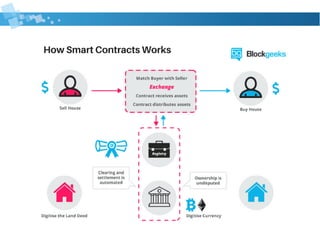
Blockchain technology allows participants to interact without a central authority by maintaining a distributed ledger of an shared database. It has applications beyond digital currencies like voting, smart contracts, and digital property records. Blockchains use cryptography and consensus to securely add transactions in blocks to an immutable chain. There are public, private, and consortium blockchains depending on who can read/write to the ledger. Blockchain technology has evolved from currency in Blockchain 1.0 to supporting smart contracts in Blockchain 2.0 and now decentralized applications in Blockchain 3.0.