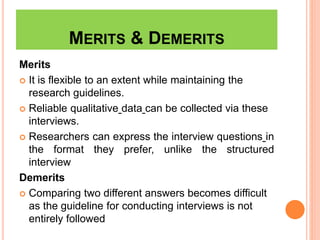
This document discusses different methods of data collection in nursing research, focusing on interviews. It defines interviews and describes their purpose as gathering information. The main types of interviews covered are structured, unstructured, semi-structured, focused group, and telephonic interviews. For each type, the document outlines their key characteristics, merits and demerits. Additional sections provide the definition of interviews, purposes of interviews, and the interview process.