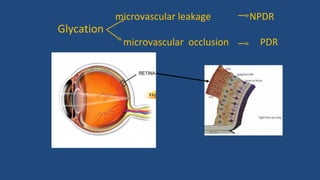
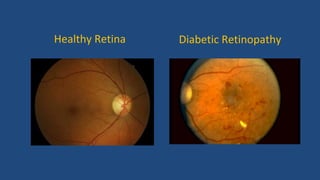
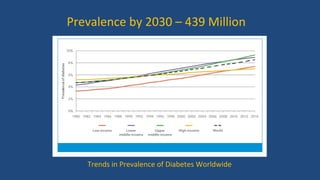
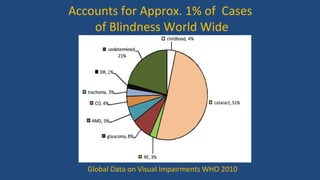
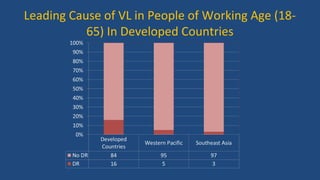
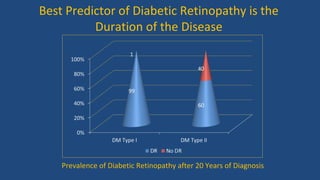
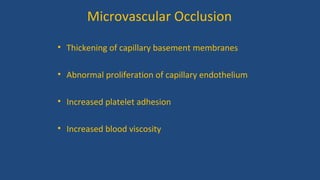
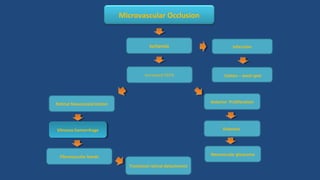
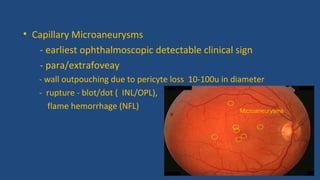
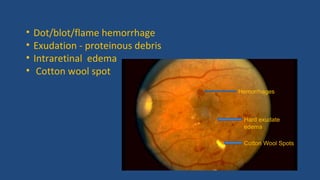
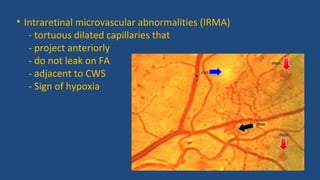
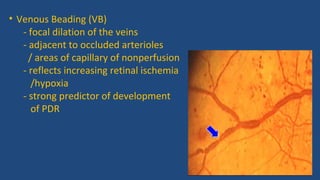
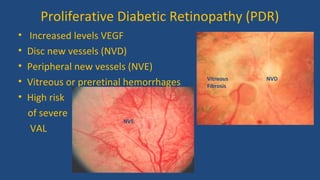
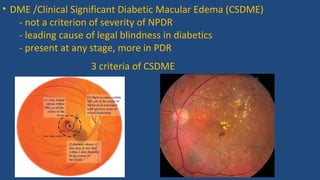
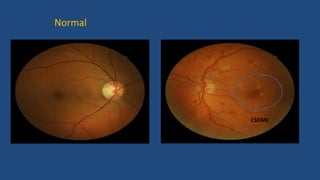
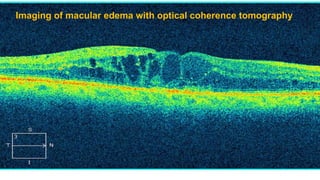
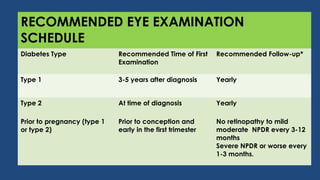
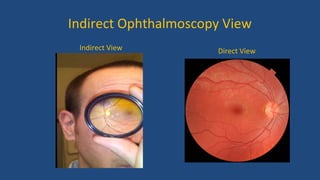
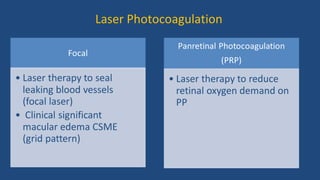
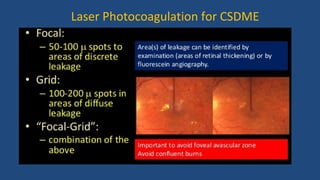
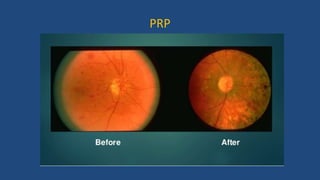
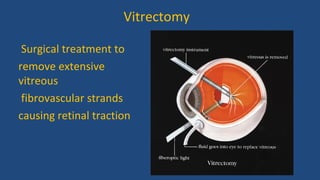
Diabetic retinopathy is a leading cause of blindness that is associated with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. It results from glycation and damage to the retinal blood vessels over time. Early stages are asymptomatic, but can progress to cause vision loss through edema, hemorrhage, or the growth of abnormal new blood vessels. Risk increases with longer duration of diabetes. Management focuses on tight glycemic control through medication and lifestyle changes, as well as regular eye exams and treatments such as laser photocoagulation or anti-VEGF injections to prevent vision loss.