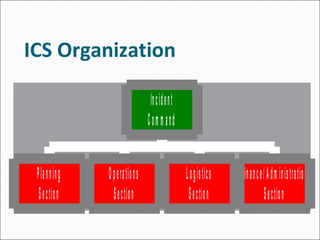
The document discusses disaster response management, including defining disasters and hazards, classifying disasters, the phases of a disaster from preparation to recovery, and details of the Incident Command System used to manage response efforts. Key aspects of disaster response outlined are emergency support functions, medical response phases, and the importance of coordination, planning, and establishing a clear command structure to effectively manage response operations.