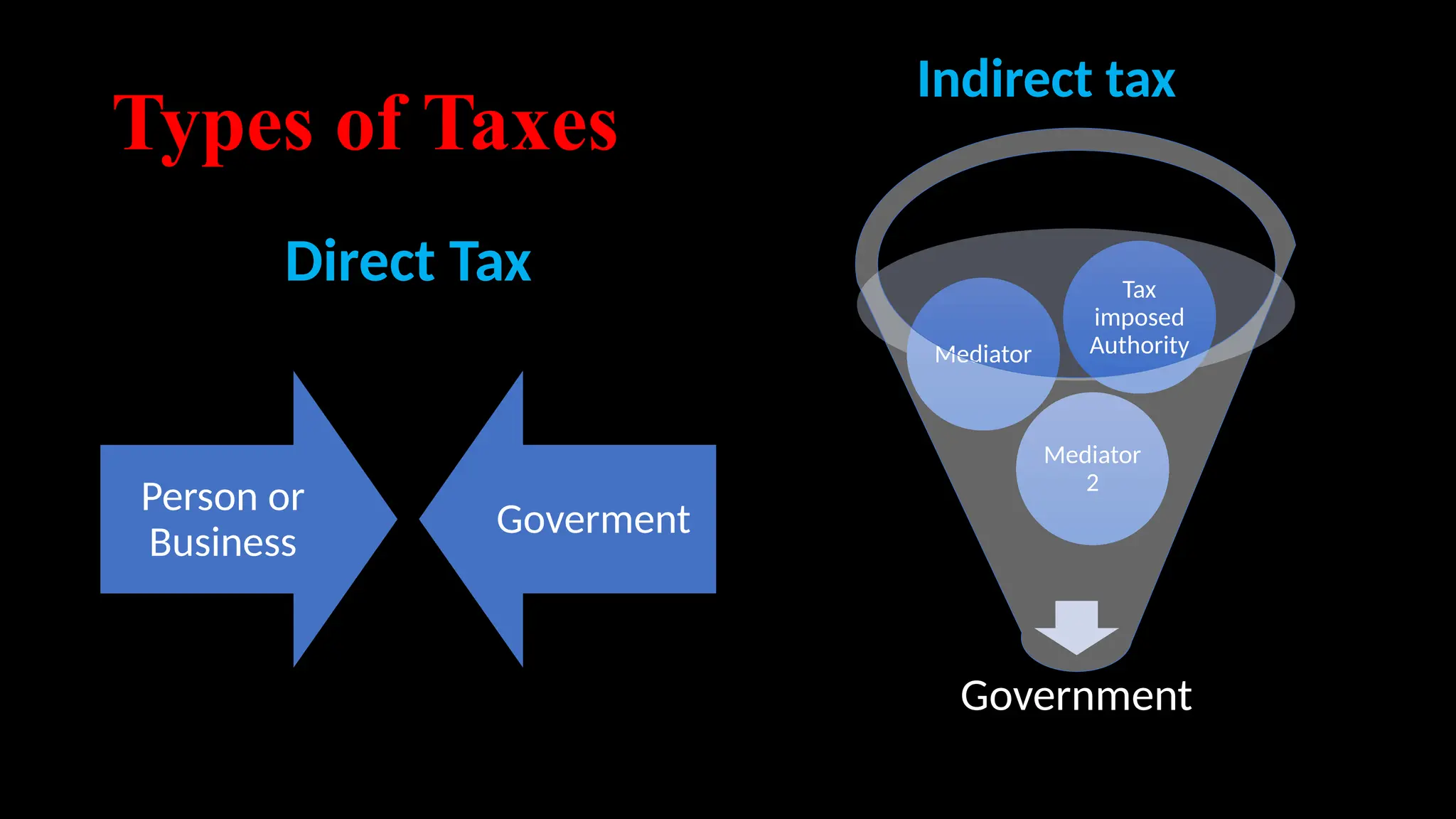
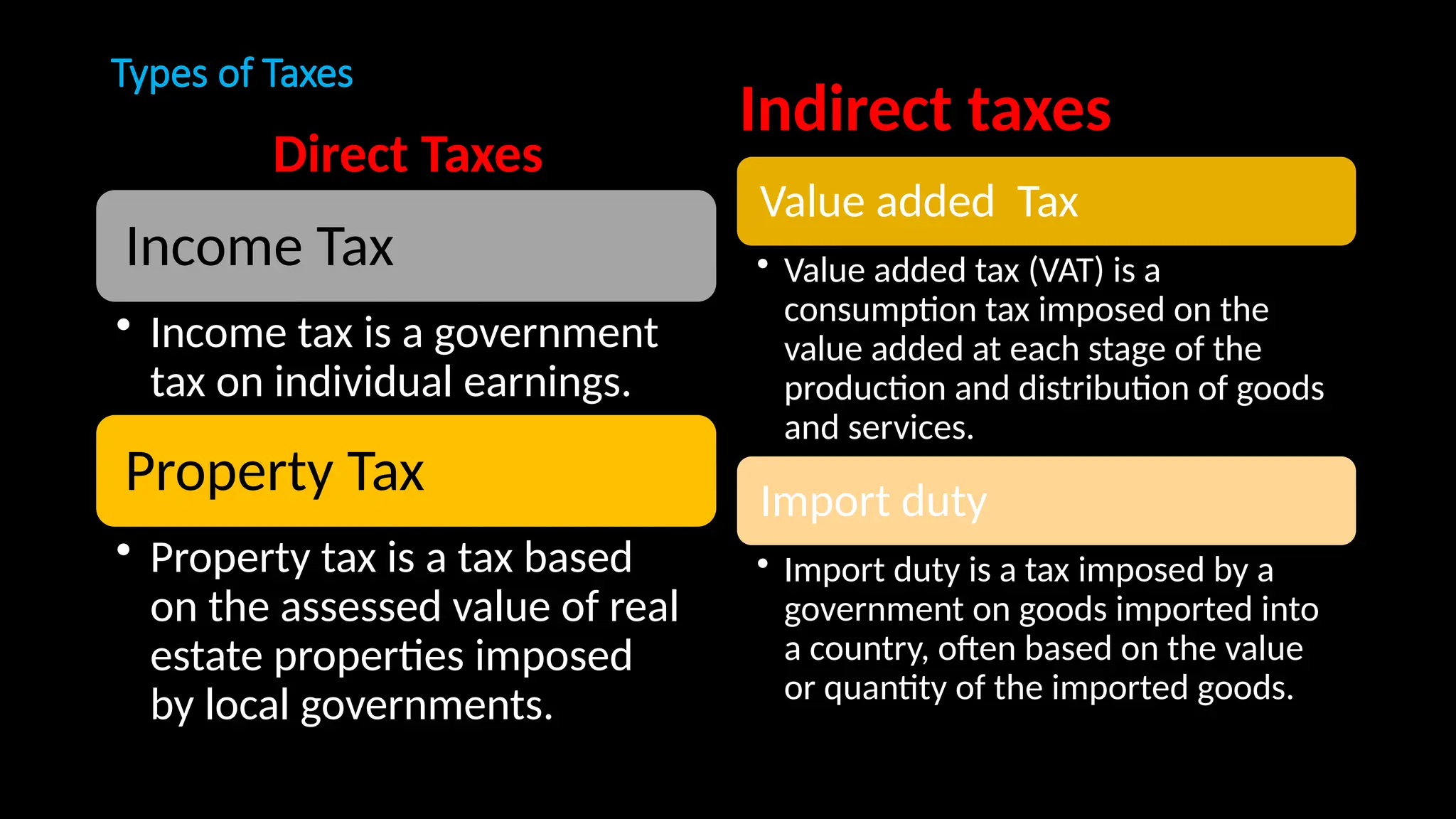
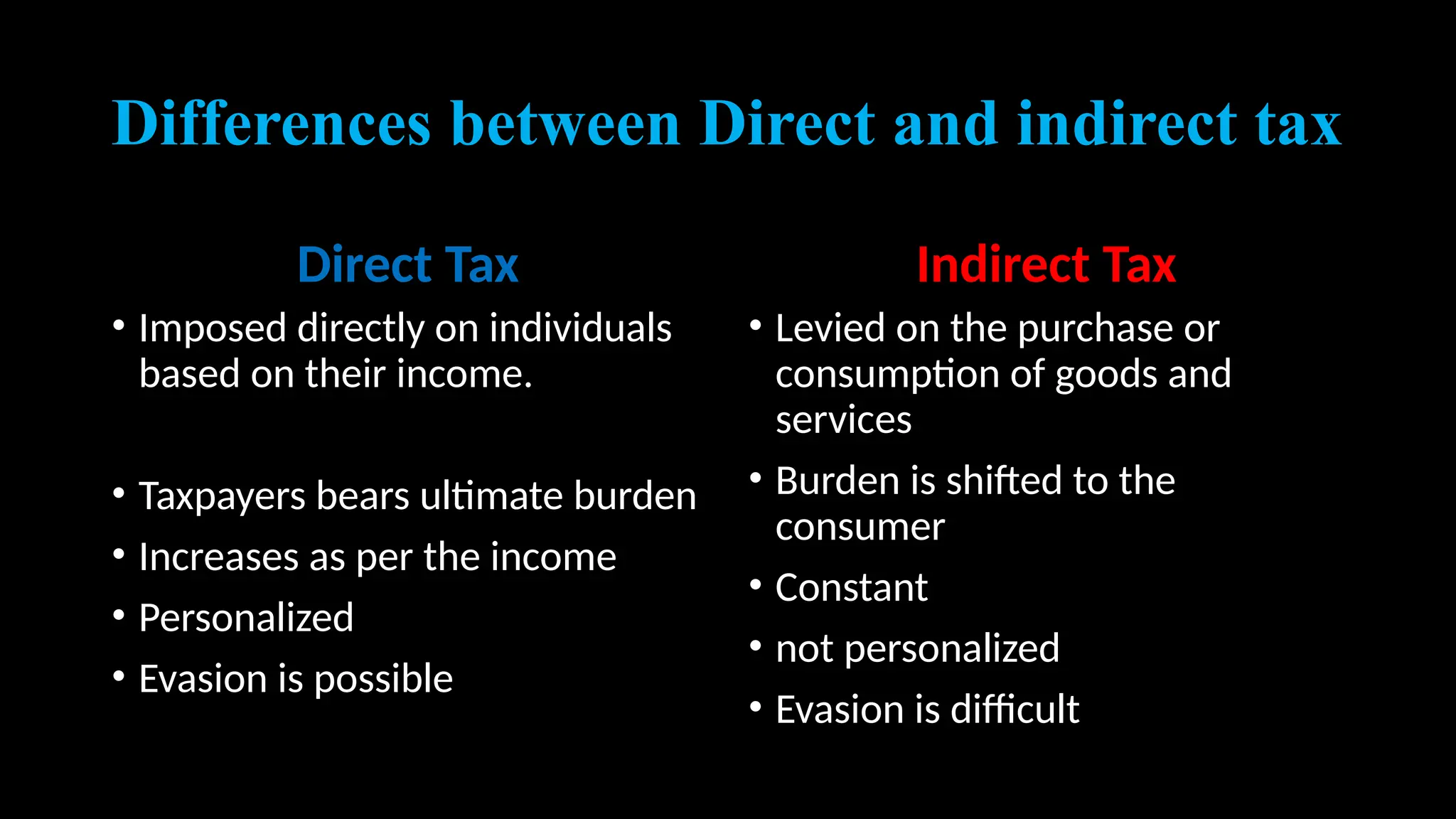
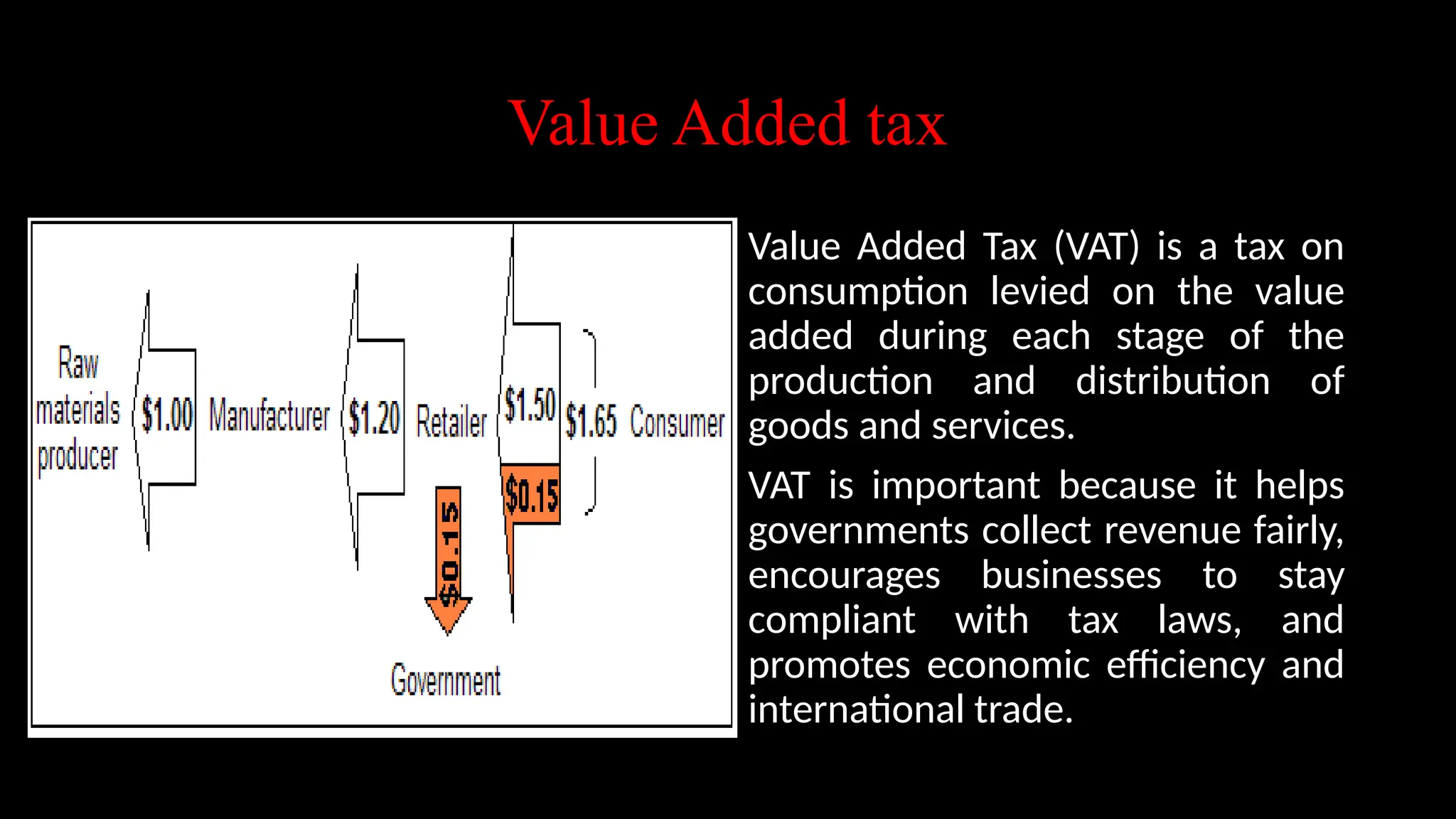
Government revenue consists of total income from taxes and non-tax sources like fees and fines, essential for public services. Taxes are mandatory payments used to finance various public expenditures, and they can be classified as direct or indirect taxes. The document also discusses tax principles, the importance of the Permanent Account Number (PAN) for tracking tax compliance, and emphasizes the role of Value Added Tax (VAT) in promoting economic efficiency.