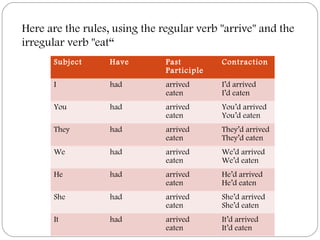
The document discusses the past perfect tense in English. It explains that the past perfect is used to relate two past events and indicate which event occurred first. It provides the rules for forming the past perfect using "have" in the past tense plus the past participle of the main verb. Examples are given of regular and irregular verbs in the past perfect. The uses and forms of the past perfect tense are then defined, including examples of completed actions before something in the past and duration before something in the past.