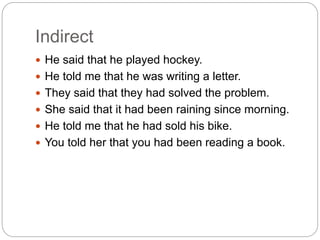
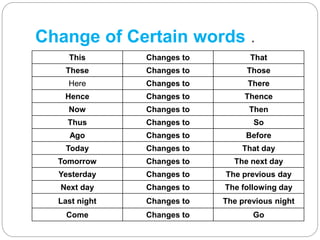
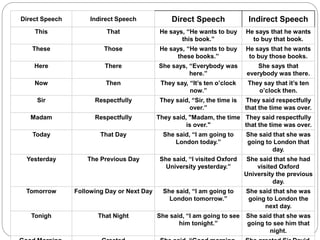
The document explains the concepts of direct and indirect narration in English, including definitions, examples, and rules for conversion. It outlines changes necessary for pronouns, verb tenses, and sentence structure when reporting speech. Additionally, it provides specific rules for assertive, interrogative, and other sentence types in both direct and indirect forms.