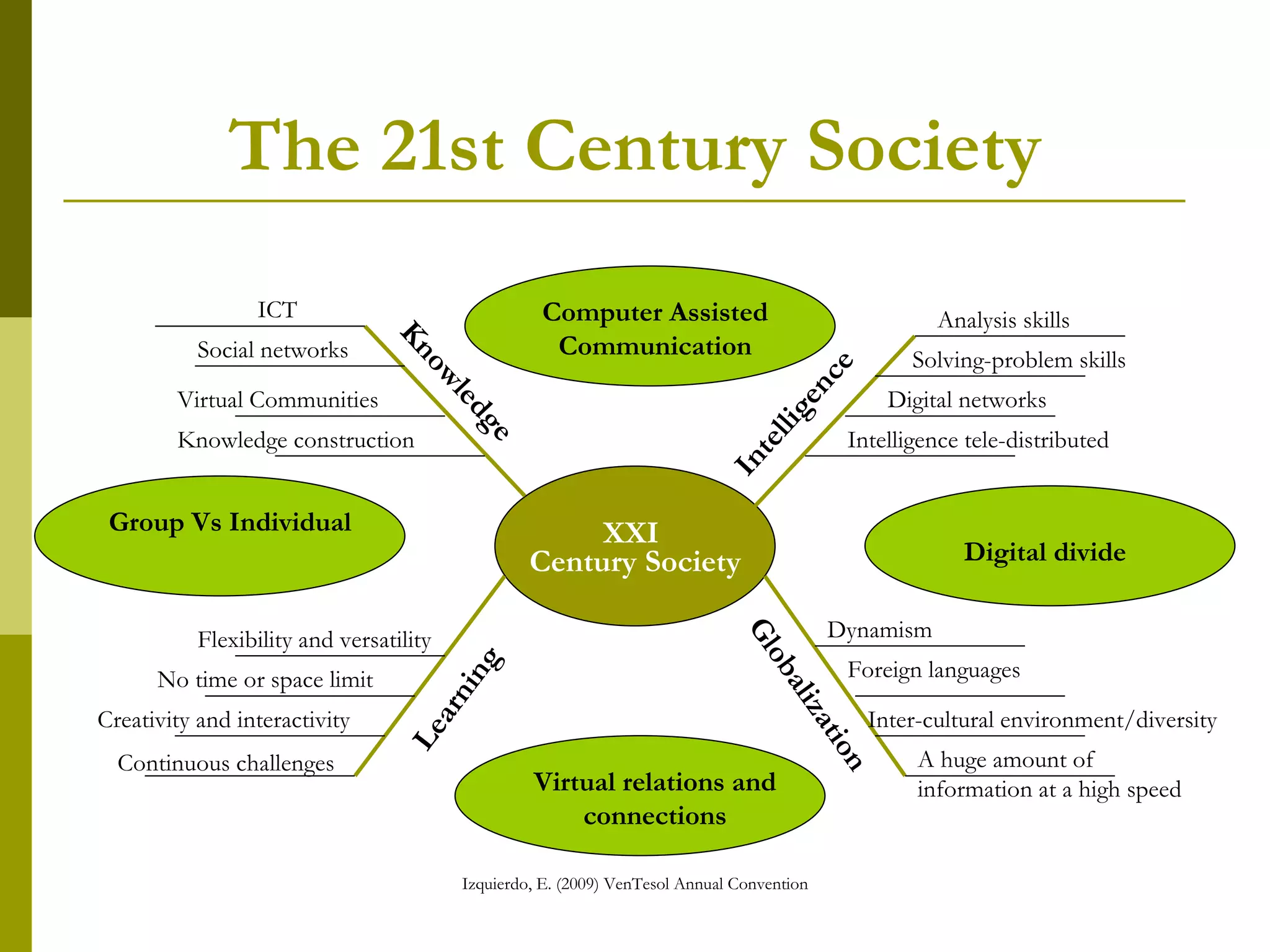
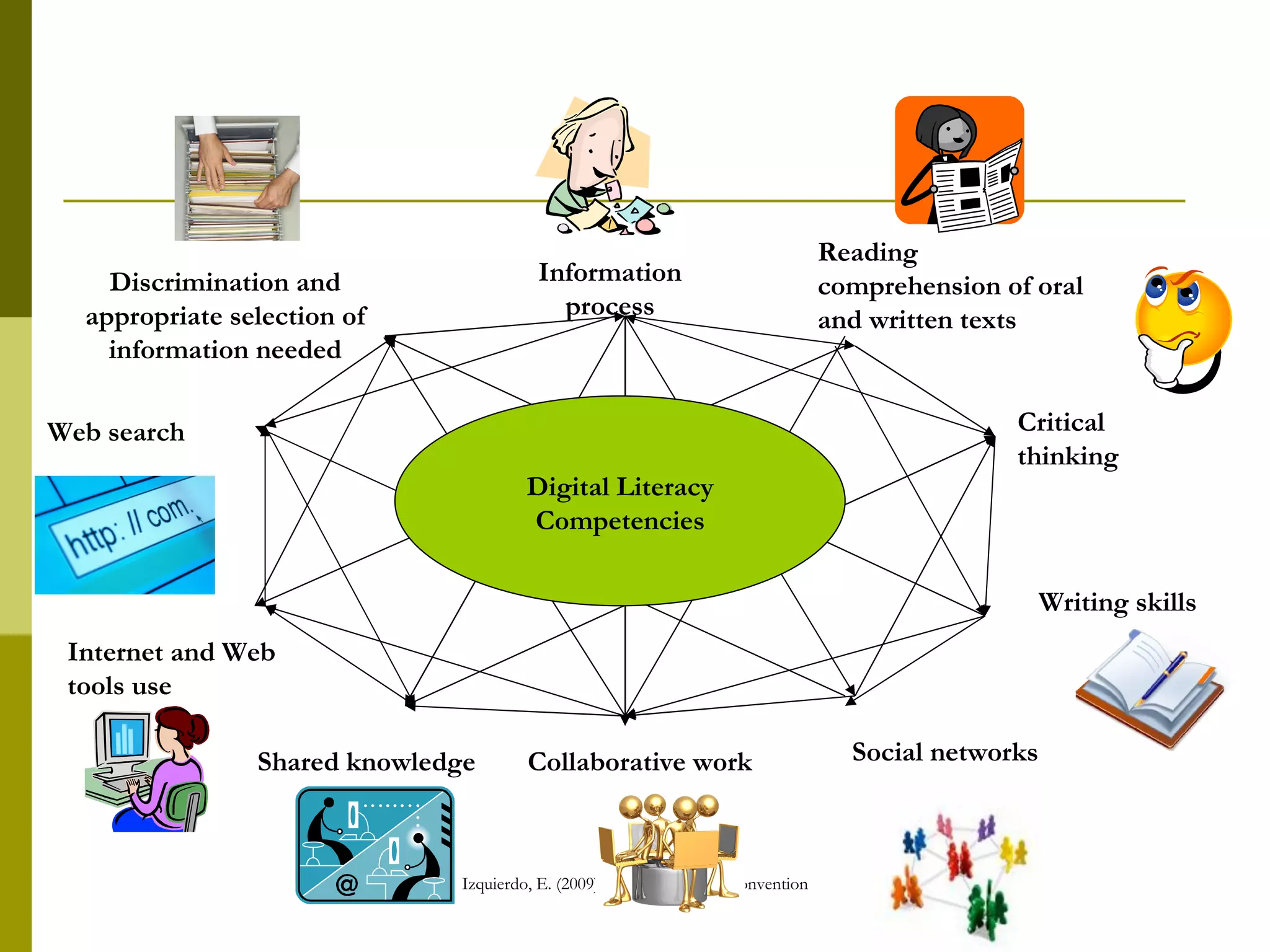
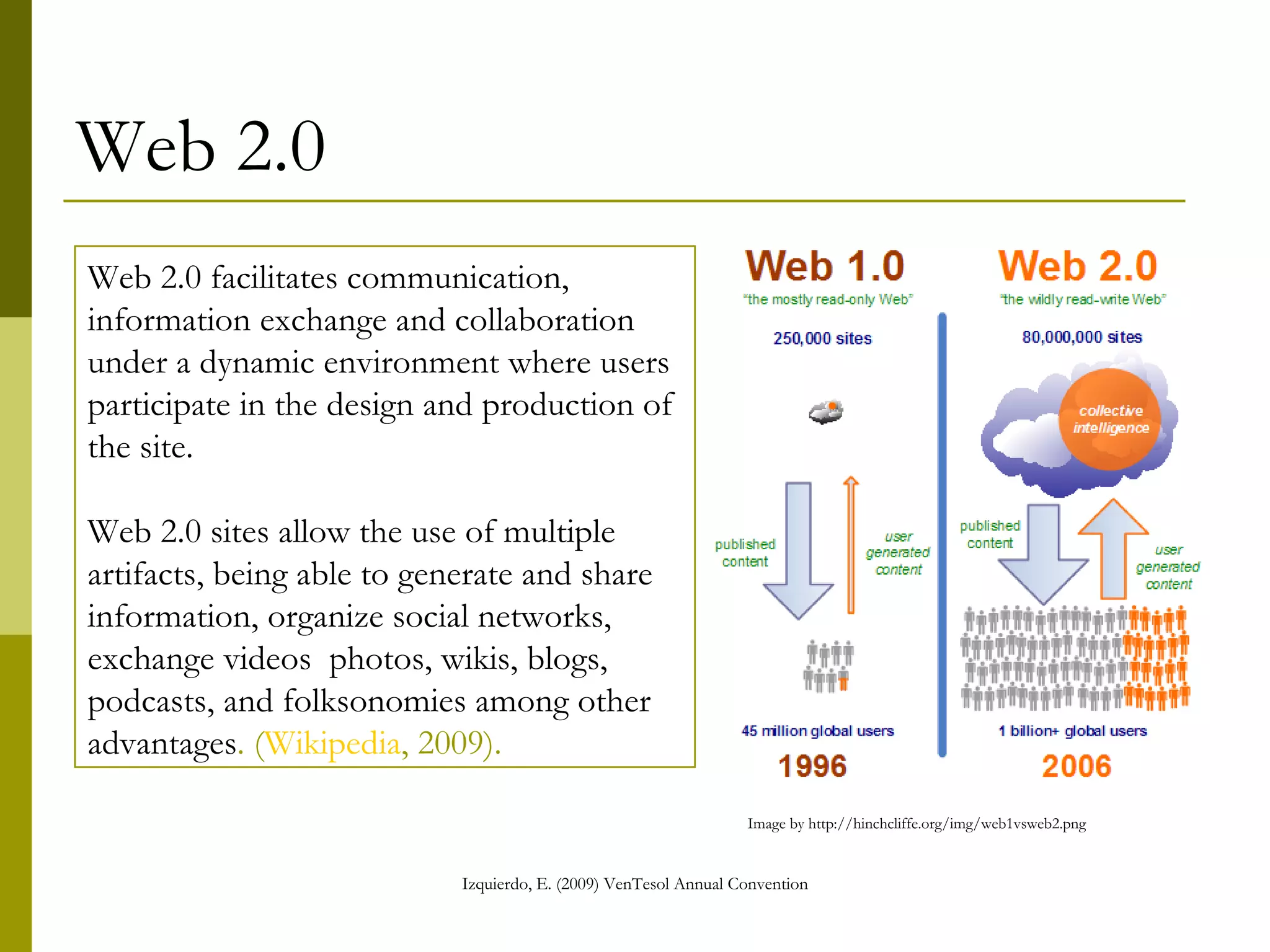
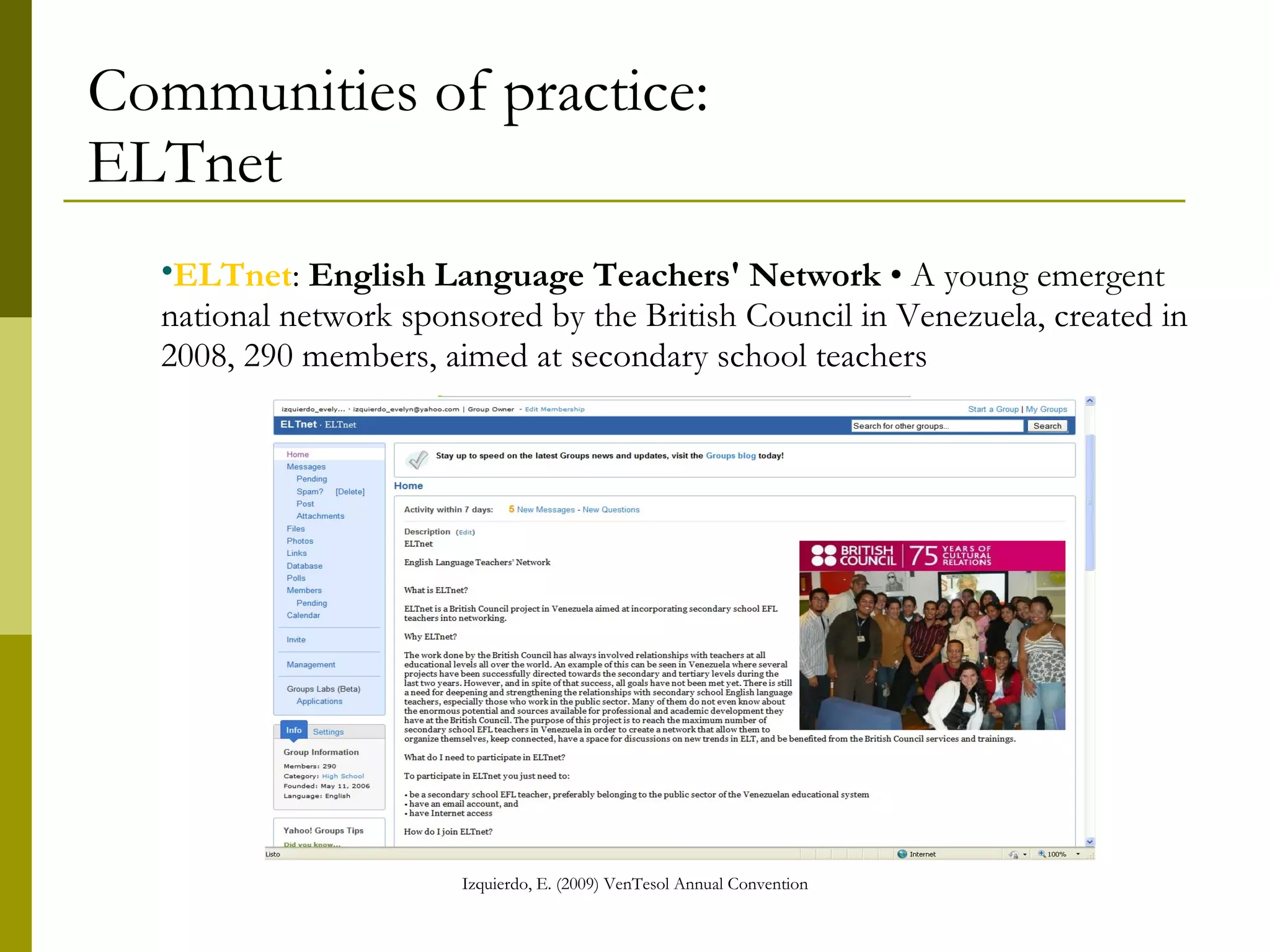
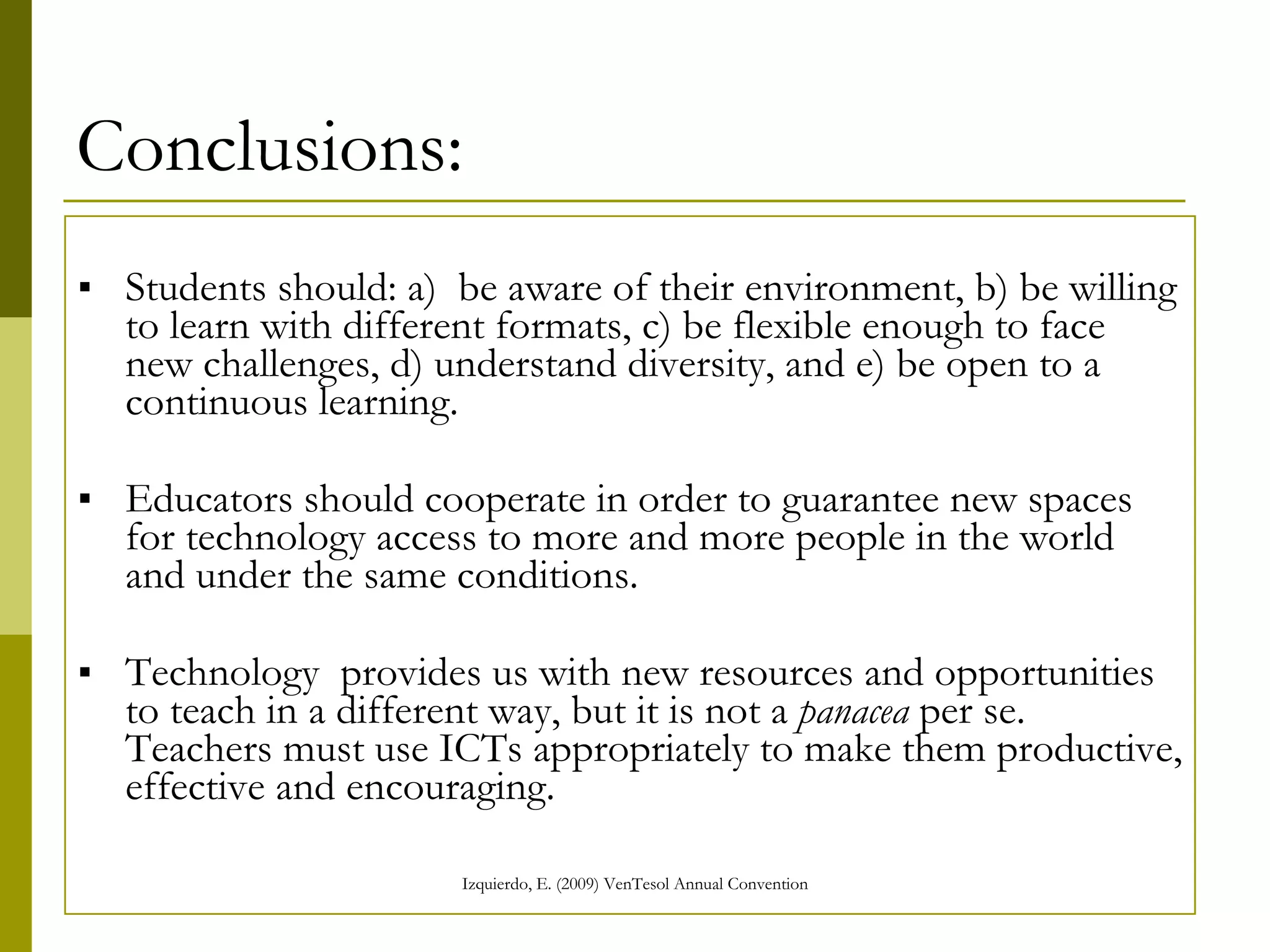
The document discusses the importance of digital literacy for 21st-century EFL teachers, emphasizing the need for skills in using technology effectively in education. It outlines the competencies required for both teachers and students, highlighting the role of ICT in fostering collaboration and interaction in learning. Additionally, it reviews various digital platforms and tools, promoting the integration of technology in language teaching and the necessity for educators to adapt to new teaching methods that meet the demands of modern society.
![XXVII VenTESOL ANNUAL CONVENTION: “BUILDING BRIDGES IN ELT” May 29-30, 2009 Digital Literacy: What a 21st Century EFL Teacher Should Know Evelyn Izquierdo Escuela de Educación Universidad Central de Venezuela [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitalliteracy-090531222958-phpapp02/75/Digital-Literacy-1-2048.jpg)


























![References American Association for Higher Education (October, 1999) and the Council of Independent Colleges (February, 2004). Information Literacy Competency Standards of Higher Education. [Online] Available at: http:// www.ala.org /ala/ mgrps / divs / acrl / standards / standards.pdf Retrieved April 15, 2009. Downes, S. (2007) What connectivism is . [En línea] Blog: Half an hour. [Online] Available at : http:// halfanhour.blogspot.com /2007/02/ what - connectivism - is.html Retrieved November 23, 2008 Educational Testing Service, International ICT Literacy Panel (2002). Digital transformation: A framework for ICT literacy (A report of the International ICT Literacy Panel). Princeton, NJ: Educational Testing Service. [Online] Disponible en: http:// www.ets.org /Media/ Research / pdf / ictreport.pdf Retrieved March 18, 2009 Izquierdo, E. (2008). Networking - Redes de apoyo para profesores de inglés. Presentation at Lenguas y Contemporaneidad. Universidad Metropolitana, Caracas, May 30-31, 2008. [Online] Available at: http://docs.google.com/Presentation?id=dgbxs8sn_200gg24mdc4 Izquierdo, E. y Verschoor, J. (2009). Social Bookmarks . Integrating Technology for Instruction and Learning. [Online] Available at: http:// www.slideshare.net / EvelynIzquierdo /social-bookmarking-1293488 Retrieved April 3, 2009 Jones, C. (2003). What is a Community of Practice? [Online] http://groups.yahoo.com/ group /evonline2002_webheads/files/2003/ colloquium / CoP.ppt Retrieved August 14, 2005.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitalliteracy-090531222958-phpapp02/75/Digital-Literacy-34-2048.jpg)
![References Marquès, P. (2000, ). Nueva cultura, nuevas competencias para los ciudadanos . [Online] Updated in 2007 and 2009. Available at: http:// dewey.uab.es/PMARQUES/competen.htm Retrieved November 22, 2004 Rheingold, H. (1993). “ The Virtual Community ”,. Reading, MA, Addison-Wesley. Siemmens, G. (2004). Connectivism: A learning theory for the digital age. [Online] Available at http:// www.elearnspace.org/Articles/connectivism.htm Retrieved March 12, 2009 UNESCO (2008, en Eduteka). ICT Competency Standards for Teachers[Online, Eduteka Website] Available at http:// www.eduteka.org/EstandaresDocentesUnesco.php Retrieved January 18, 2009 Webopedia (2009). History of Blogging . [Online] Available at: http:// www.webopedia.com/quick_ref/history_of_blogging.asp Retrieved July 29, 2008 Wikipedia (2009). Virtual online environments. [Online encyclopedia]. Available at http:// es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ambiente_Educativo_Virtual Retrieved April 16, 2009. Wikipedia (2009). Podcast. [Online encyclopedia]. Available at http:// es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Podcasting Retrieved April 18, 2009. Wikipedia (2009). Tim Berners-Lee. [Online encyclopedia]. Available at http:// en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tim_berners -lee Retrieved April 16, 2009. Wikipedia (2009). Web 2.0 . [Online encyclopedia]. Available at http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Web_2.0 . Retrieved April 14, 2009](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitalliteracy-090531222958-phpapp02/75/Digital-Literacy-35-2048.jpg)
![Thank you very much for your attention! Evelyn Izquierdo Escuela de Educación Universidad Central de Venezuela [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitalliteracy-090531222958-phpapp02/75/Digital-Literacy-36-2048.jpg)