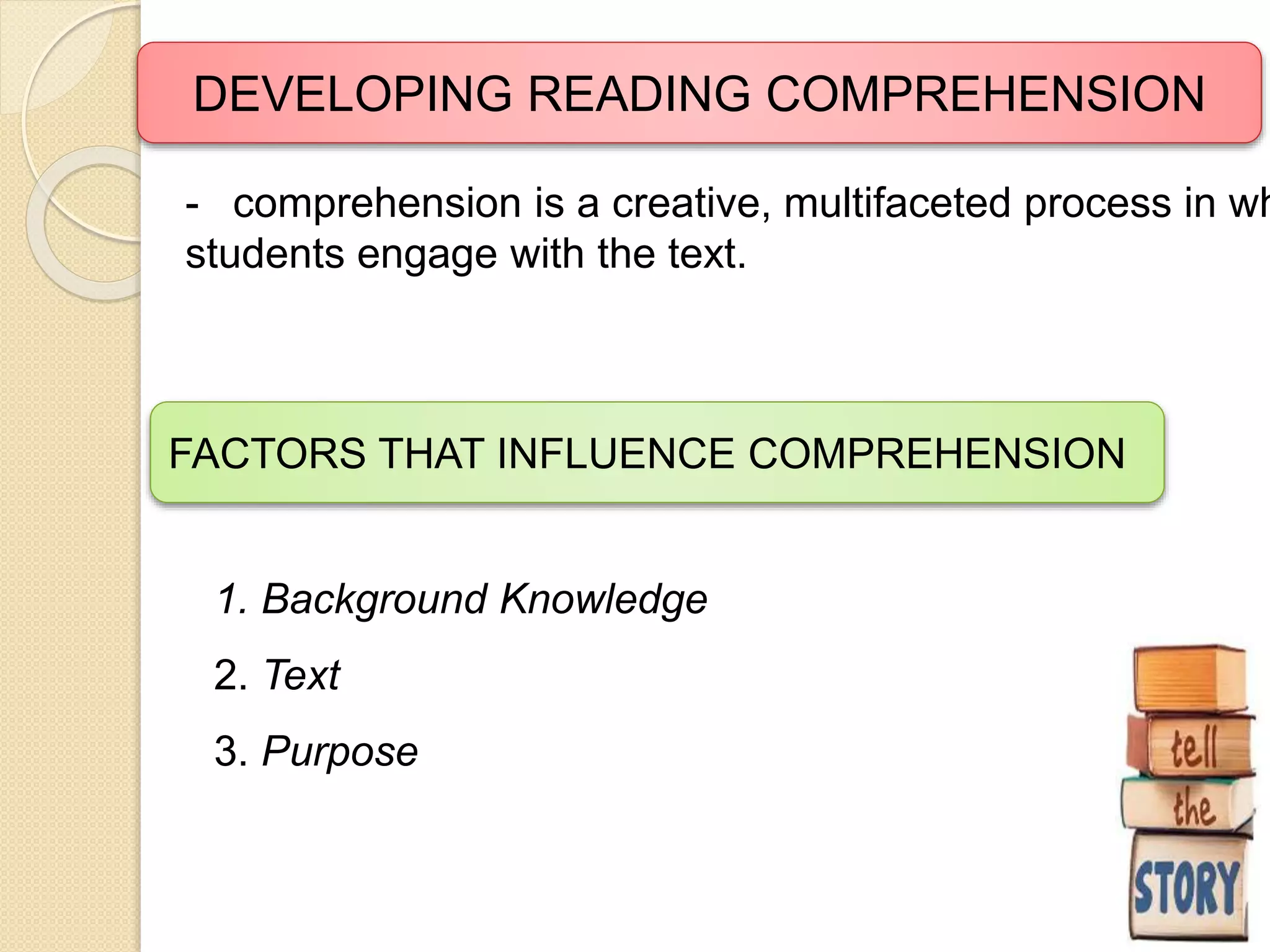
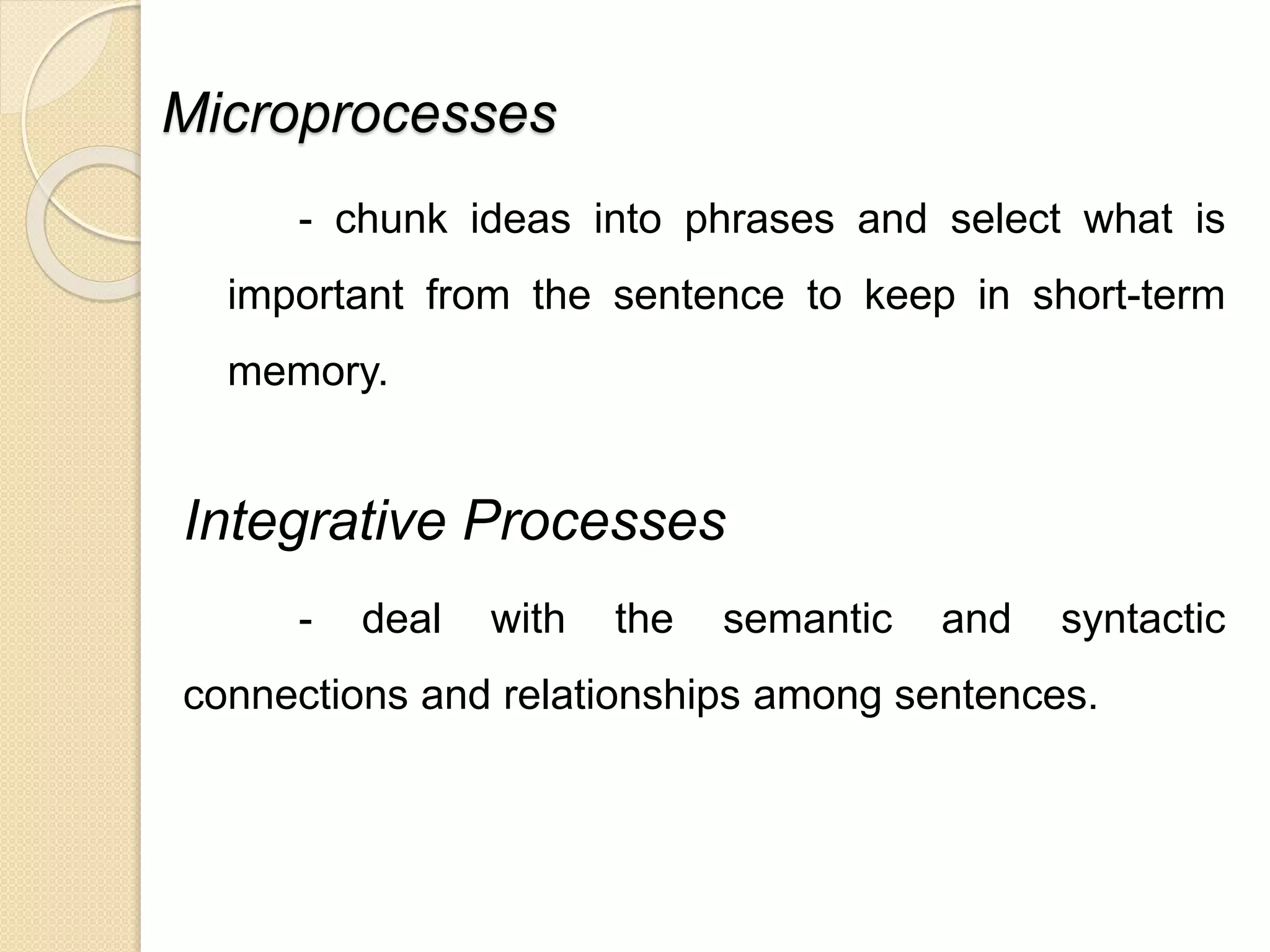
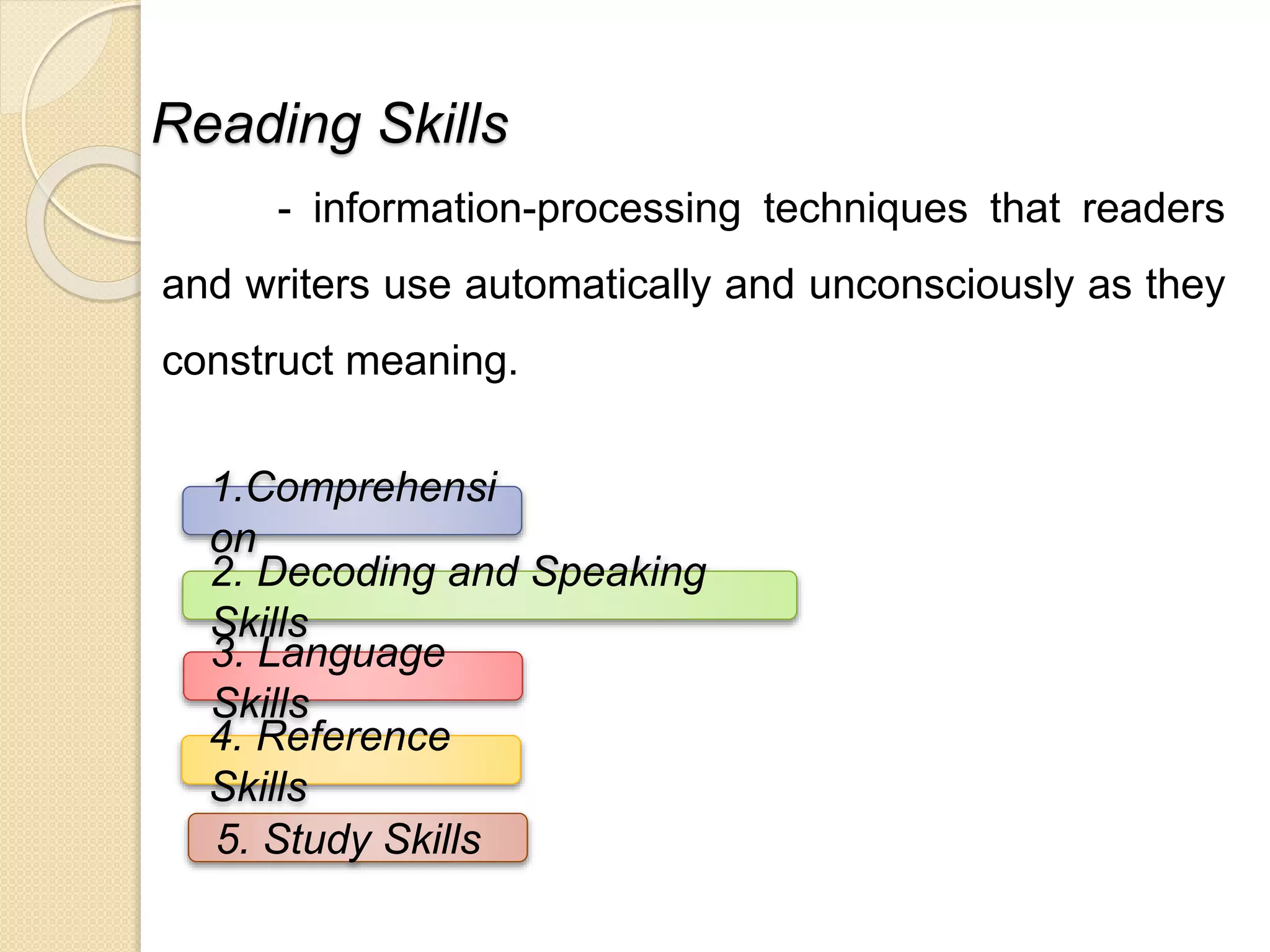
The document outlines a four-pronged approach to reading instruction consisting of developing a genuine love of reading, critical thinking skills, mastery of language structures, and applying reading skills in other contexts. It provides details on developing various reading comprehension skills such as understanding at the micro, integrated, macro, elaborative and metacognitive levels. It also describes teaching oral and silent reading, factors that influence comprehension, and taxonomy of cognitive and affective dimensions of reading.