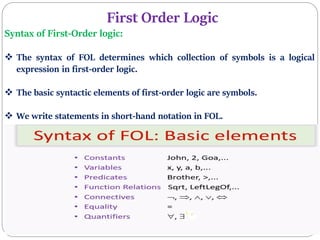
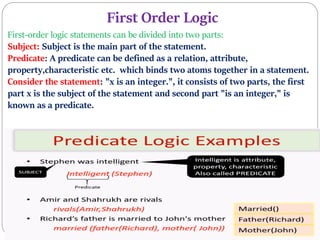
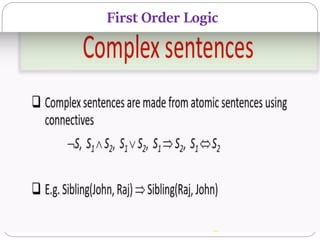
The document discusses First Order Logic (FOL), highlighting its necessity over Propositional Logic for expressing complex statements and relationships. FOL is described as a powerful knowledge representation language suitable for natural language statements, comprising syntax and semantics. It introduces quantifiers, subjects, and predicates as essential components of logical expressions.