- There are two ways to report someone's words: direct speech and indirect speech.
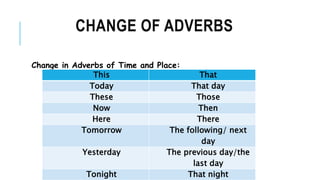
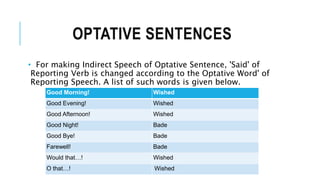
- Direct speech uses quotation marks and reports the exact words. Indirect speech does not use quotation marks and changes pronouns, verb tenses, and adverbs of time and place.
- Punctuation like commas and capitalization is used differently between direct and indirect speech. Indirect speech also uses conjunctions like "that."