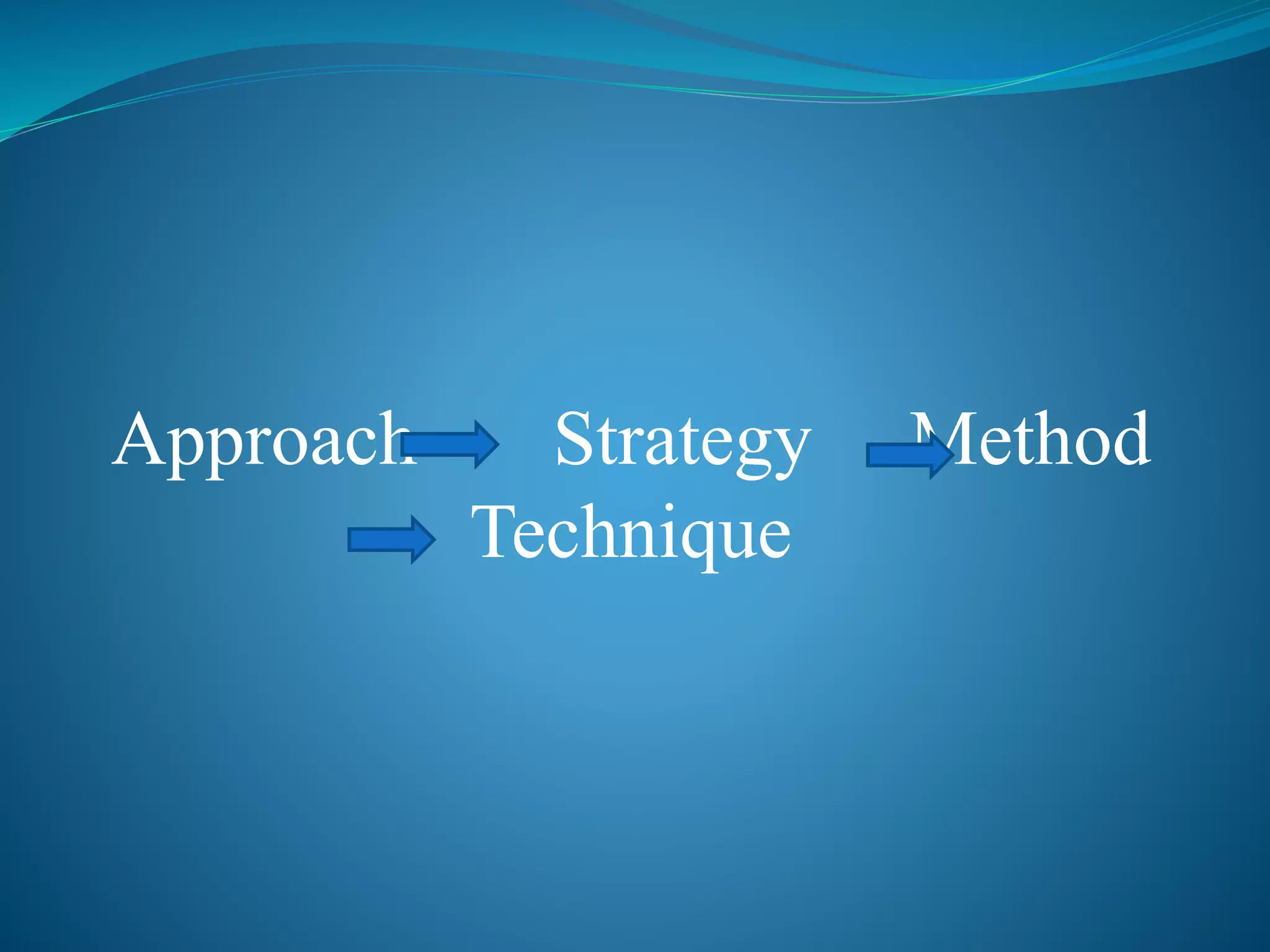
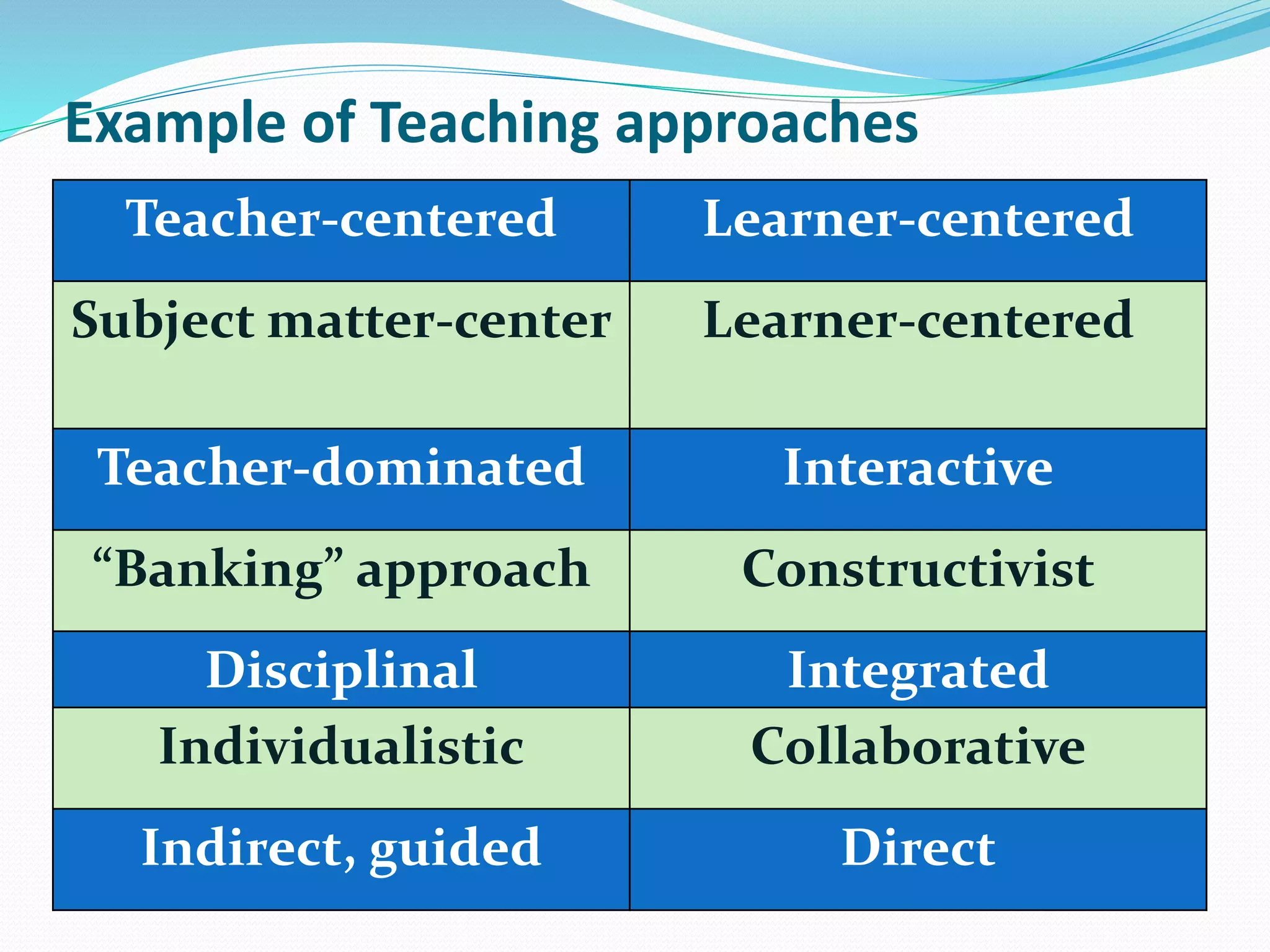
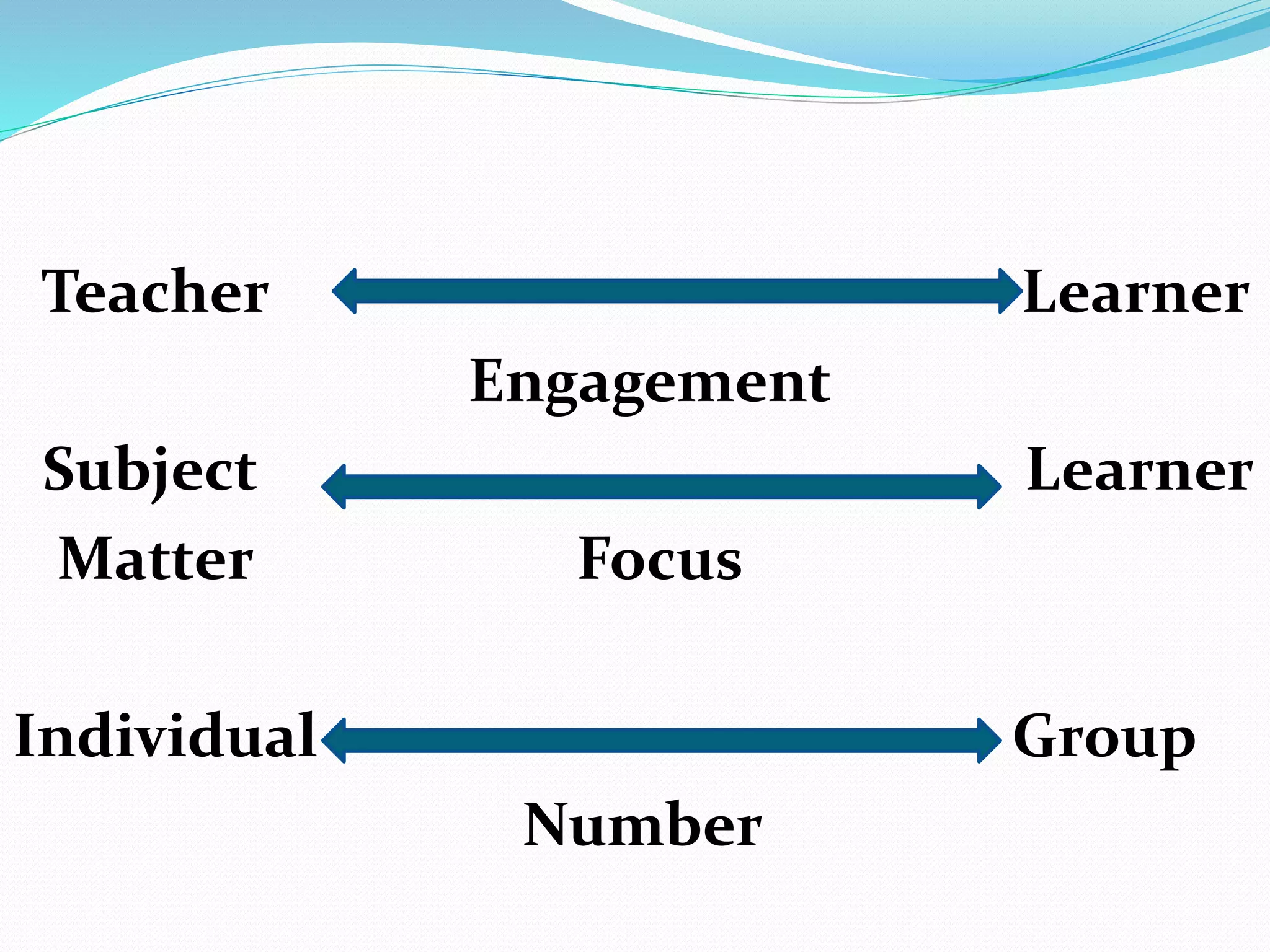
Teaching approaches, strategies, methods, and techniques are different but related concepts for instructing students. Approaches are based on beliefs about learning and derive from a teacher's philosophy, while strategies are long-term plans to achieve goals. Methods are systematic arrangements of steps, and techniques are specific procedures to accomplish tasks. Examples of approaches include teacher-centered, learner-centered, and constructivist models that vary in teacher and learner engagement and participation.