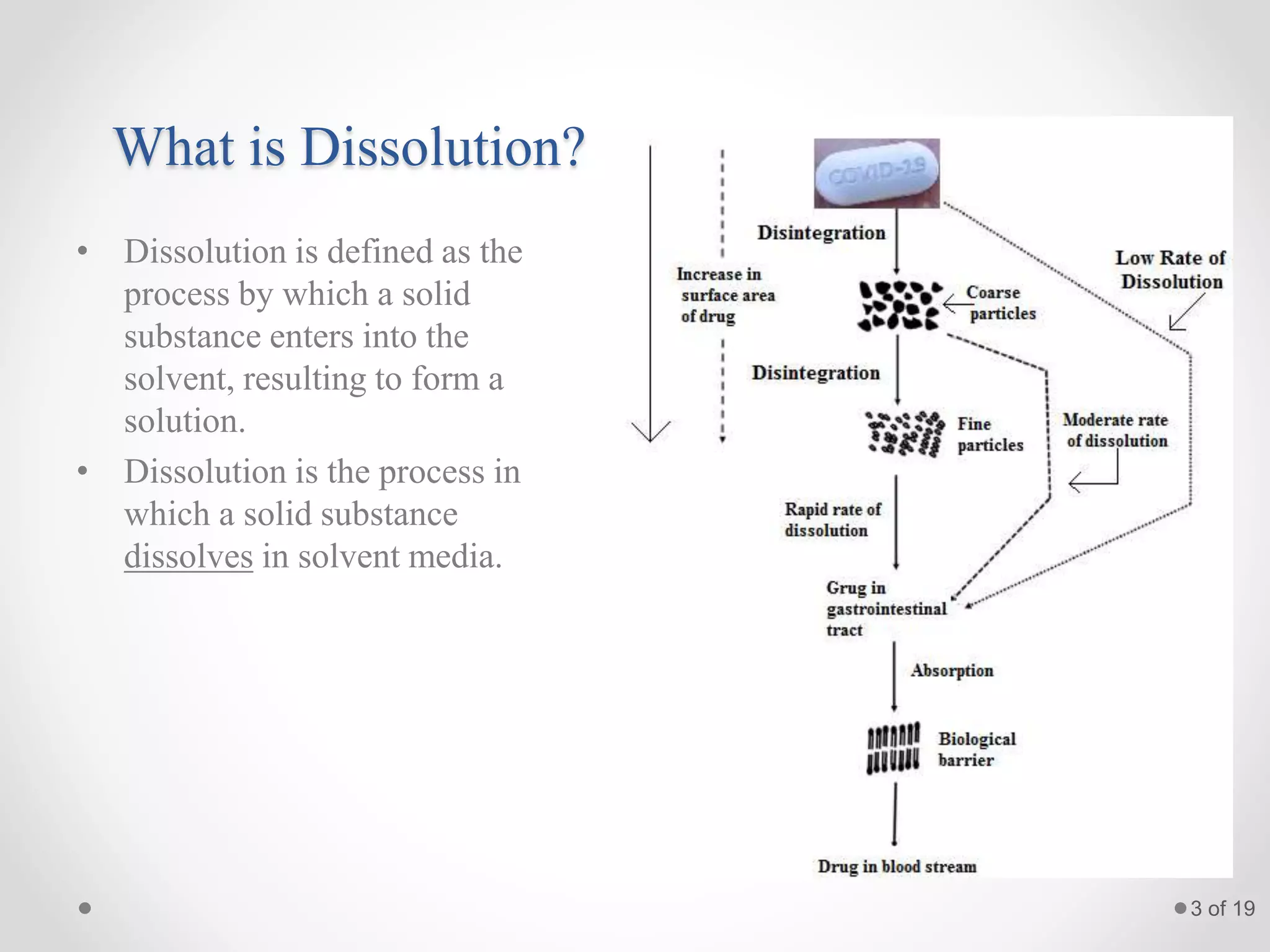
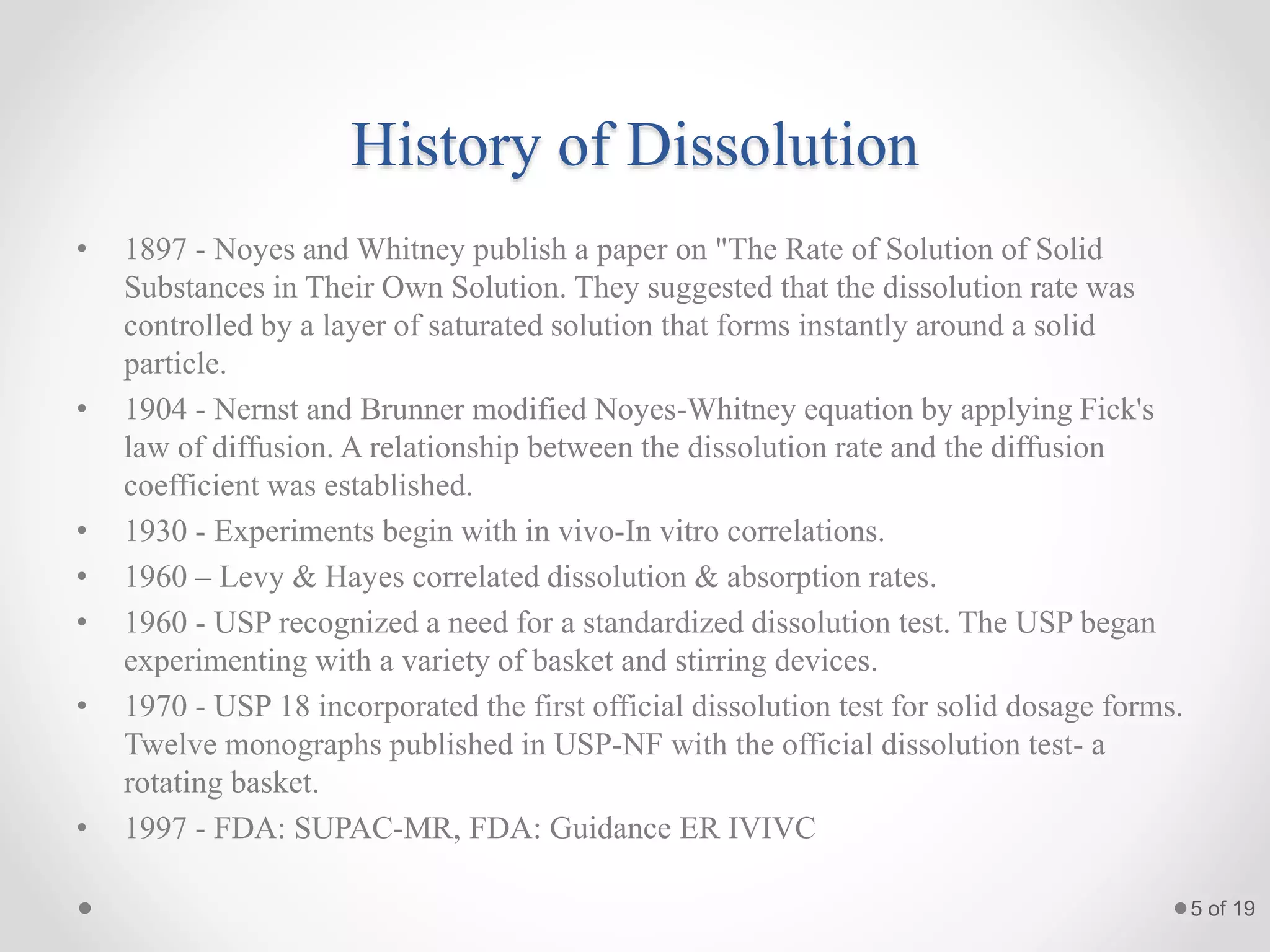
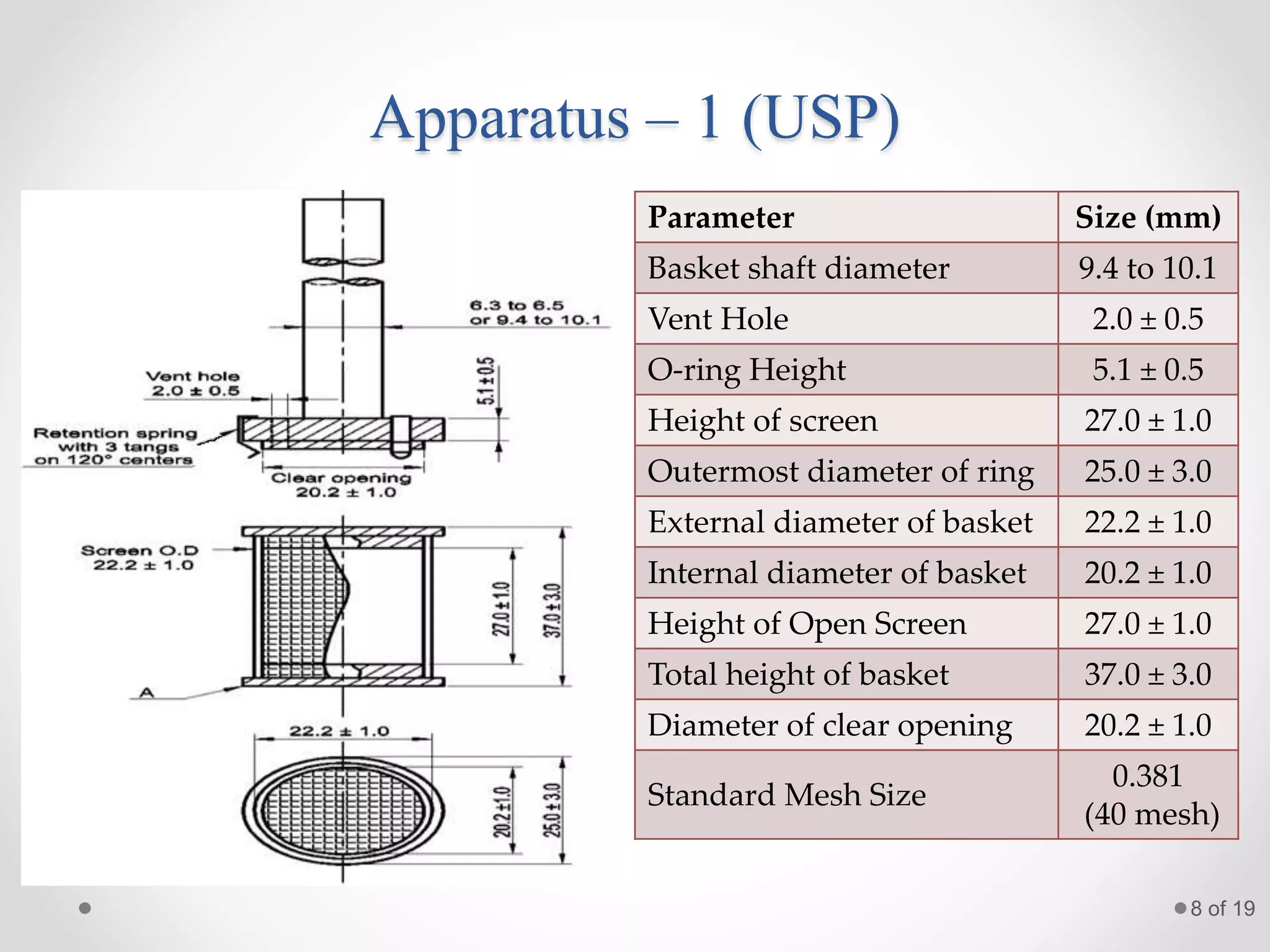
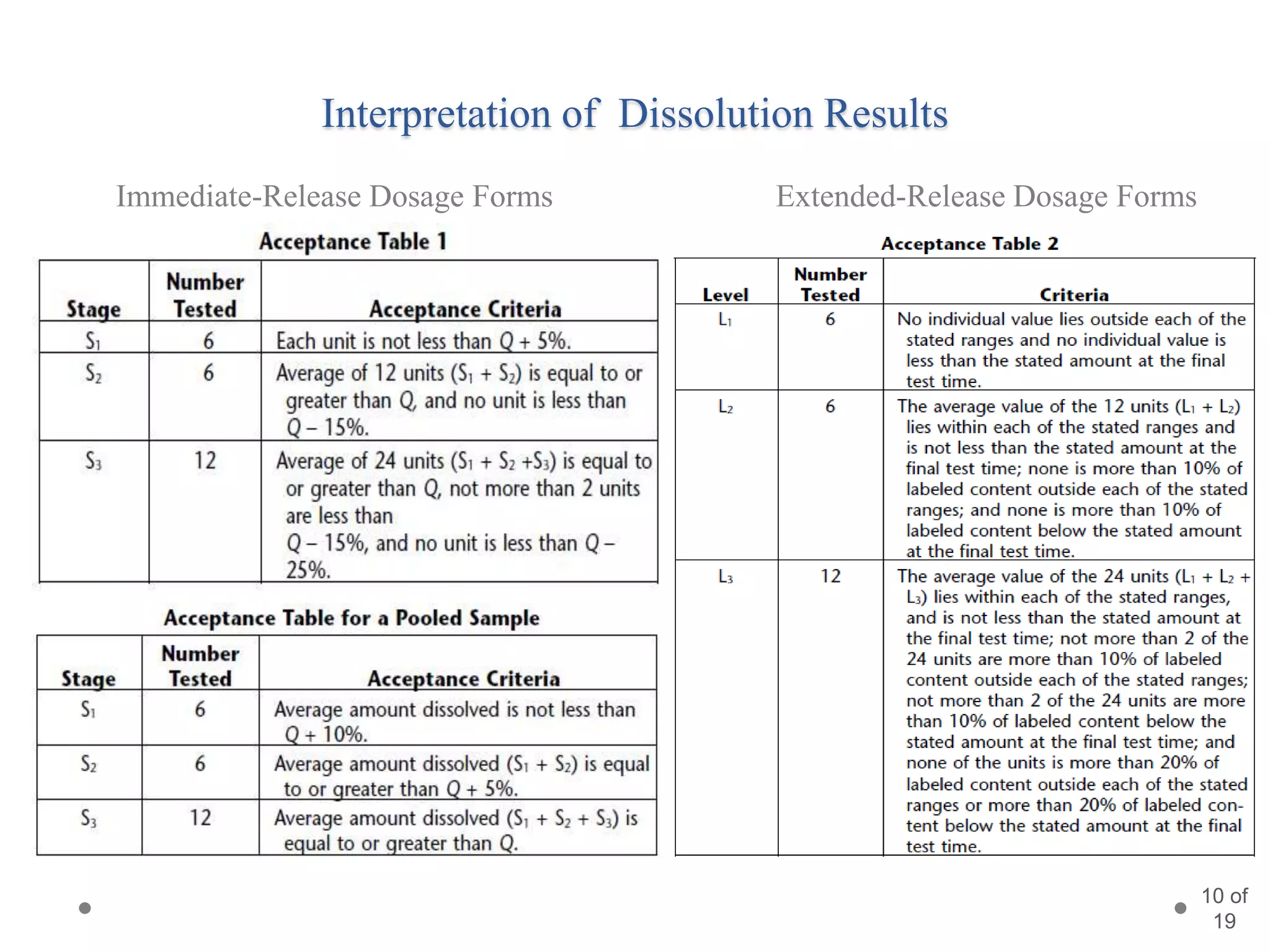
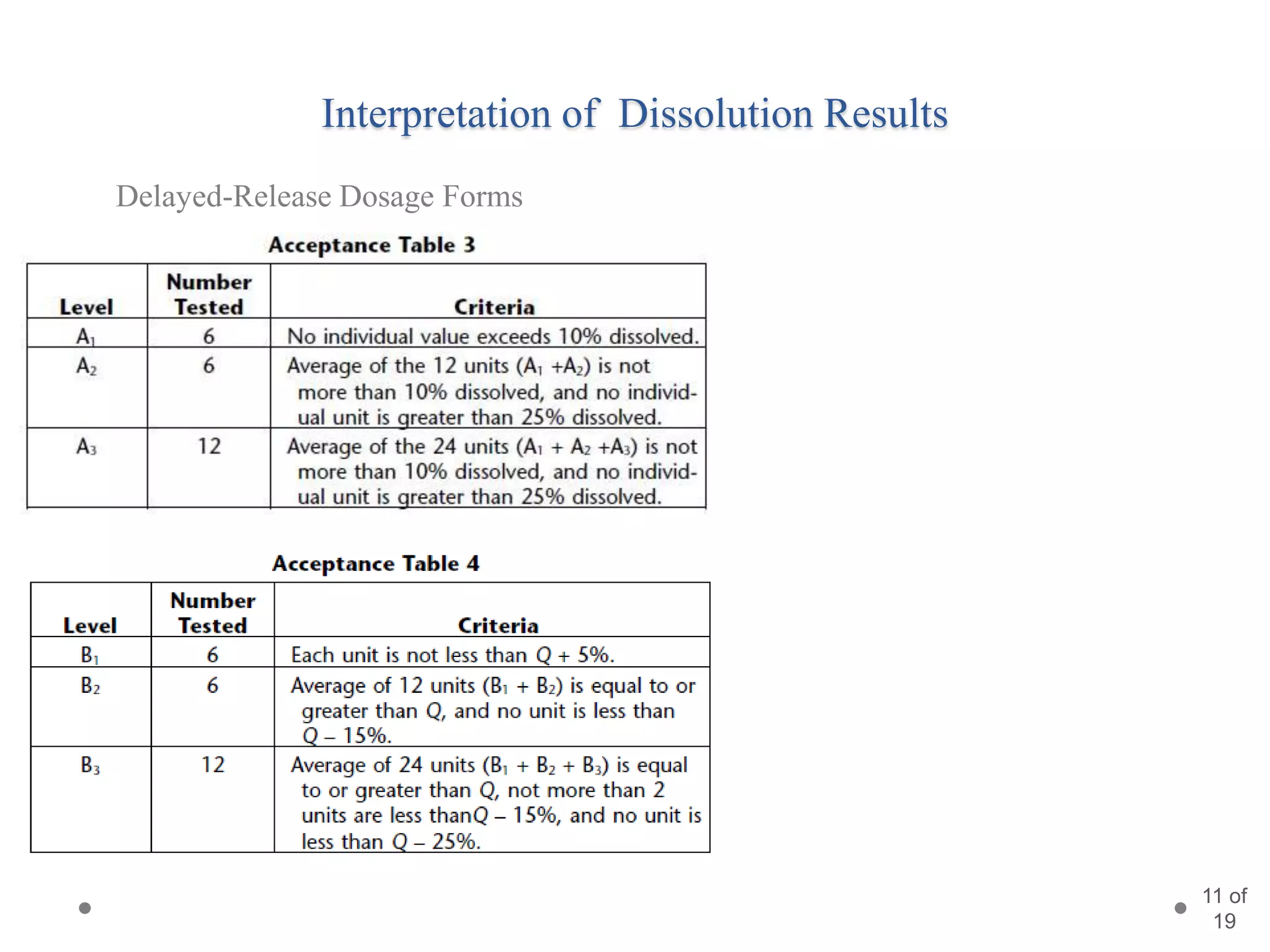
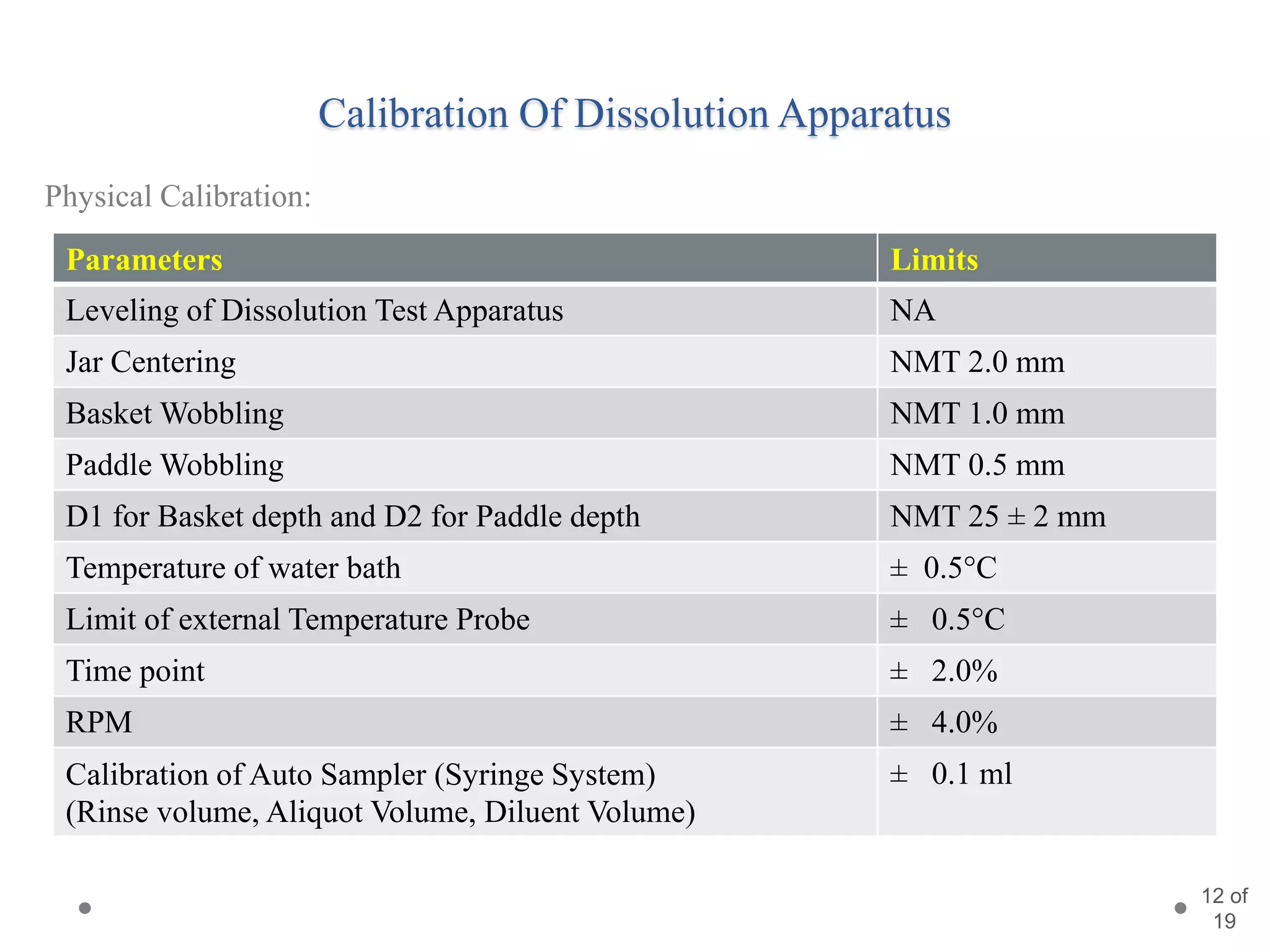
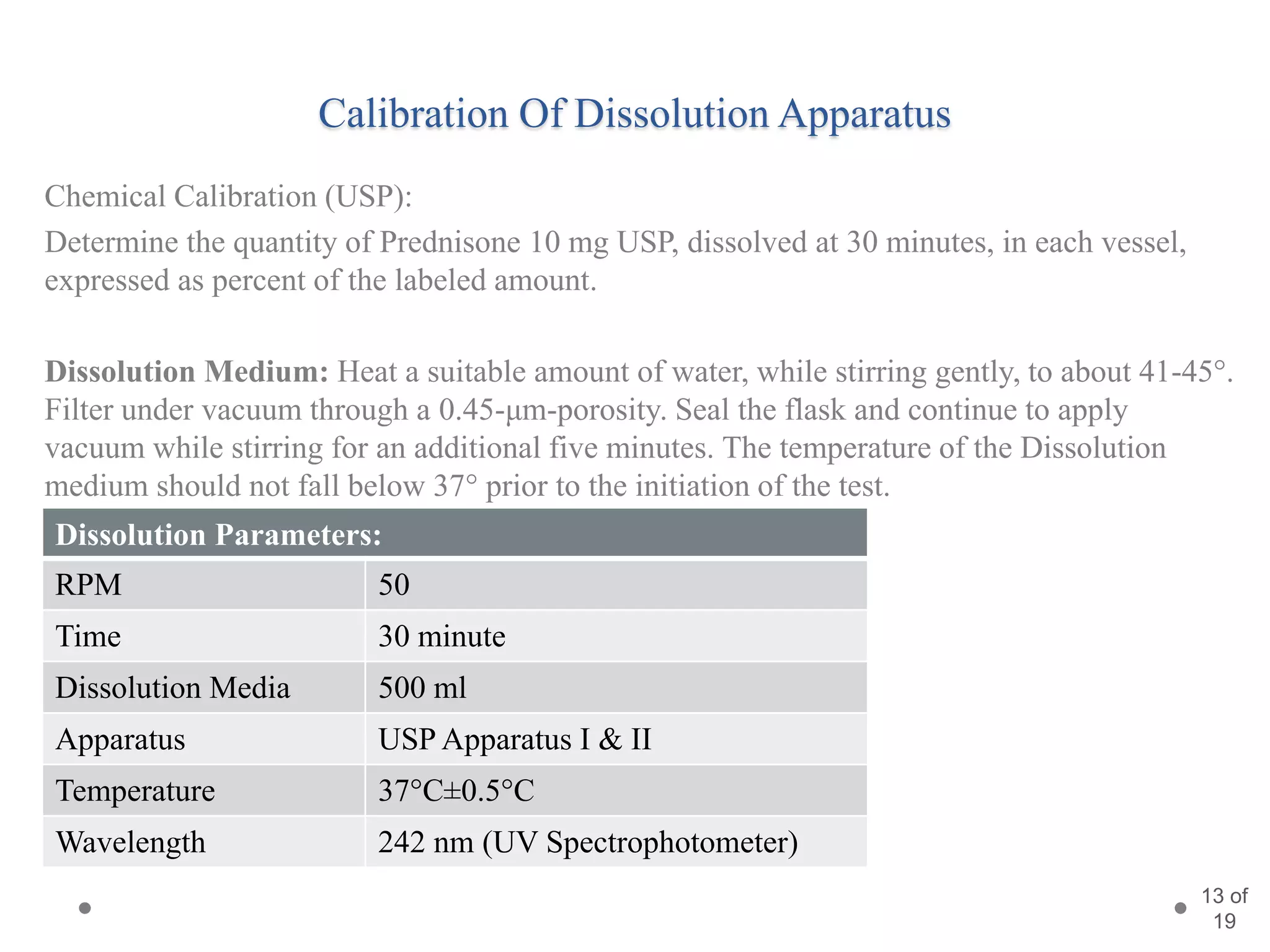
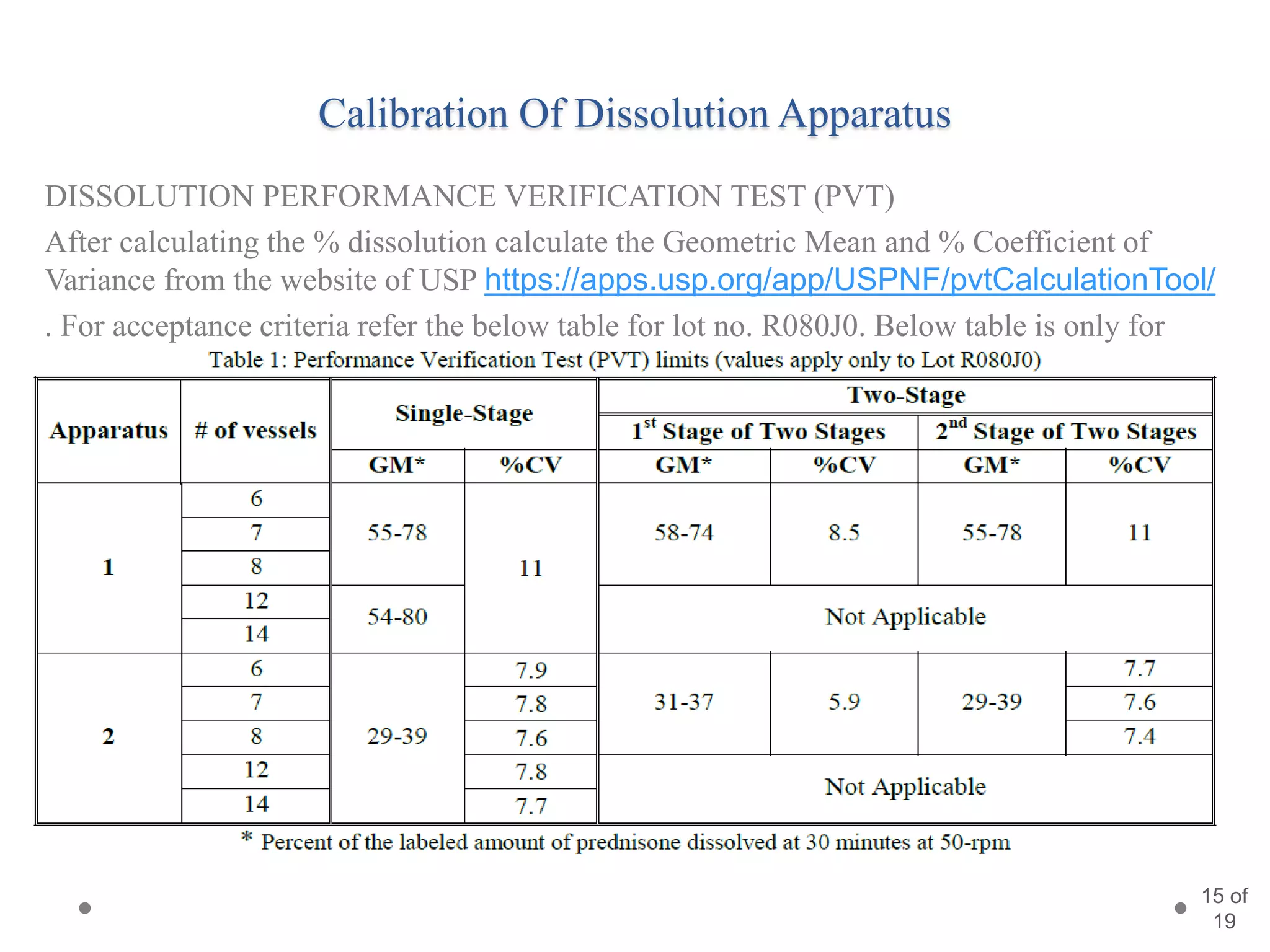
This presentation summarizes information about dissolution techniques used in the pharmaceutical industry. It discusses the importance of dissolution testing, provides a brief history of dissolution testing development, and describes the main types of dissolution apparatus as defined in various pharmacopoeias. The presentation also covers topics like interpreting dissolution results, calibrating dissolution apparatus, common tools used for calibration, and proposed revisions to WHO guidelines for testing solid oral dosage forms and suspensions.