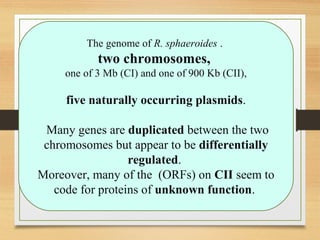
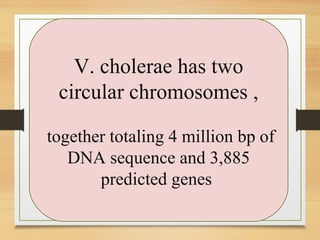
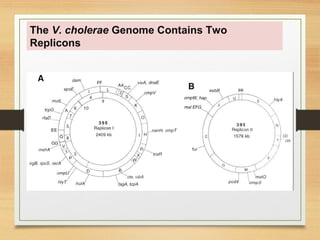
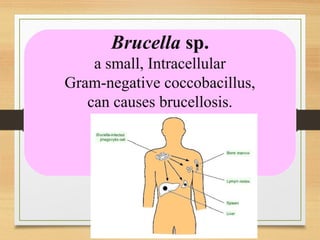
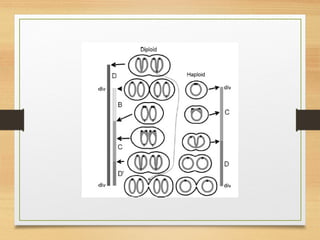
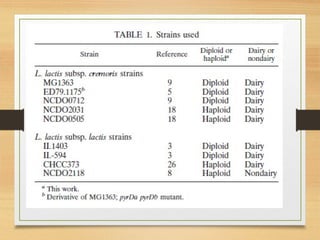
The document discusses various forms of bacterial chromosomes, highlighting that most bacteria possess a single circular DNA molecule while some have multiple chromosomes or linear chromosomes. Examples include Vibrio cholerae and Brucella melitensis, which exhibit two dissimilar chromosomes, and Lactococcus lactis, which remains diploid with two non-replicating chromosomes. The study also notes differences in chromosome organization across bacterial species, including linear and circular structures, and explores the implications of linear genomes in prokaryotes.