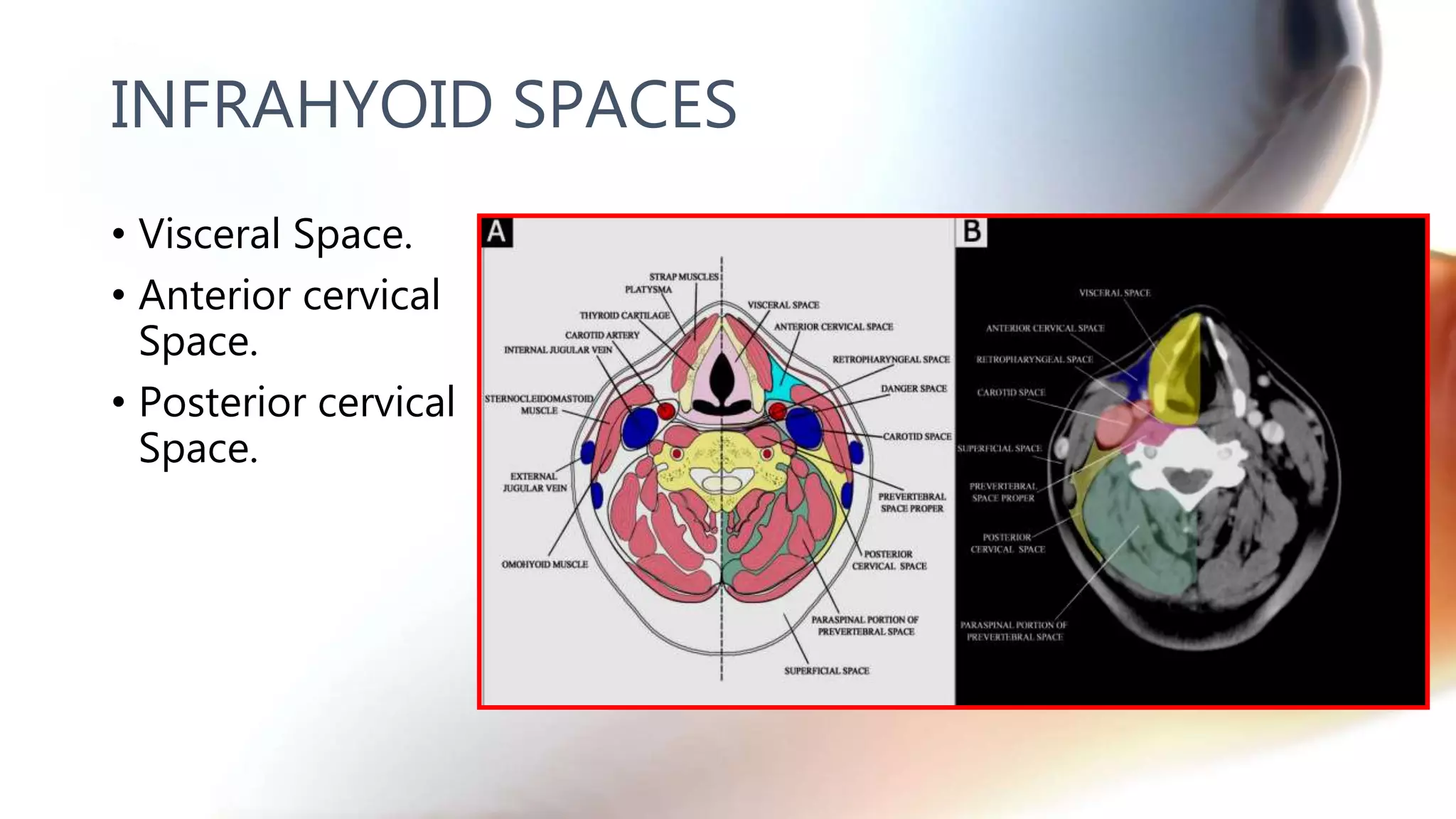
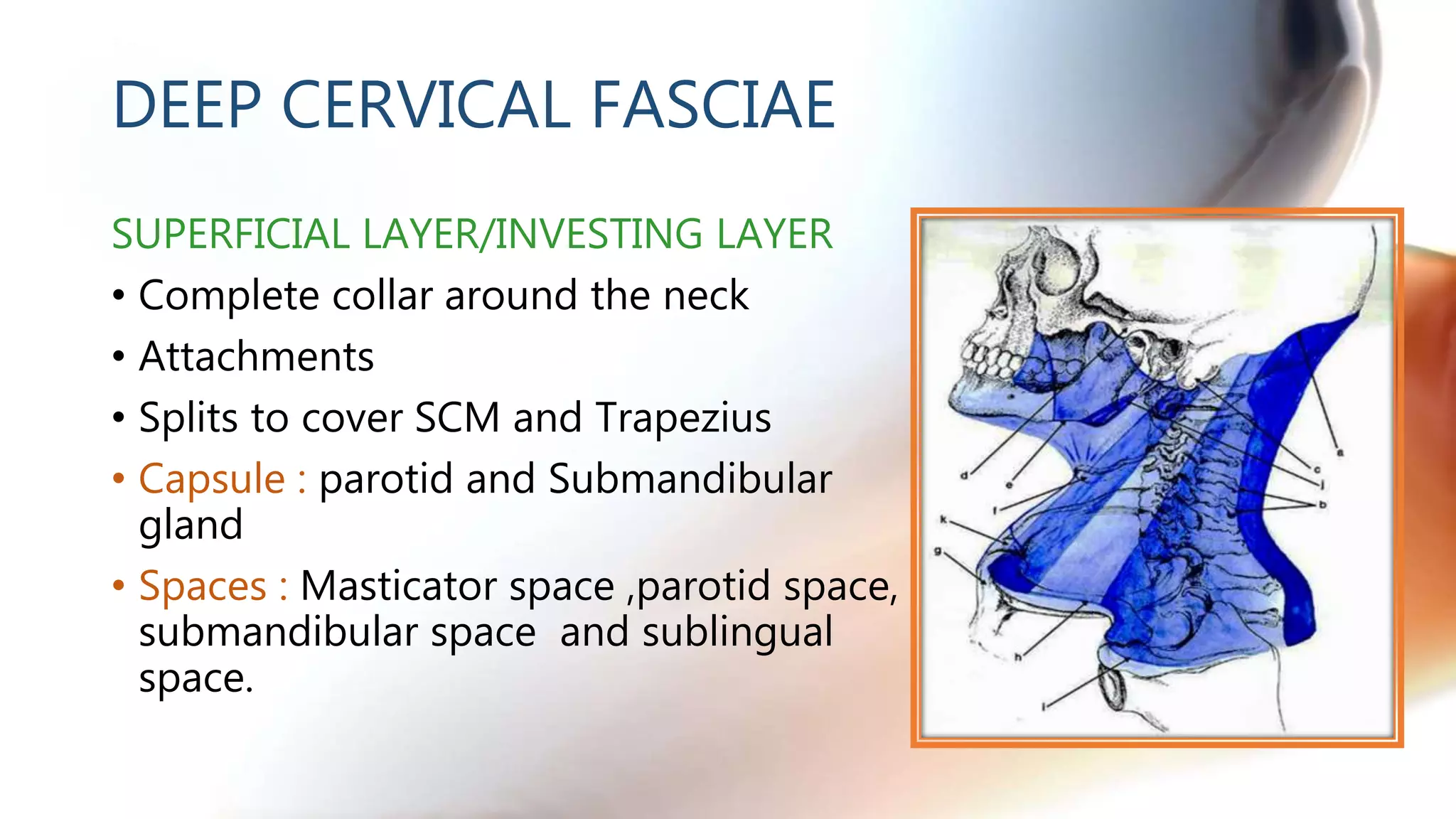
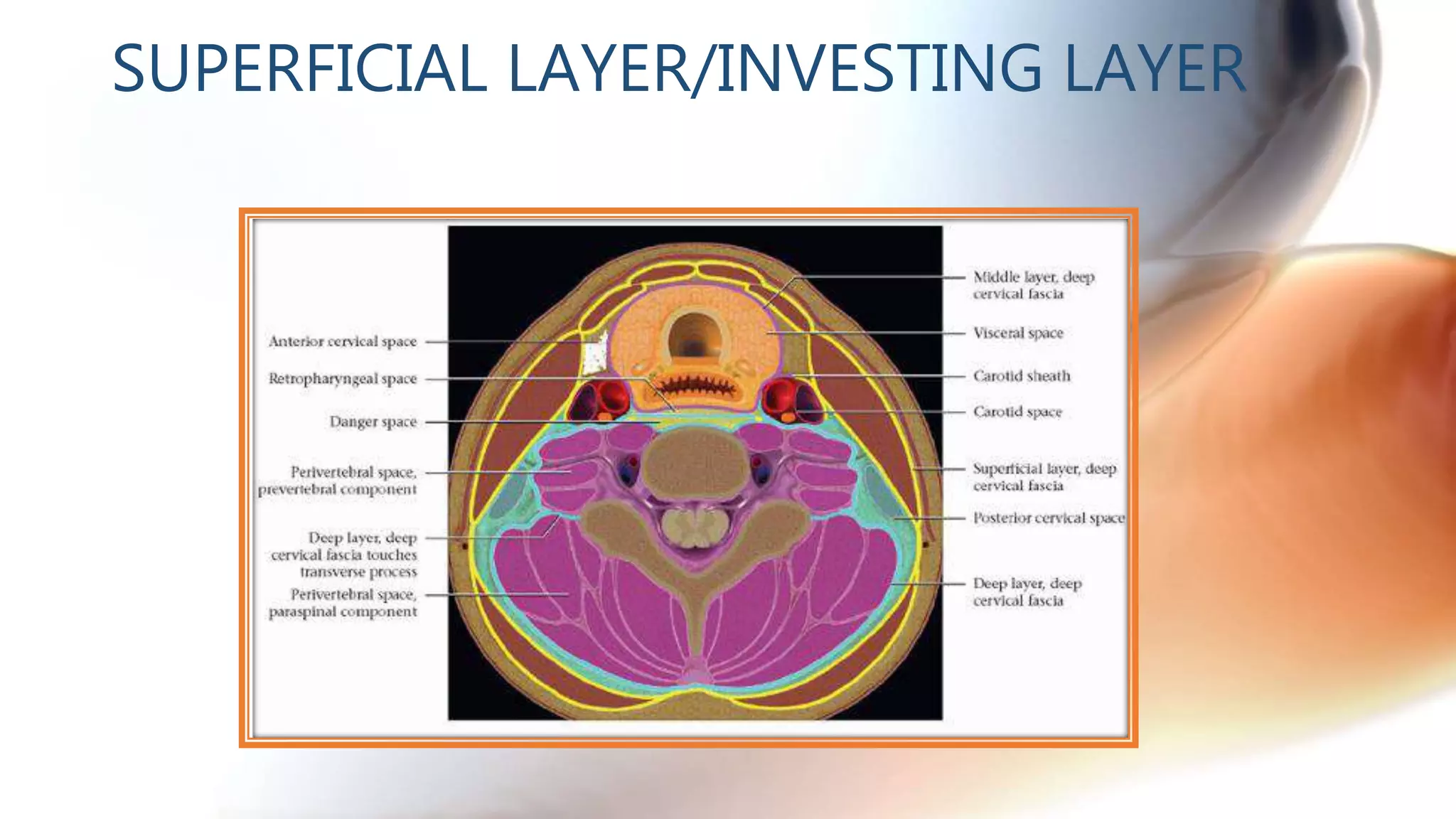
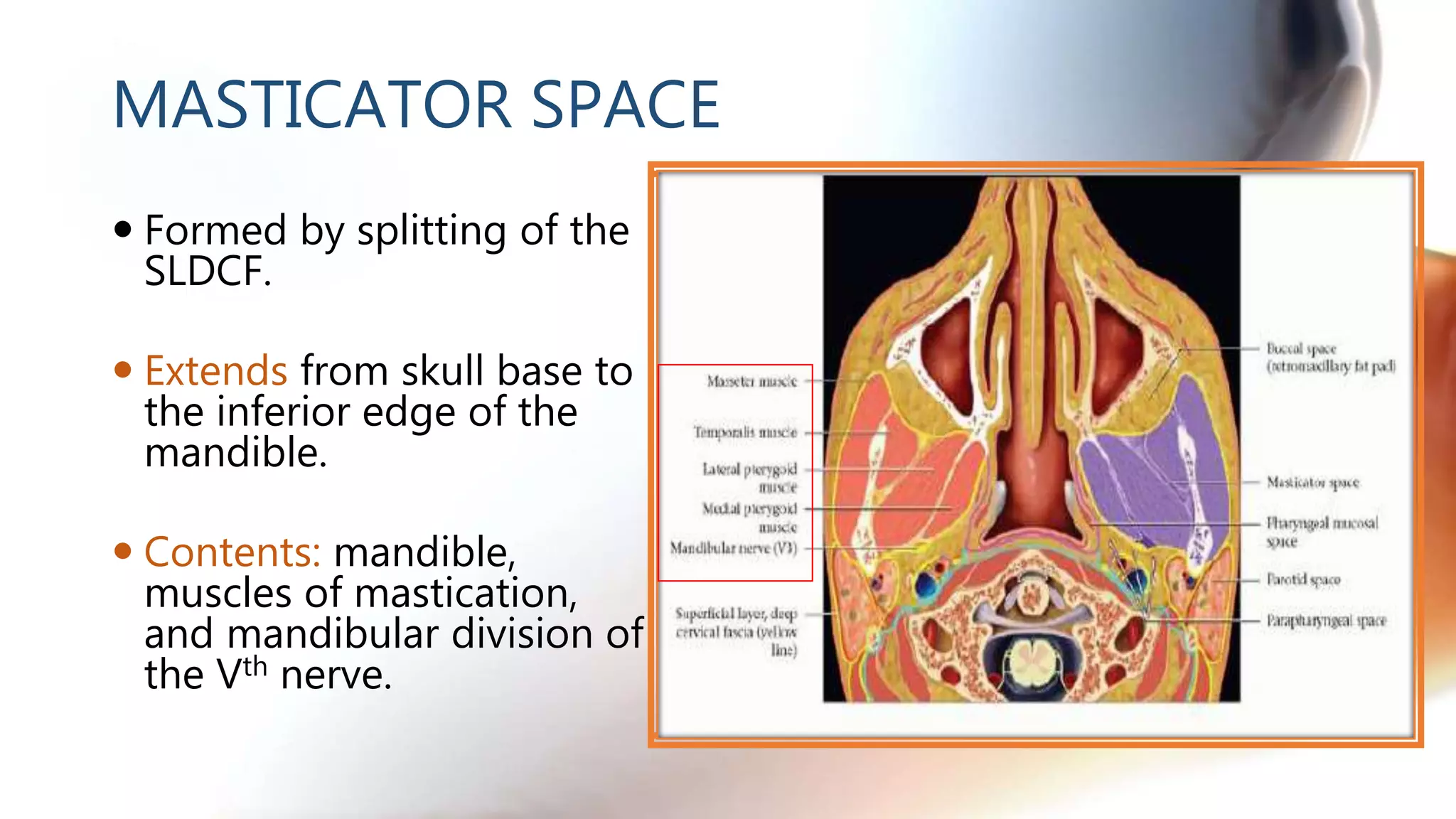
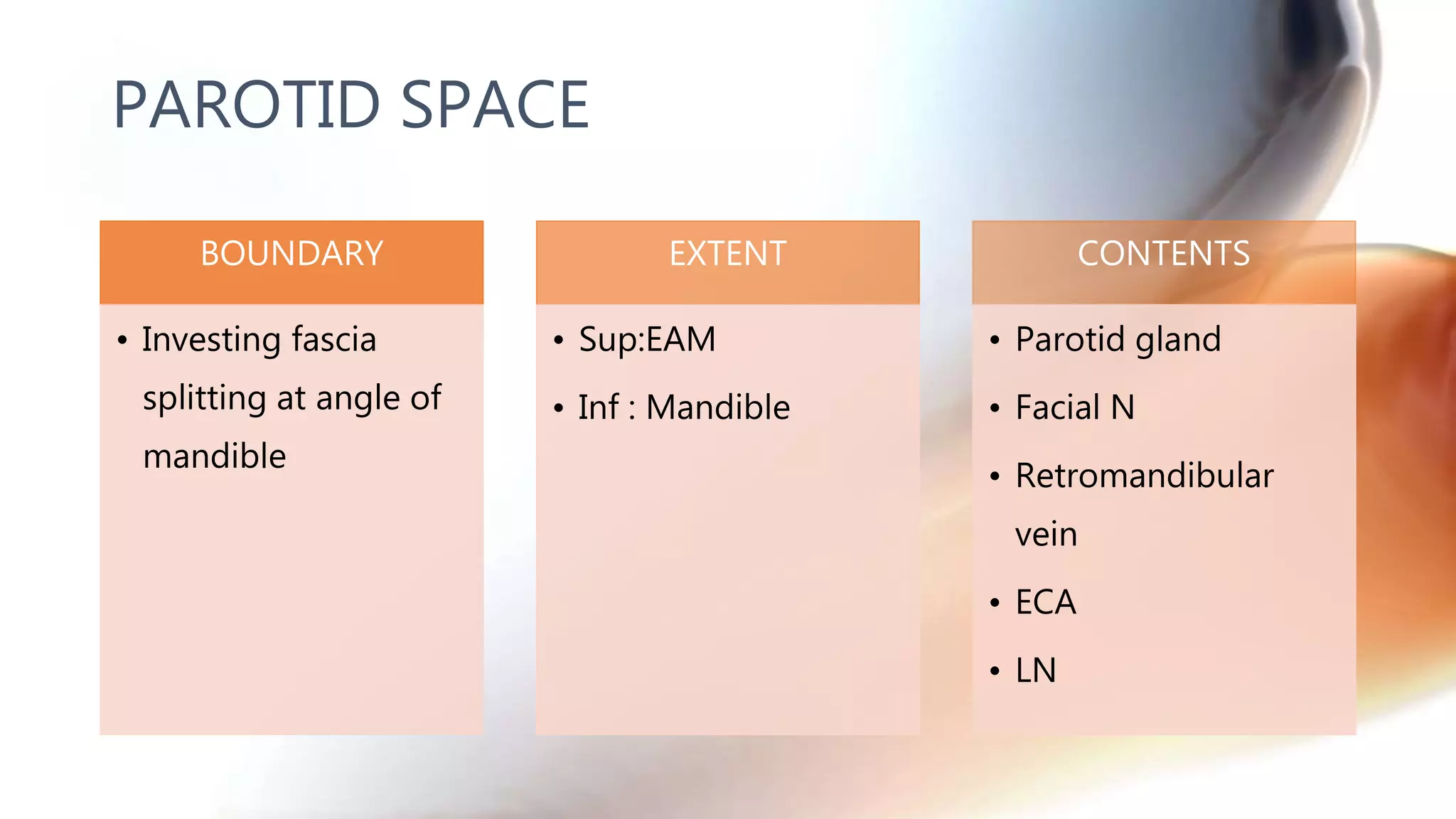
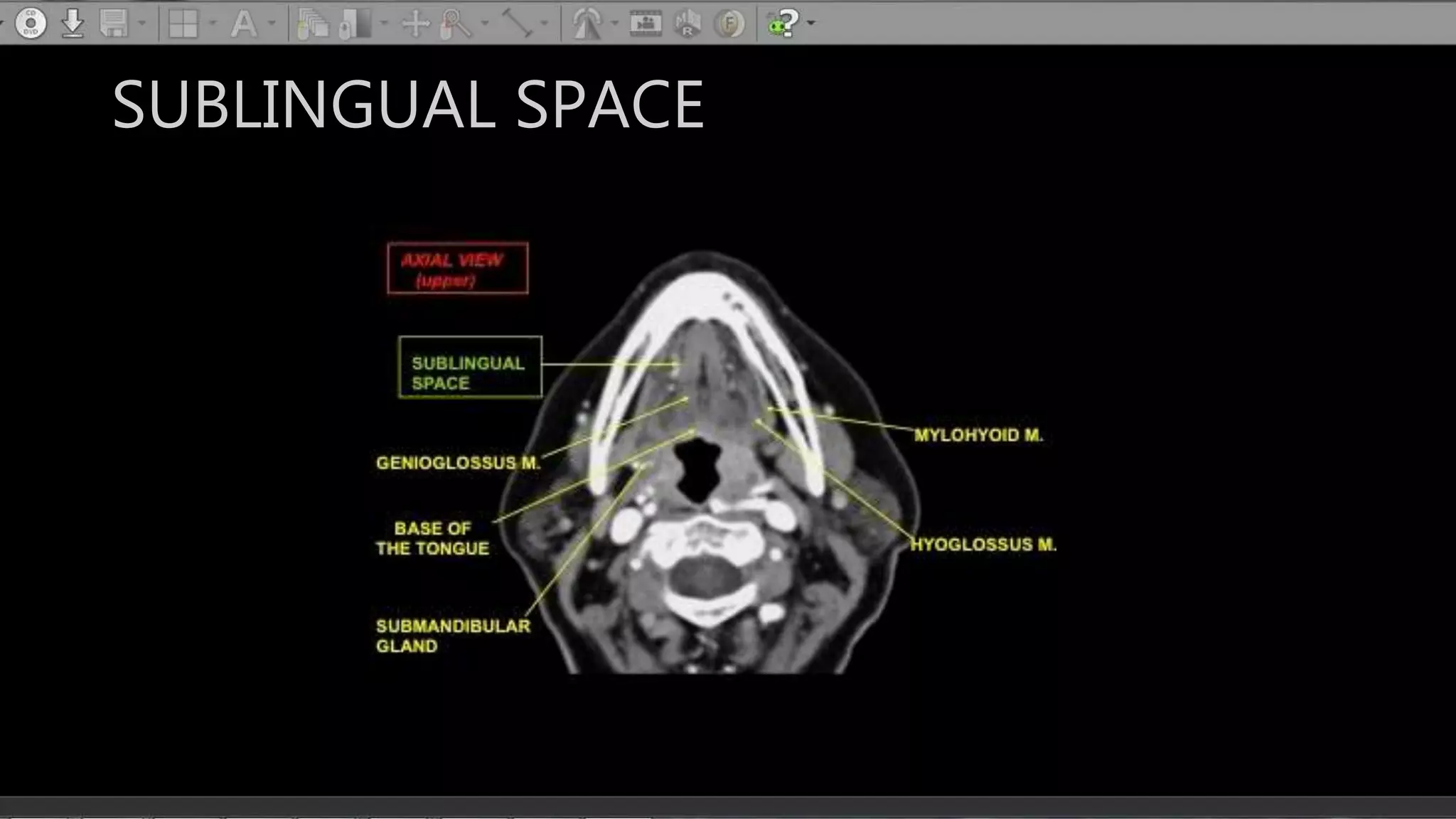
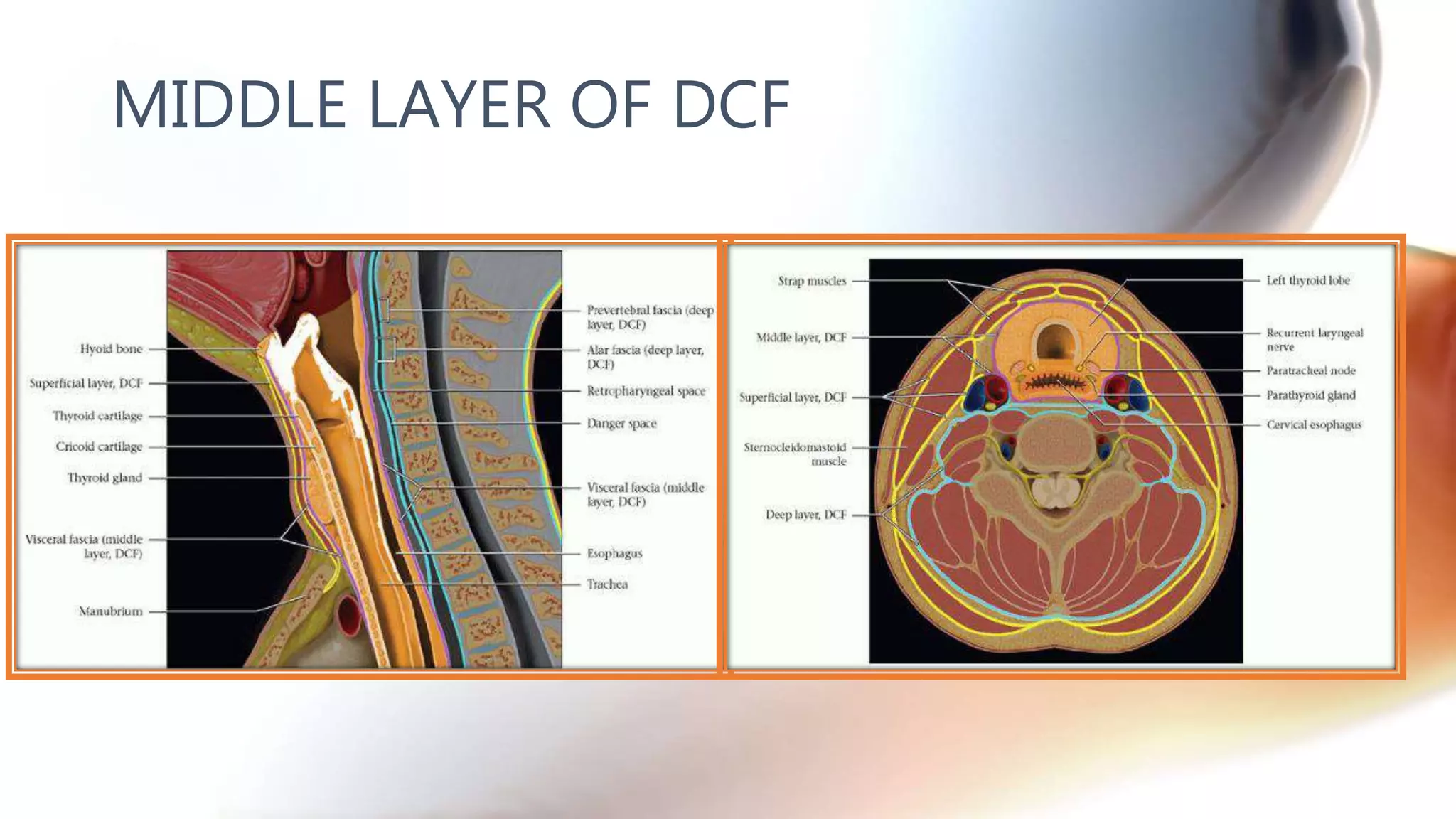
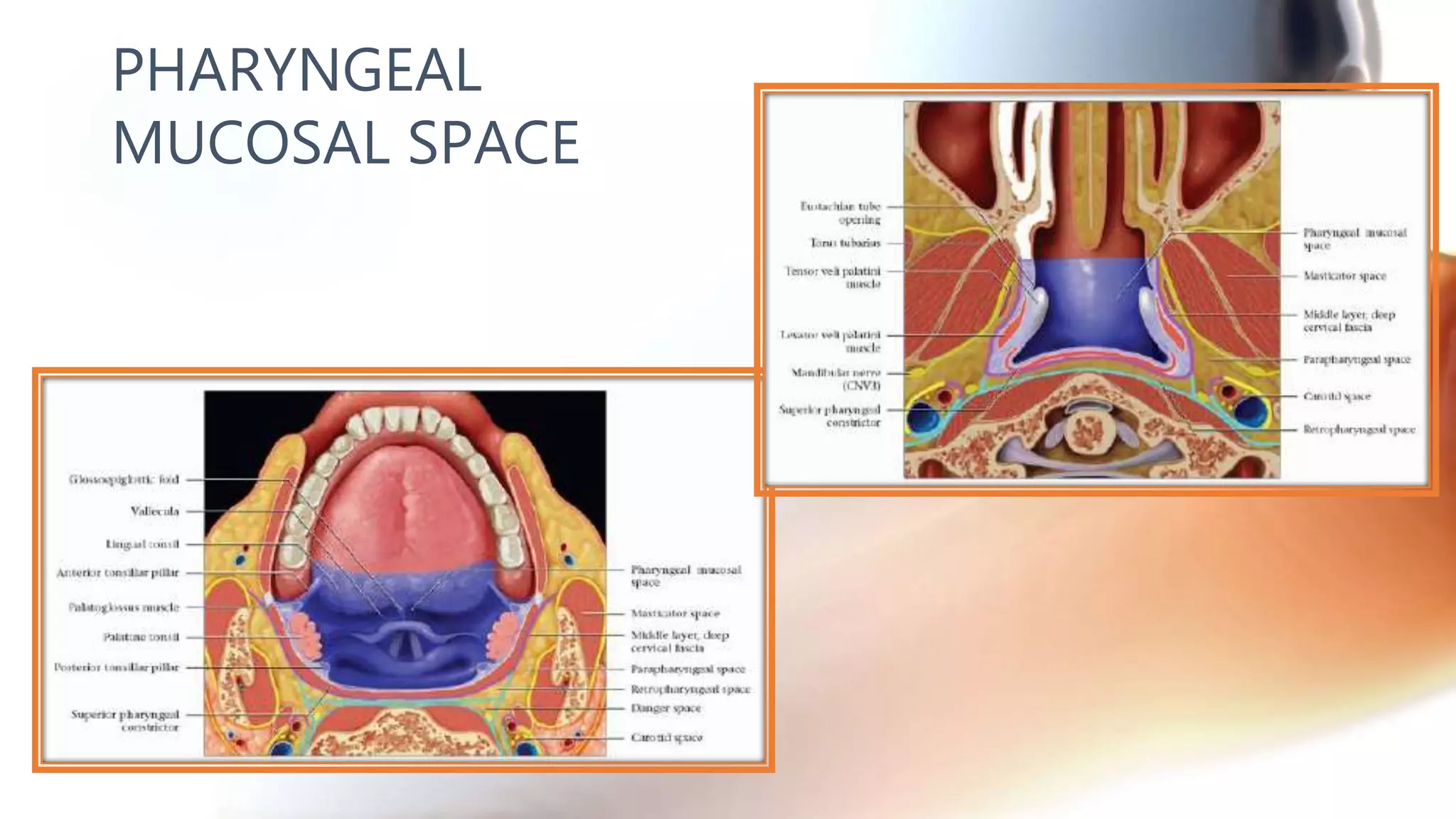
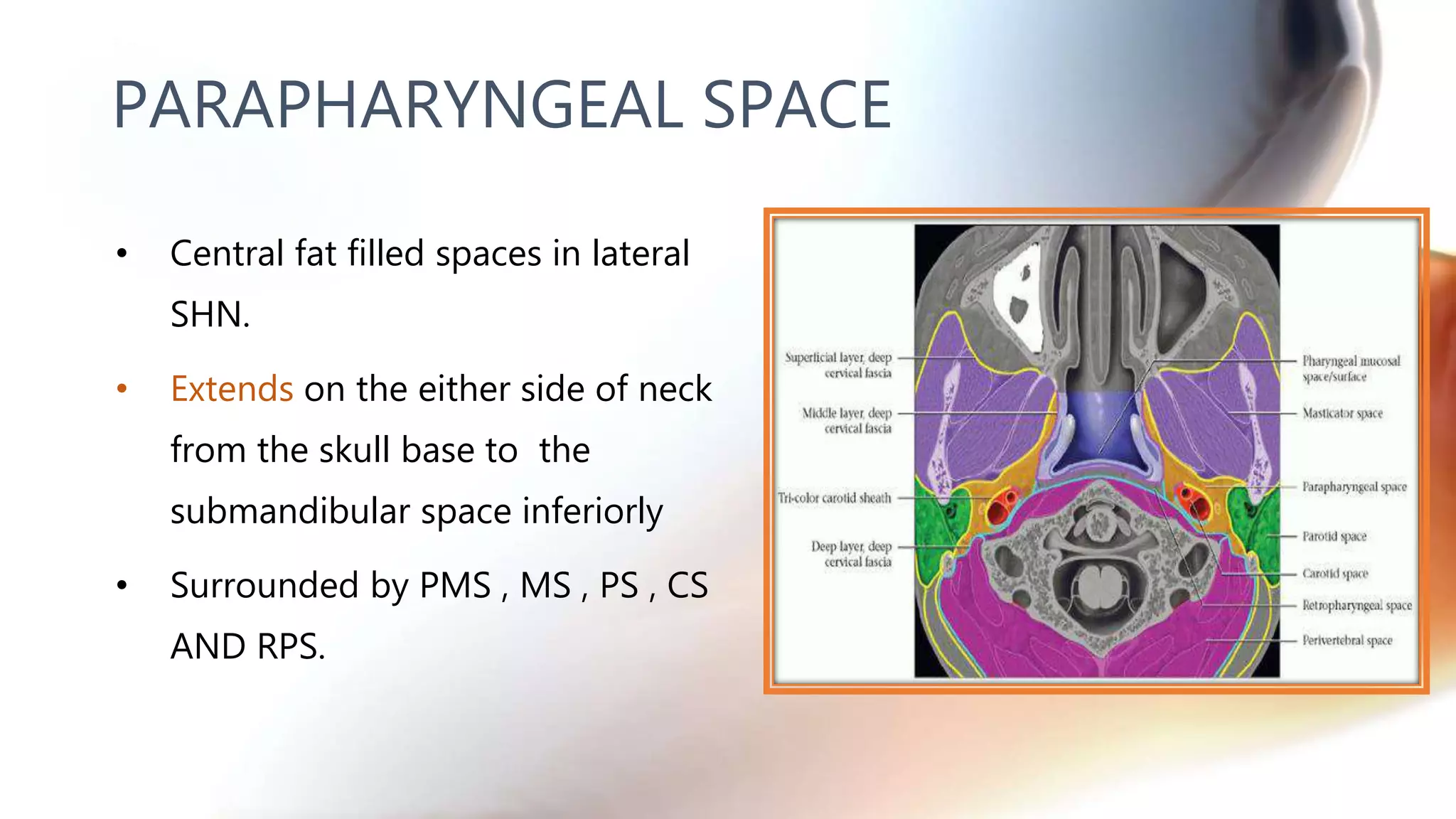
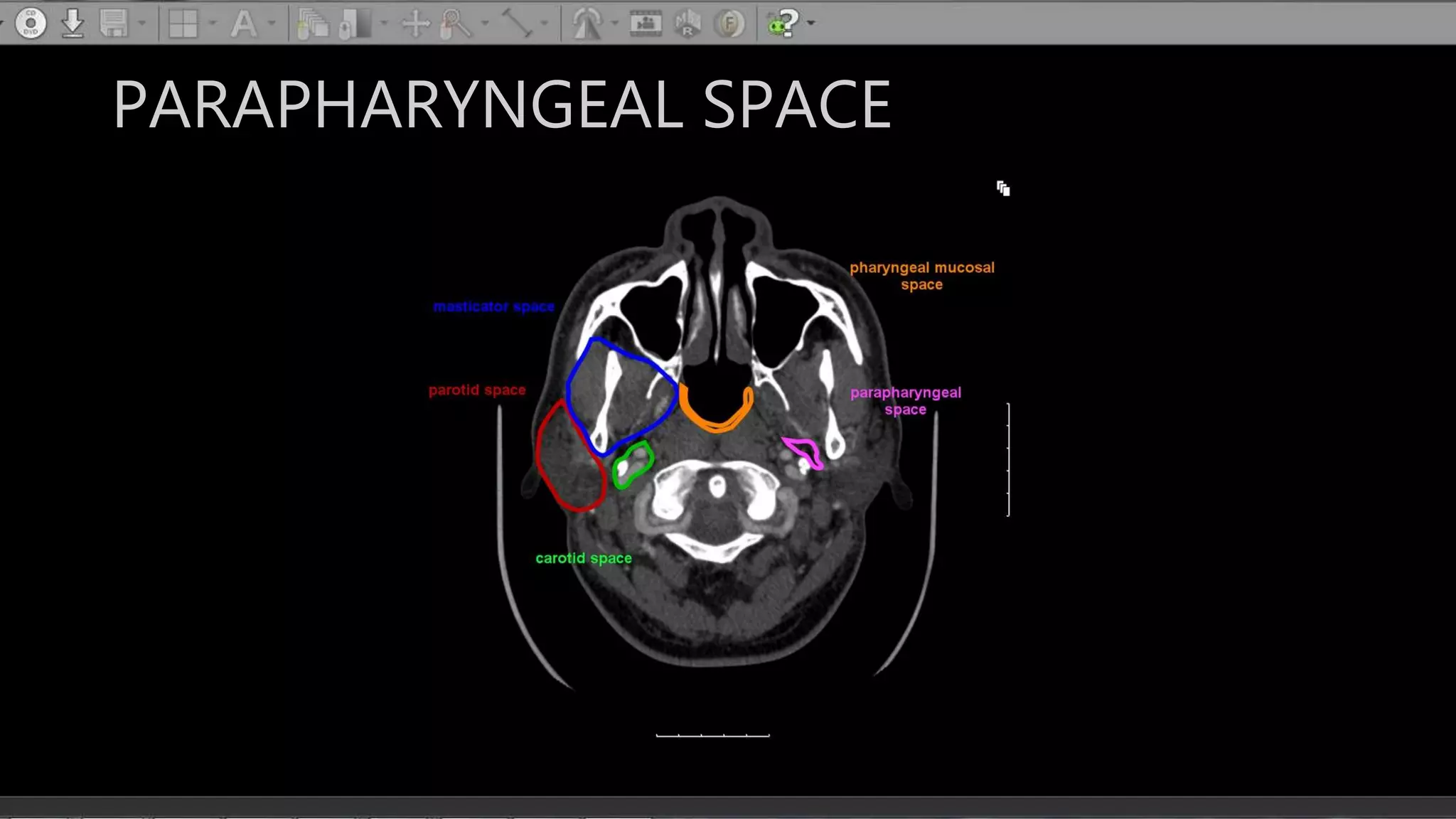
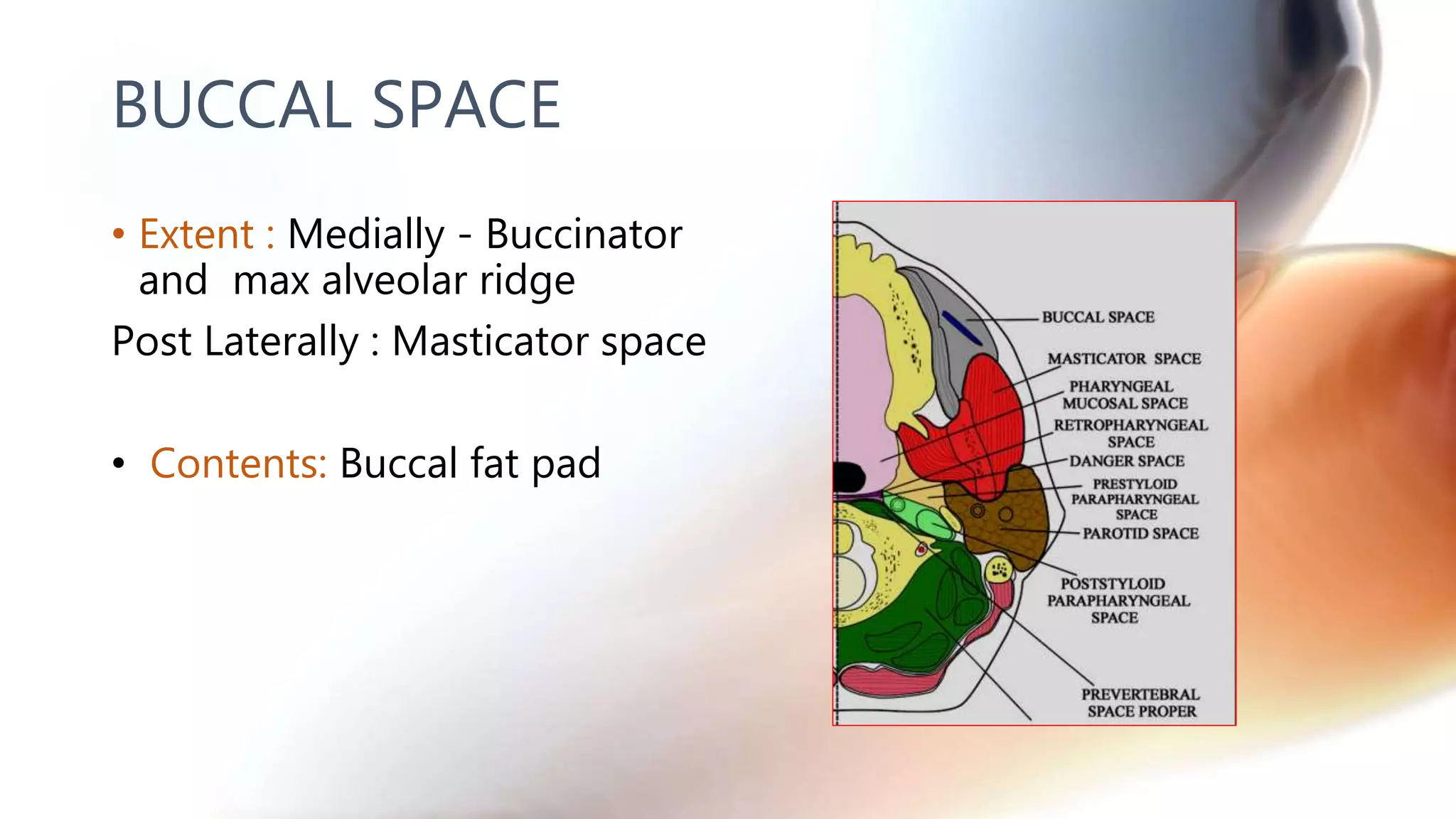
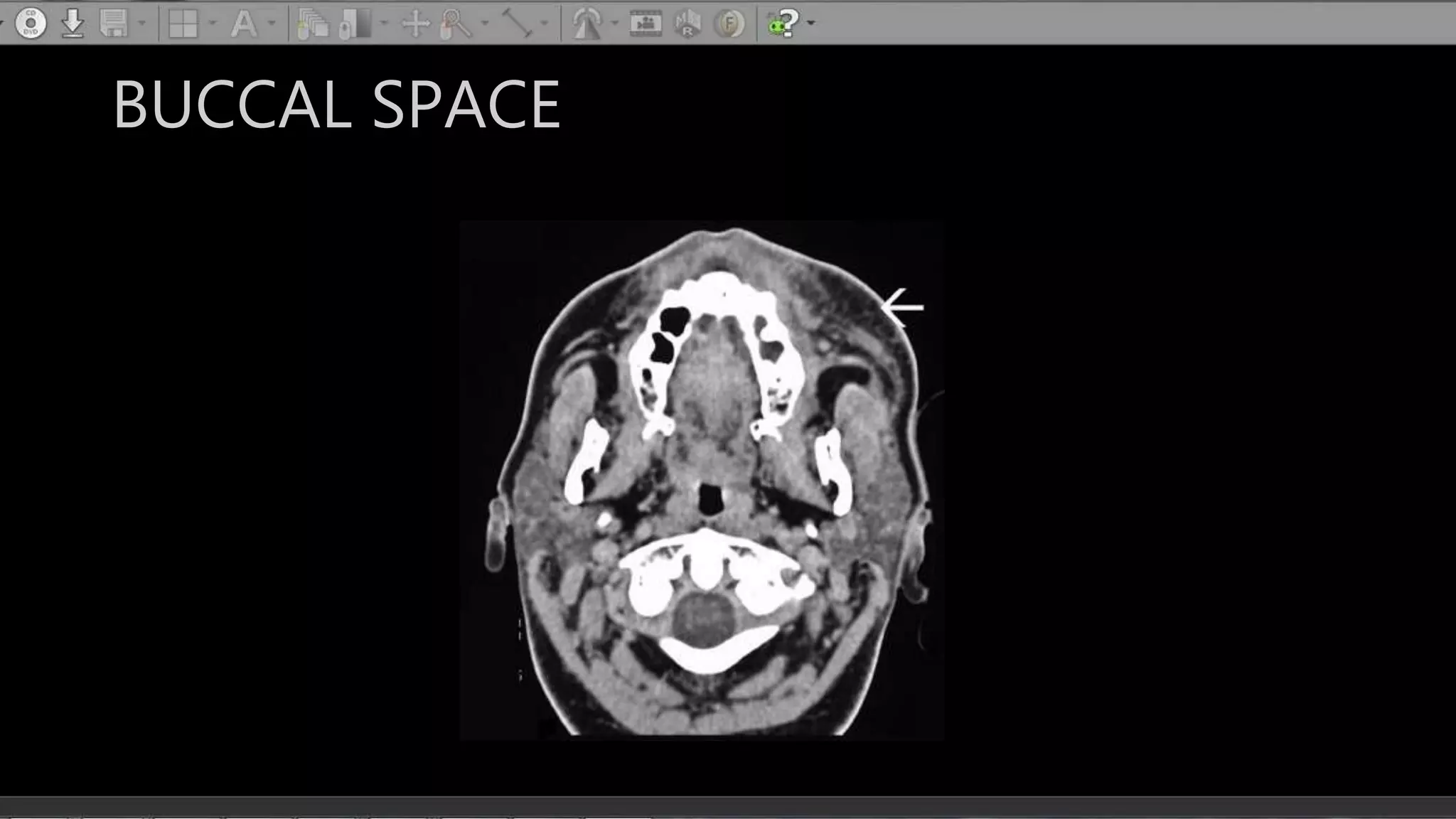
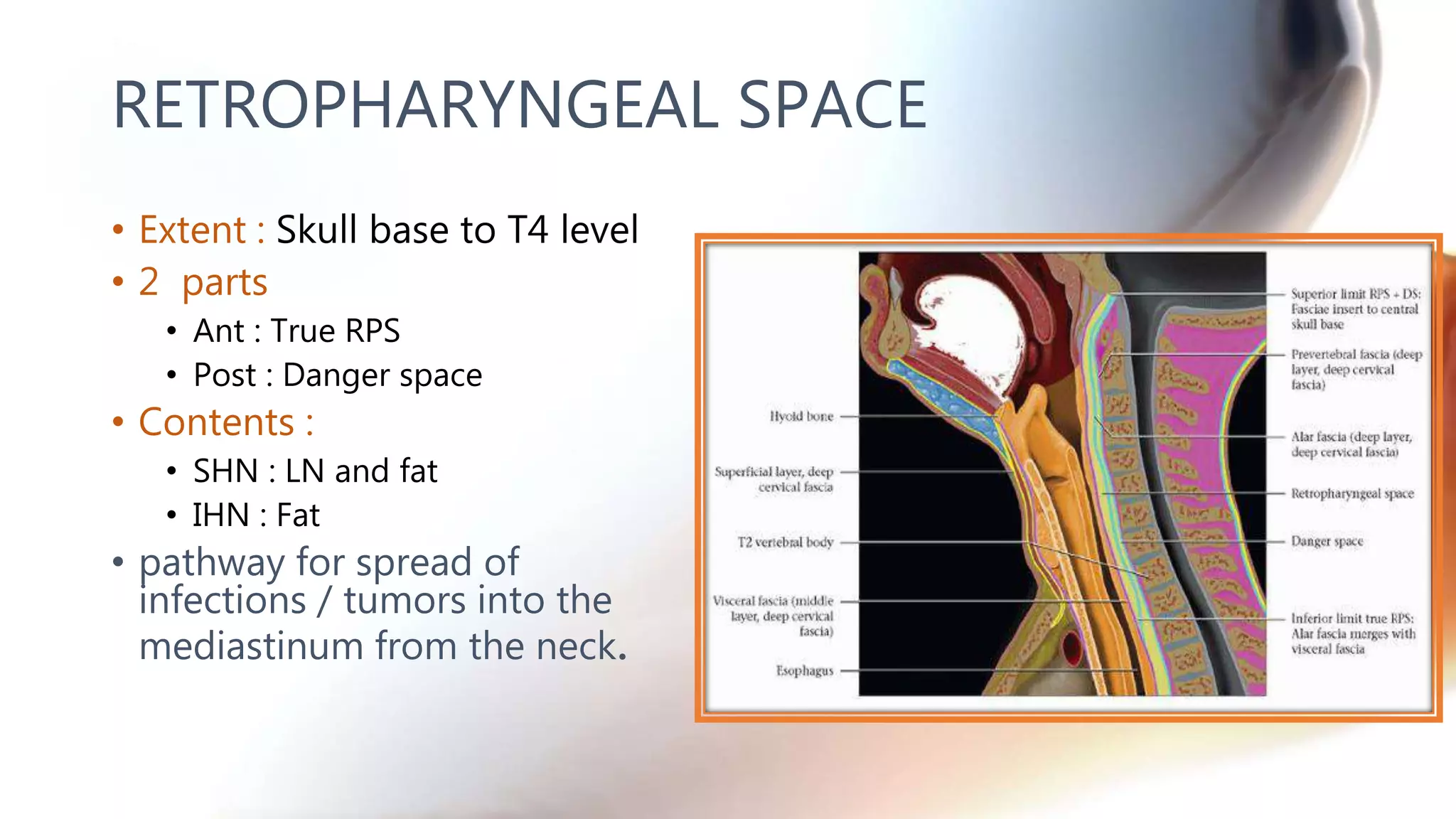
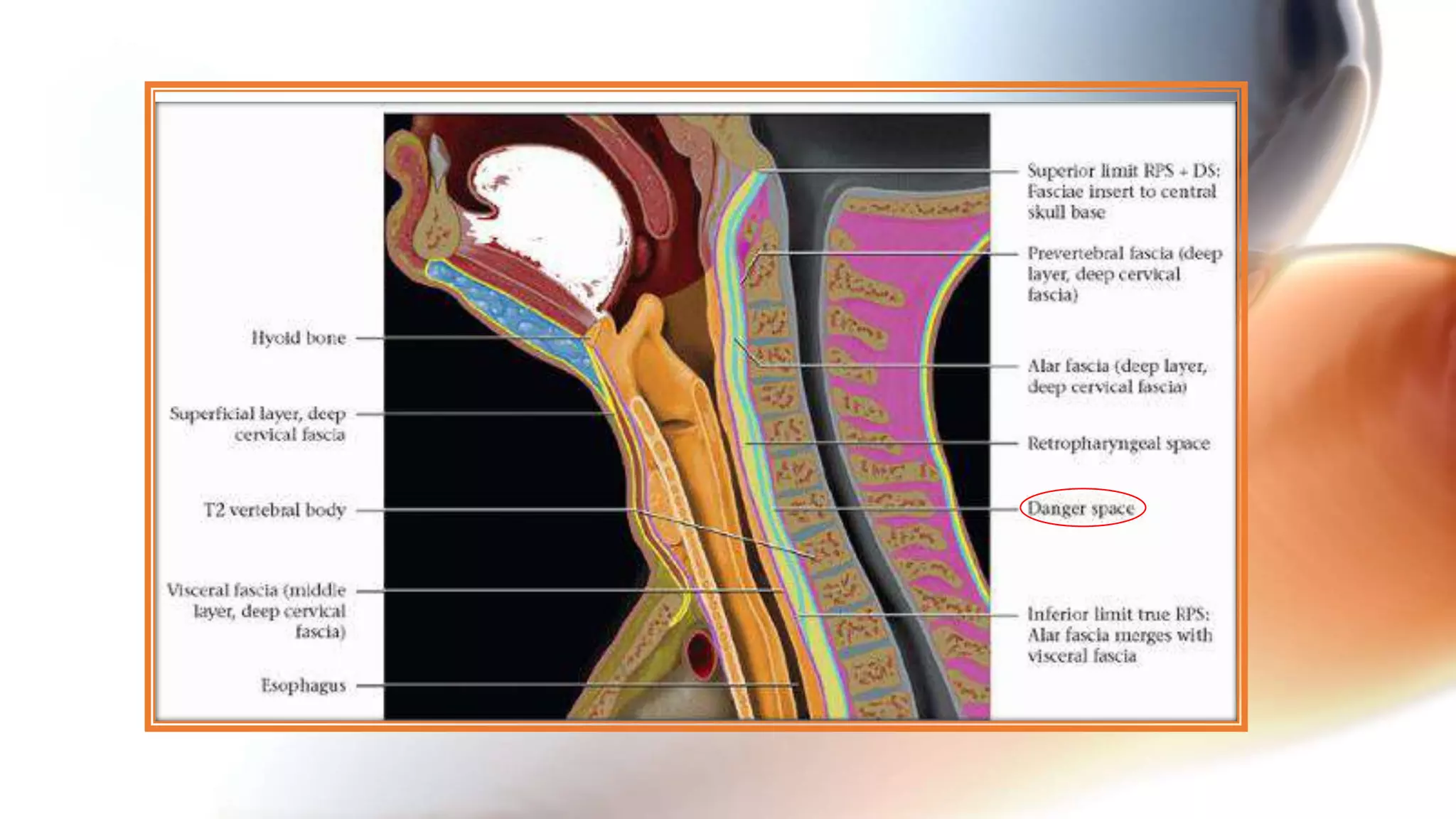
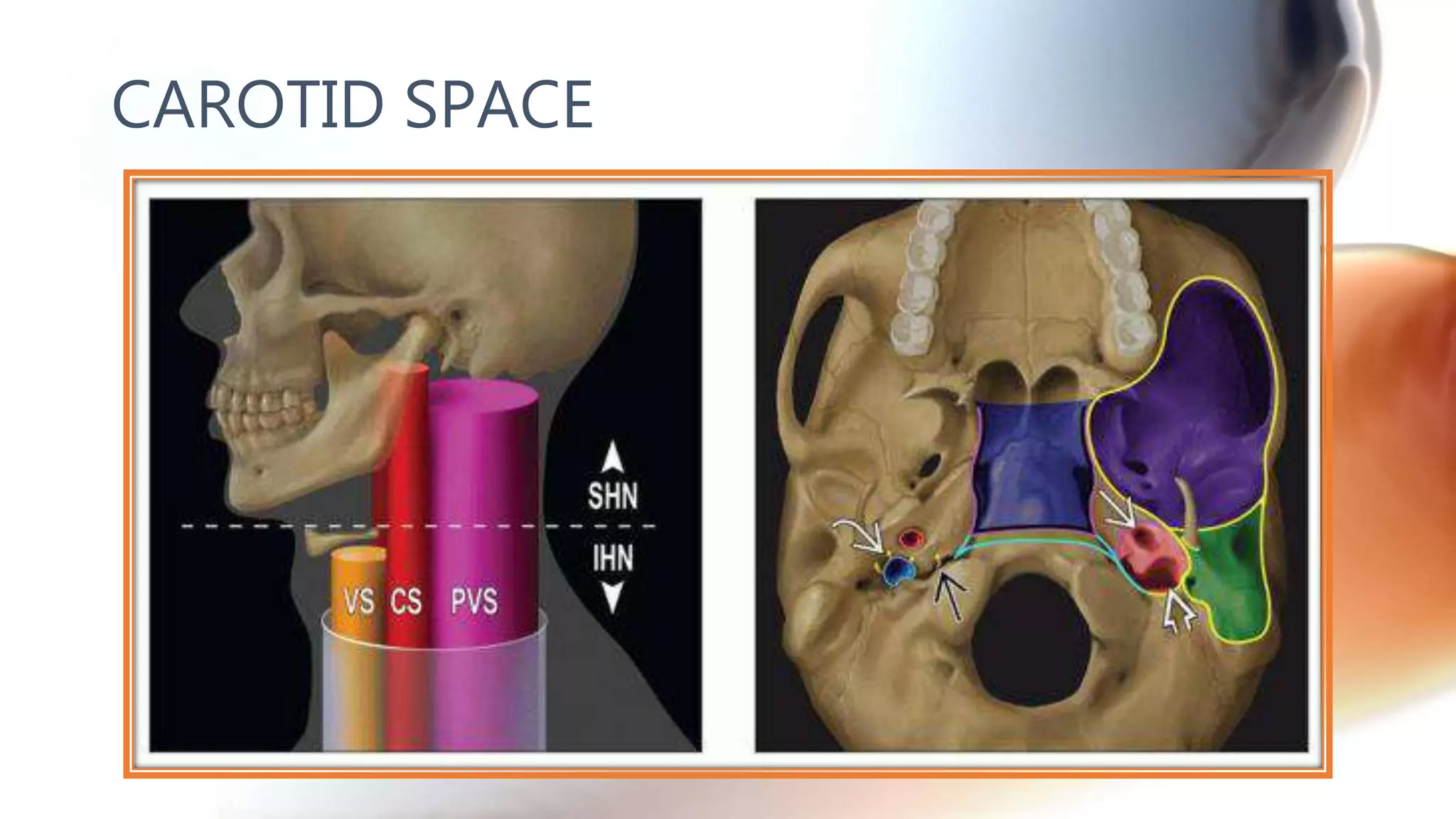
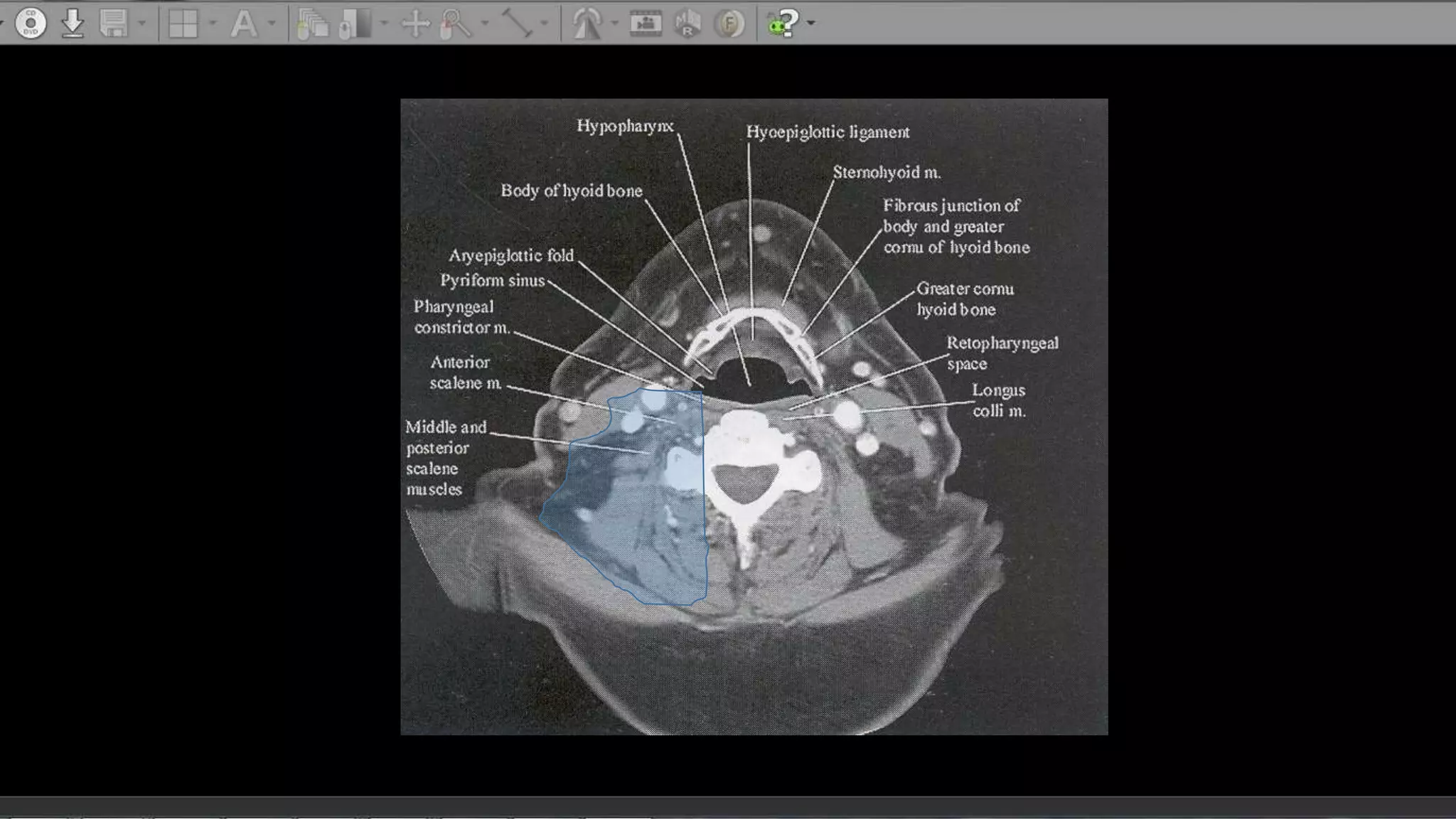
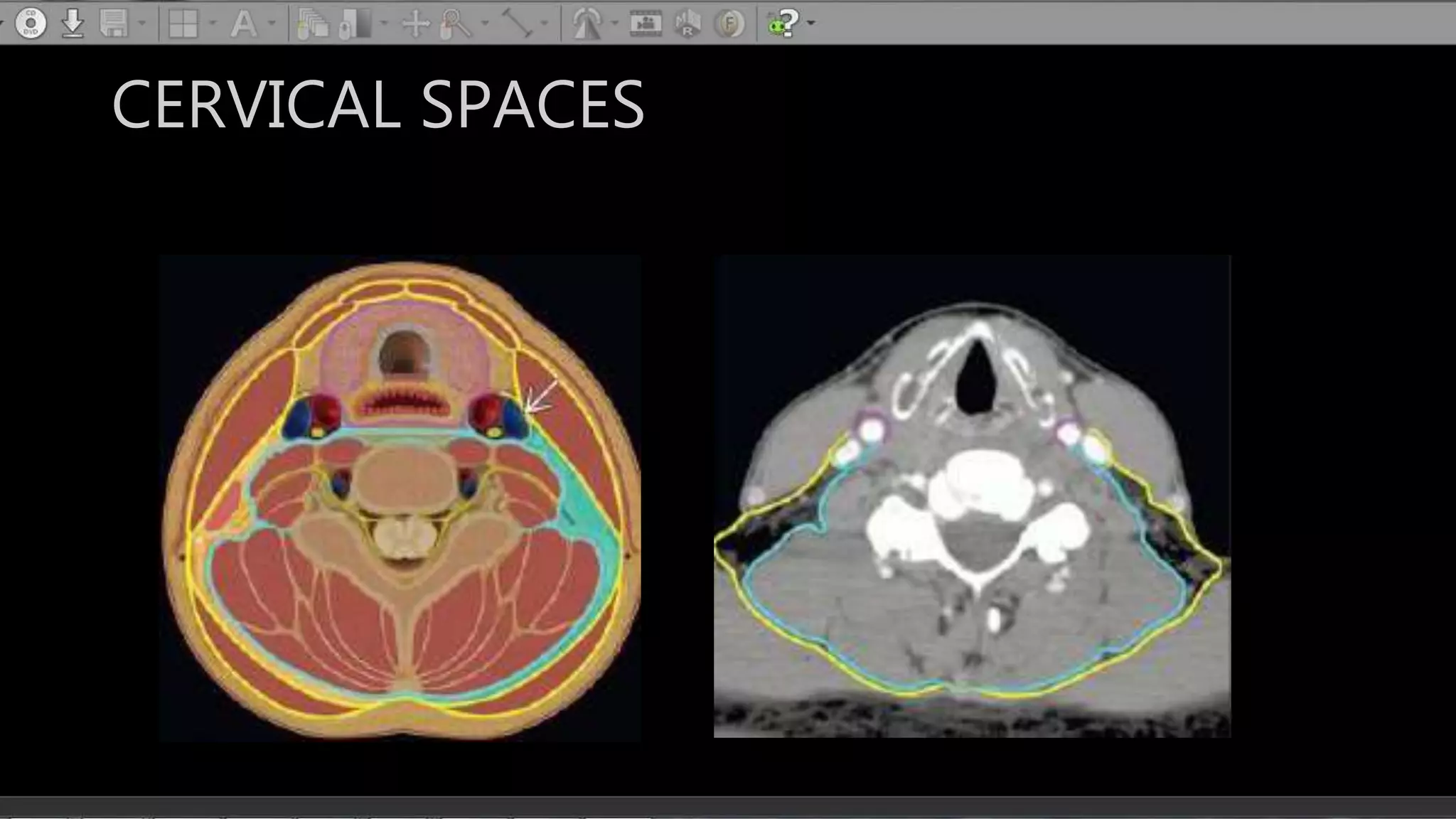
The document describes the anatomy of neck spaces. It discusses that the neck can be divided into suprahyoid and infrahyoid spaces based on the hyoid bone. Specific spaces described include the sublingual, submandibular, buccal, masticator, parotid, pharyngeal mucosal, parapharyngeal, visceral, anterior cervical, posterior cervical, carotid, retropharyngeal, prevertebral, and danger spaces. The spaces are delineated by layers of cervical fascia including the superficial, middle, and deep layers. Understanding these neck spaces is important for diagnosing conditions and limiting the spread of infections and tumors.