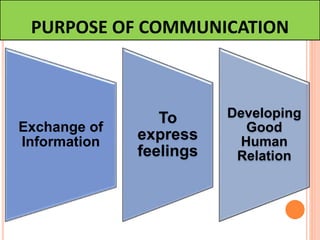
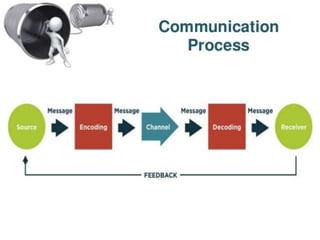
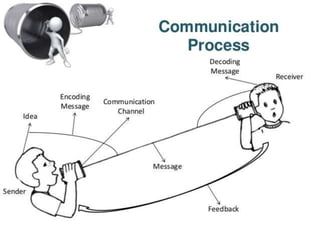
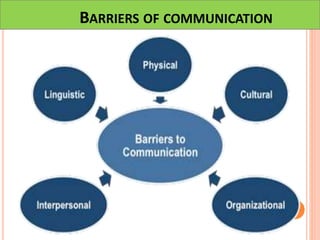
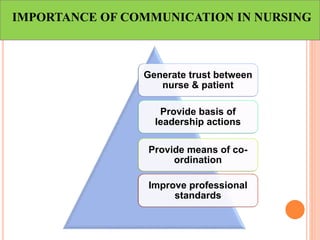
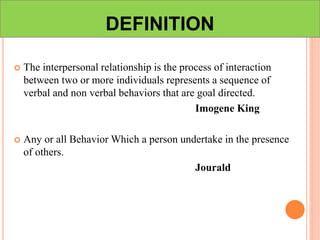
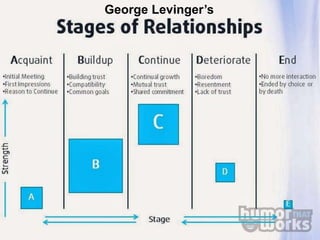
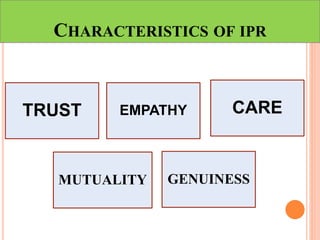
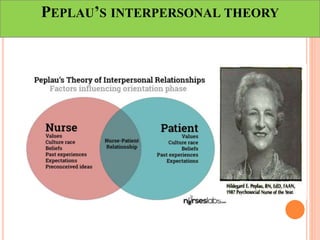
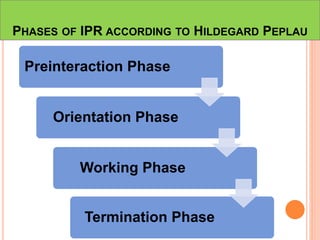
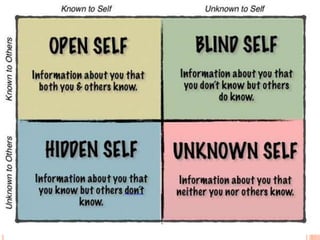
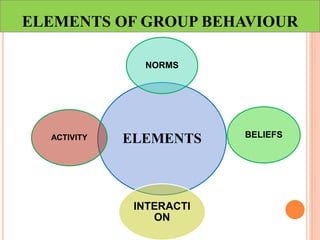
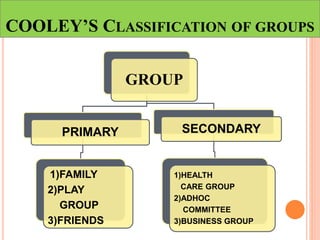
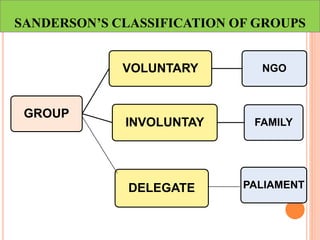
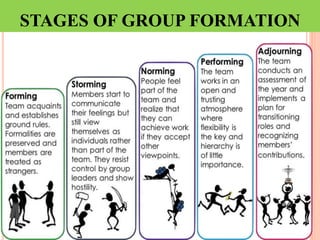
This document discusses communication, interpersonal relationships, and group dynamics. It defines communication and discusses its purpose and types, including verbal and non-verbal communication. Interpersonal relationships are defined as connections between two or more people and different relationship types are outlined. Theories of interpersonal relationships from theorists like Peplau are also mentioned. Groups are defined and group characteristics like norms and interactions are covered. The stages of group formation are outlined.