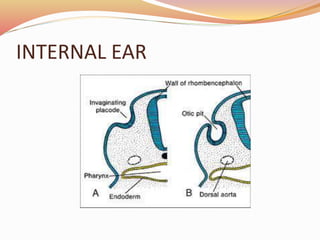
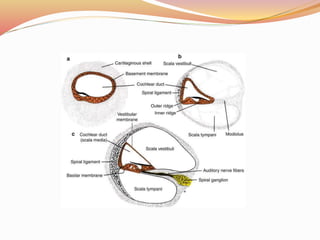
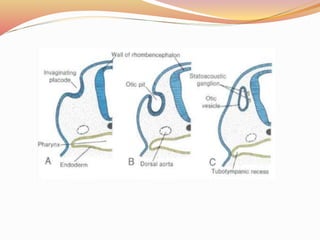
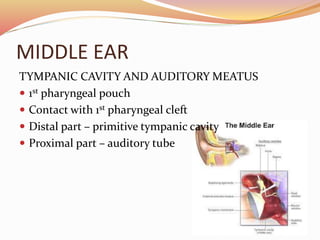
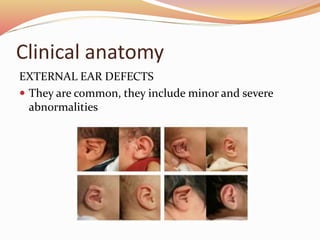
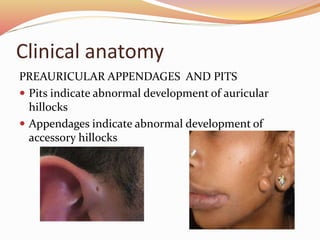
The document provides an overview of the embryonic development of the ear, detailing the formation of the external, middle, and inner ear structures. It covers the differentiation of components such as the cochlea, semicircular canals, and the tympanic cavity, as well as the role of sensory cells in hearing and equilibrium. Additionally, it discusses common developmental abnormalities, including congenital deafness and external ear defects.