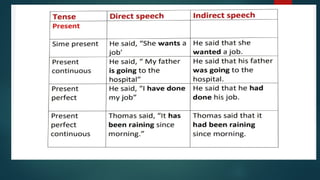
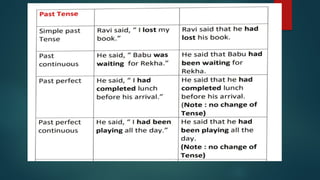
The document outlines the concepts of direct and indirect speech, detailing key elements such as tense, pronouns, and the processes for converting direct speech to indirect speech. It provides examples and rules for transformation, emphasizing the removal of quotation marks and the correct change of personal pronouns and tenses. Additionally, it includes activities aimed at applying these principles through practical exercises.