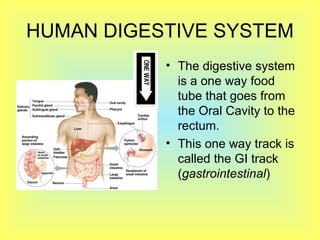
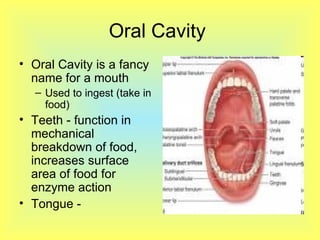
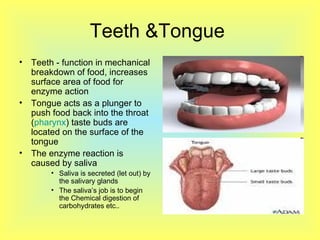
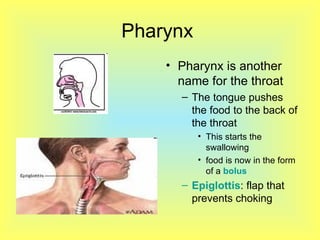
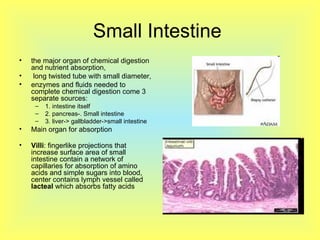
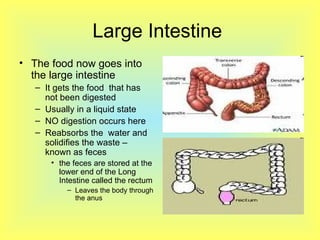
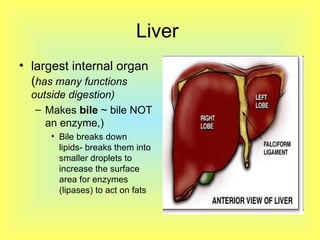
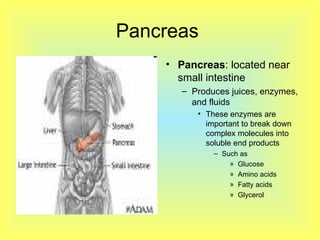
The document summarizes the human digestive system in three parts. It describes the four main parts of digestion as ingestion, digestion, absorption, and elimination. It then explains the two types of digestion - mechanical and chemical digestion. Finally, it provides an overview of the major organs that make up the digestive system, including the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, liver, gallbladder and pancreas and their functions in digesting food.