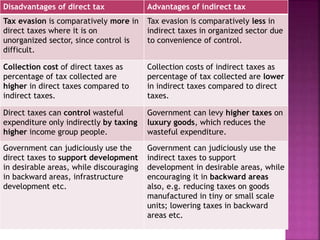
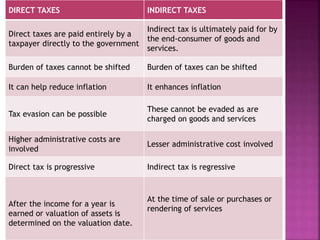
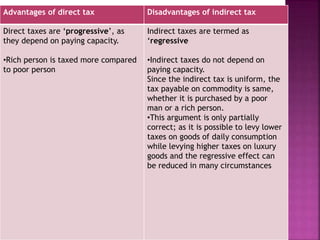
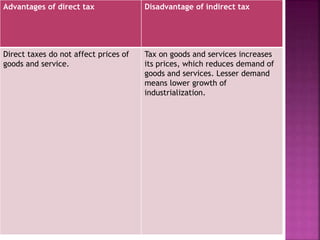
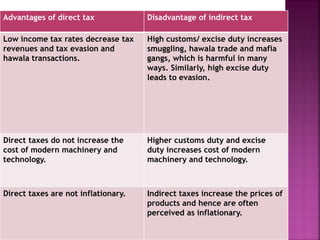
Direct taxes are paid directly to the government by taxpayers based on their income or assets. Indirect taxes are ultimately paid by consumers through higher prices of goods and services. Direct taxes are generally progressive, where higher incomes face higher tax rates, while indirect taxes are often regressive with the same tax rates regardless of income. Both direct and indirect taxes have advantages and disadvantages related to issues like tax evasion, prices, revenues, and economic impacts.



![Disadvantages of direct tax Advantages of indirect tax
It is psychologically very difficult for a
person to pay some amount after it is
received in his hands. Hence, there is
psychological resistance .
•[This is the reason why even Income Tax
Act is widening the scope of “Tax
Deduction at Source’’ (TDS) and TCS.
Thus, a direct tax is converted to an
indirect tax].
Since the price of commodity or service is
already inclusive of indirect taxes, the
customer i.e. the ultimate tax payer does
not feel a direct pinch while paying
indirect taxes and hence, resistance to
indirect taxes is much less compared to
resistance to direct taxes.
•Manufacturer’s/ Dealer’s Psychology
favours indirect taxes- The
manufacturer/ trader
who collects the taxes in his Invoice and
pays it to Government, has a
psychological feeling that he is only
collecting the taxes and is not paying out
of his own pocket](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dtvsit-190727075336/85/Direct-Tax-vs-Indirect-Tax-8-320.jpg)