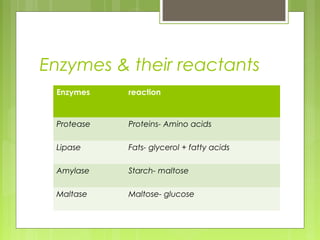
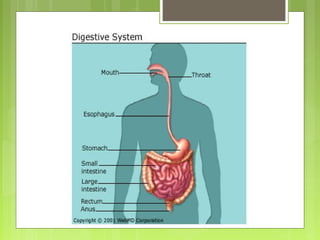
Digestion is the process by which food is broken down into smaller molecules that can be absorbed by the body. It involves both mechanical and chemical breakdown of food. In the mouth, teeth chew food and saliva contains the enzyme amylase. The esophagus transports food to the stomach through peristalsis. The stomach contains acid and enzymes that break food down further. The pancreas and liver secrete enzymes and bile that aid in digestion within the small intestine. Nutrients are then absorbed through the intestinal walls and remaining waste is eliminated from the anus.