:3-5 min
onset:1-3 mn
Metabolism:liver(1,3-
glyceryl dinitrate, 1,2-
glyceryl dinitrate, and
glyceryl mononitrate
(inactive)
Eliniation: Urine
2 capsule, extended release
2.5mg
6.5mg
9mg
Angina prophylaxis ER capsule: Initial 2.5-6.5 mg PO
q6-8hr
Titrate up to effect dose.
Half life:1-4 min
DA: up to 4-8hr
onset:1-4 hr
3 tablet, SL
0.3mg
0.4mg
0.6mg
powder, SL (GoNitro)
0.4mg
Angina Pectoris
(Acute Relief)
0.3-0.6 mg SL q5min up to 3 times;
use at first sign of angina
Half life:1-4 min
DA: up to 30 min
onset:1- 3 min
Angina Pectoris
(Prophylaxis)
1 tablet SL 5-10 minutes before
activities likely to provoke angina
attacks](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nitratespptm5-170620112957/75/Nitrates-8-2048.jpg)