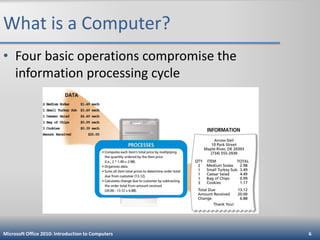
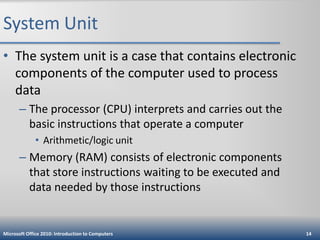
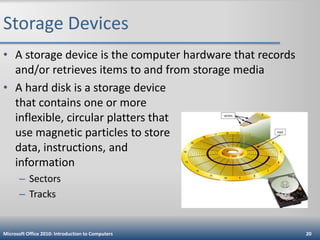
This document is an introduction to computers that defines computers and their basic operations of input, processing, output, and storage. It describes different types of personal computers like desktops, laptops, tablets, and mobile devices. It explains the main internal and external components of computers and how they are used. It also discusses computer software, networks, the internet, online security threats, and provides guidance on purchasing different types of computers and mobile devices.