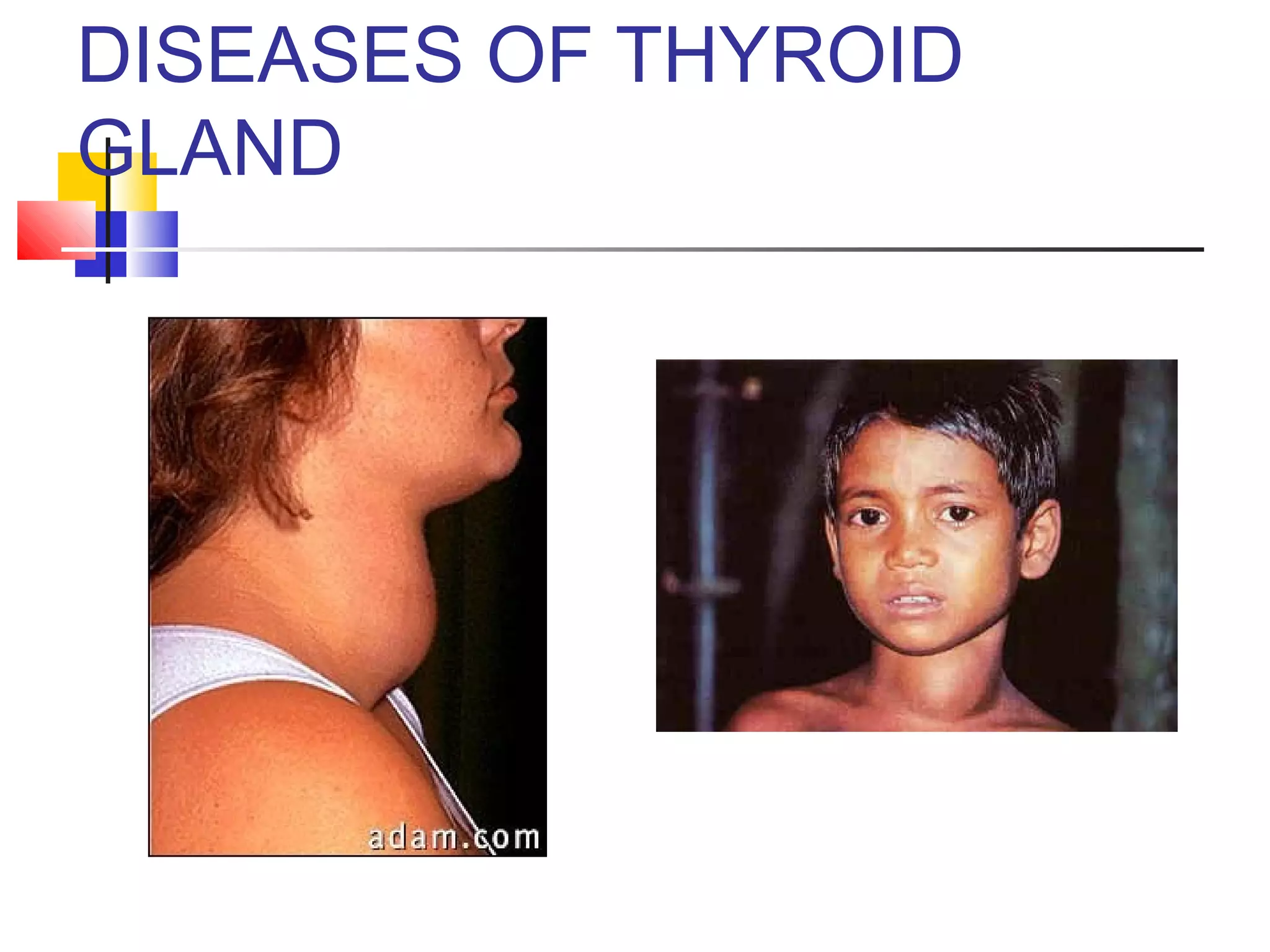
The document provides an overview of the anatomy and functions of the thyroid gland, detailing its structure, types of disorders, and related symptoms. It categorizes thyroid disorders into hypofunction, hyperfunction, goiter, nodules, and neoplastic changes, along with investigation techniques and treatment options including medical and surgical interventions. Surgical indications are outlined, emphasizing the need for preoperative assessments and potential complications associated with thyroidectomy.