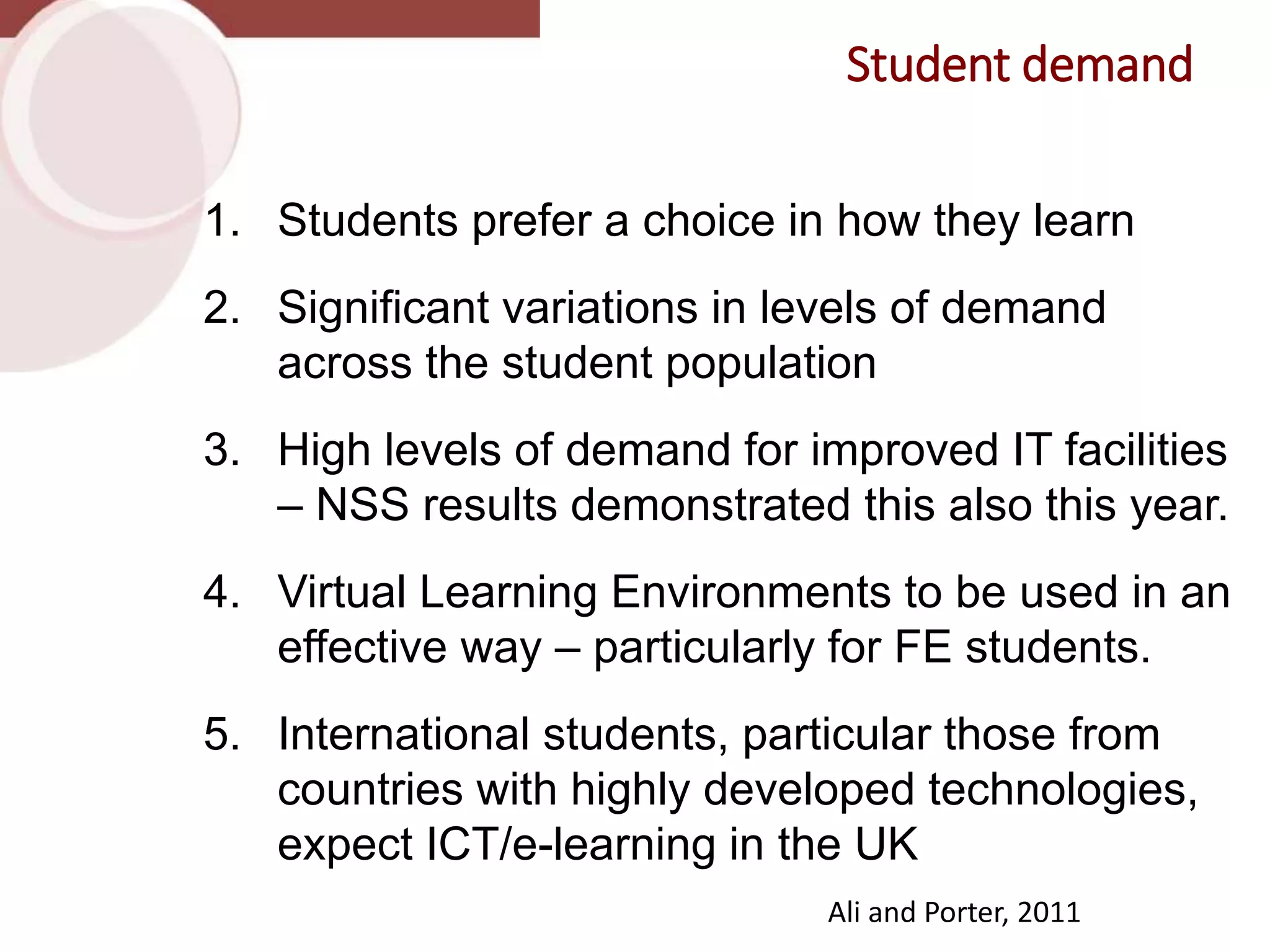
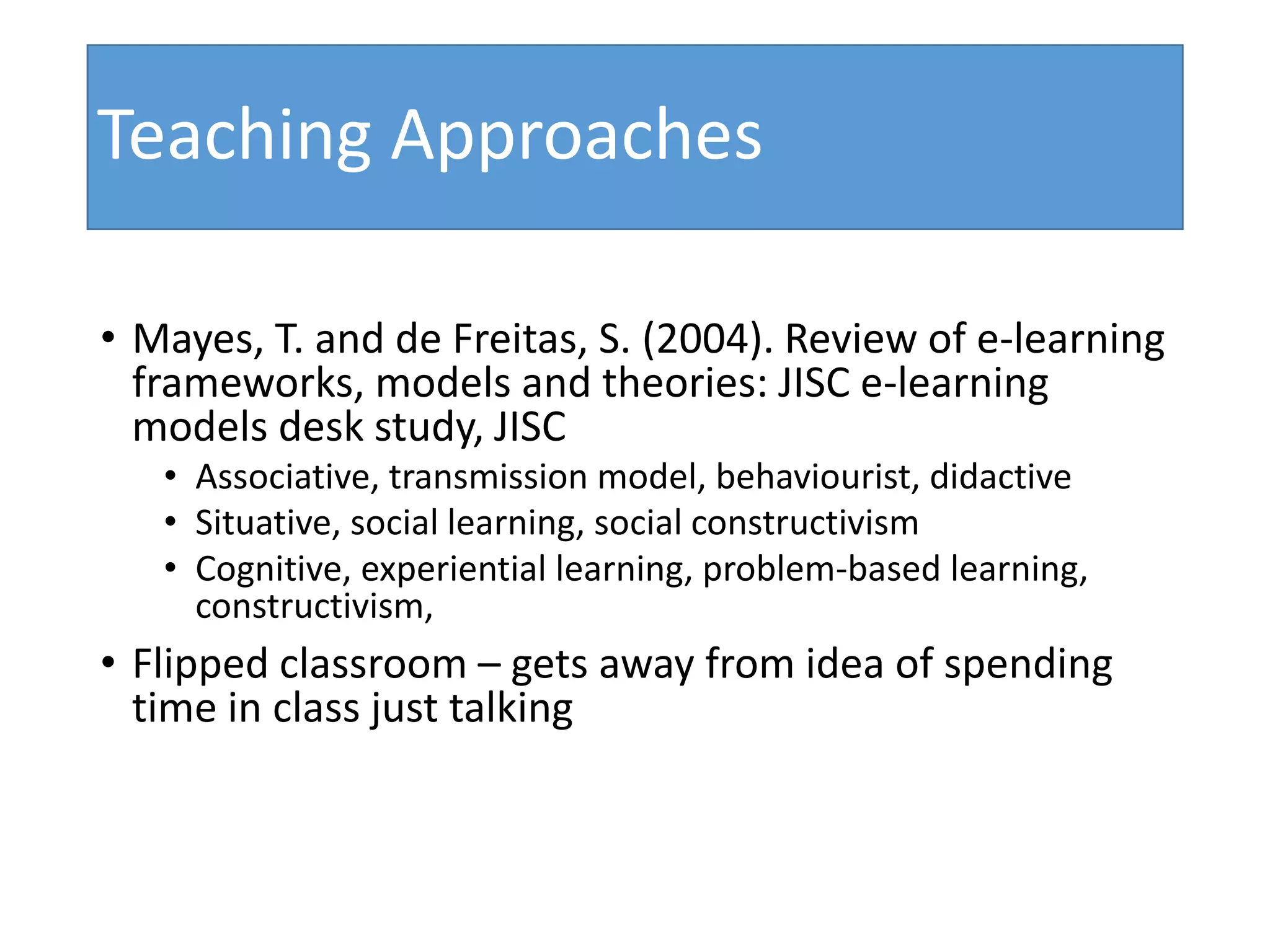
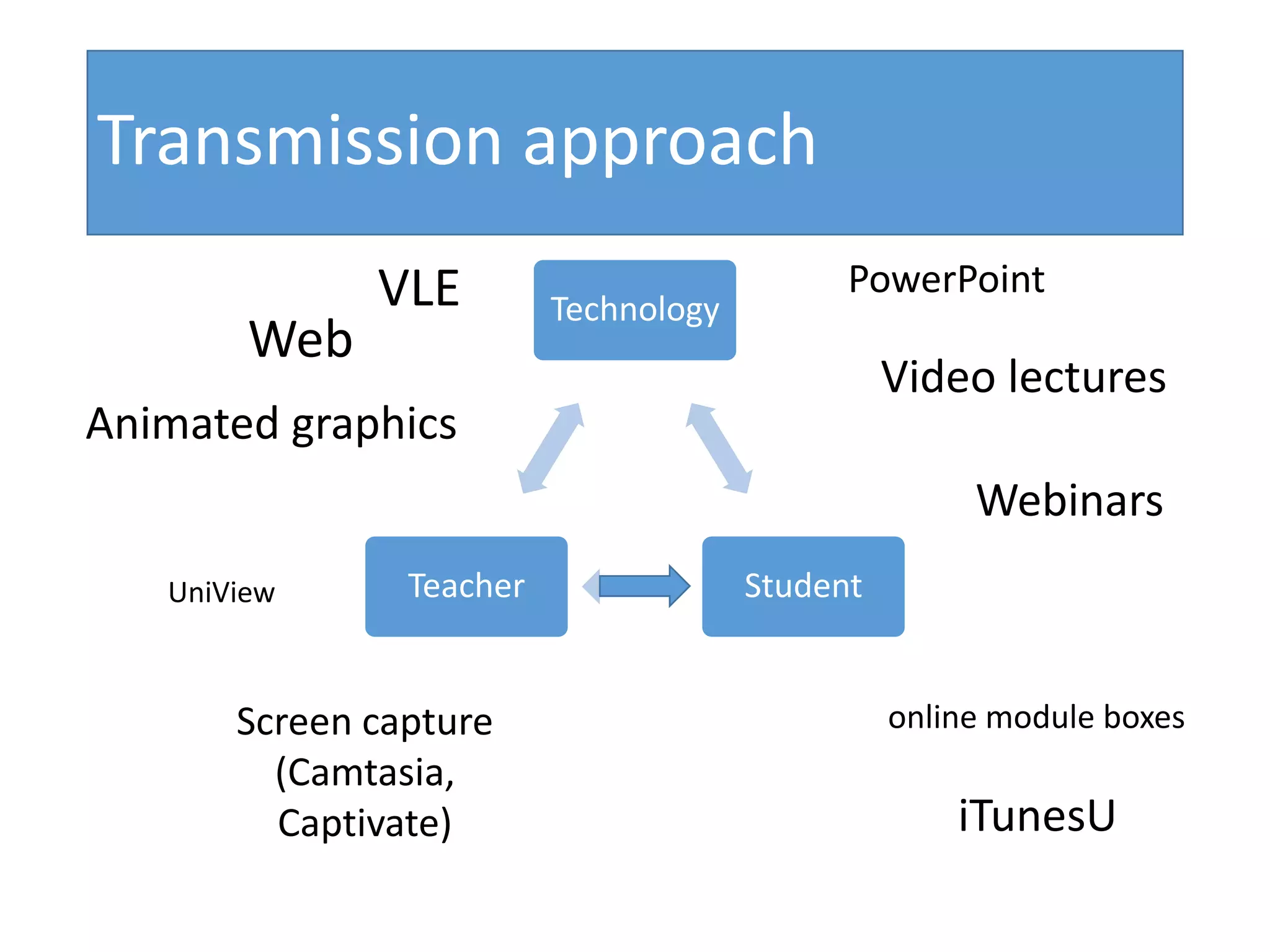
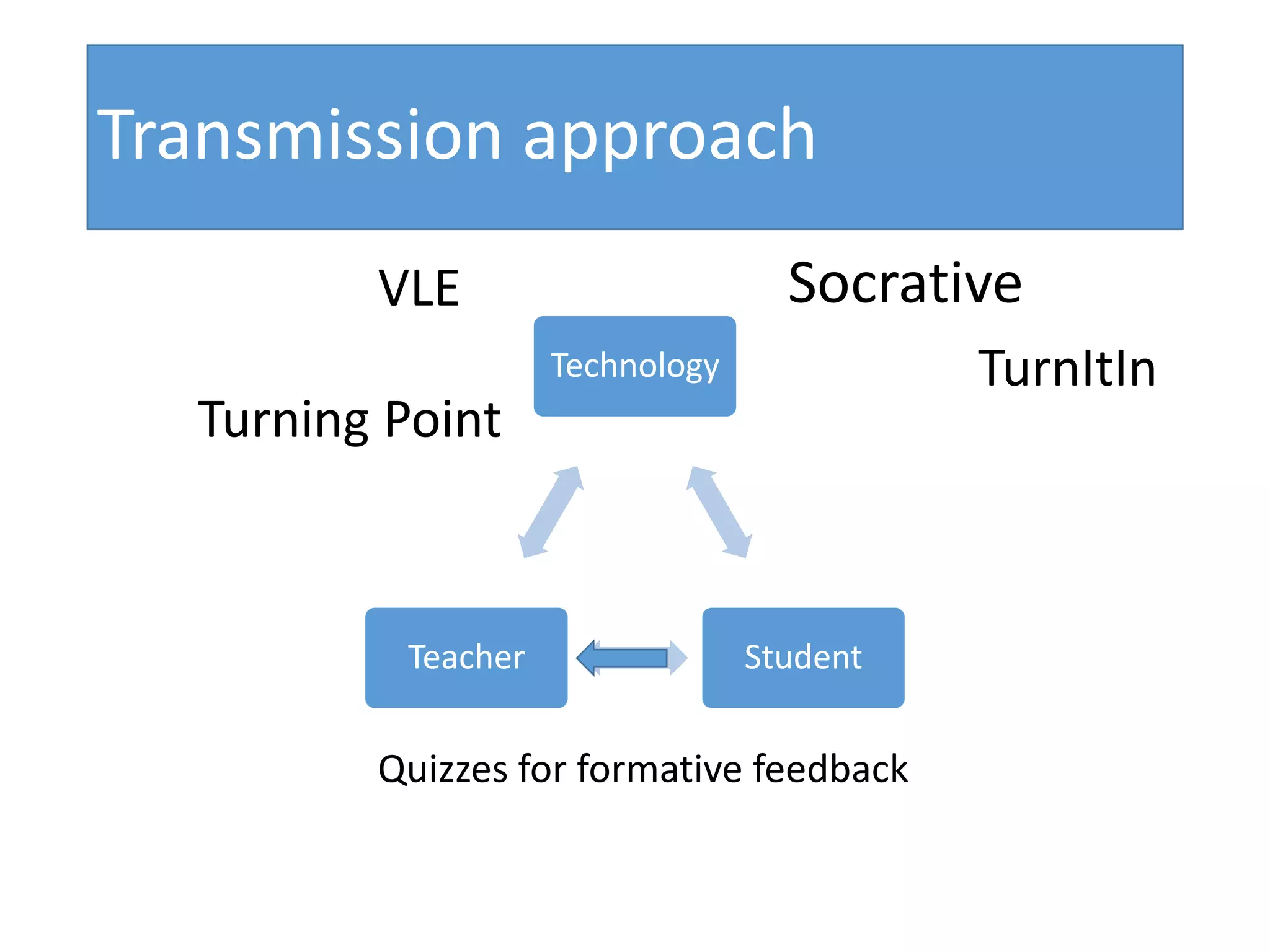
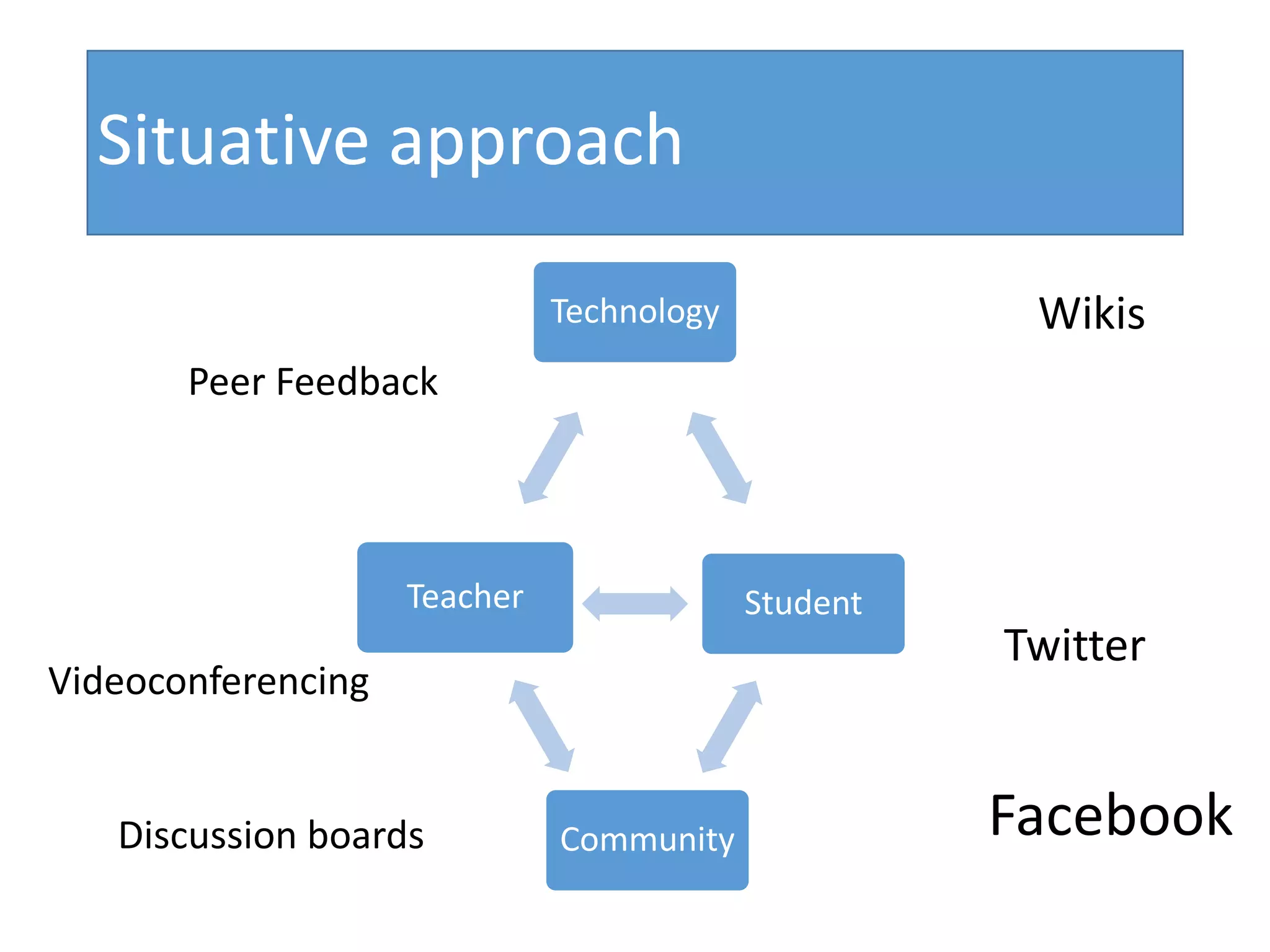
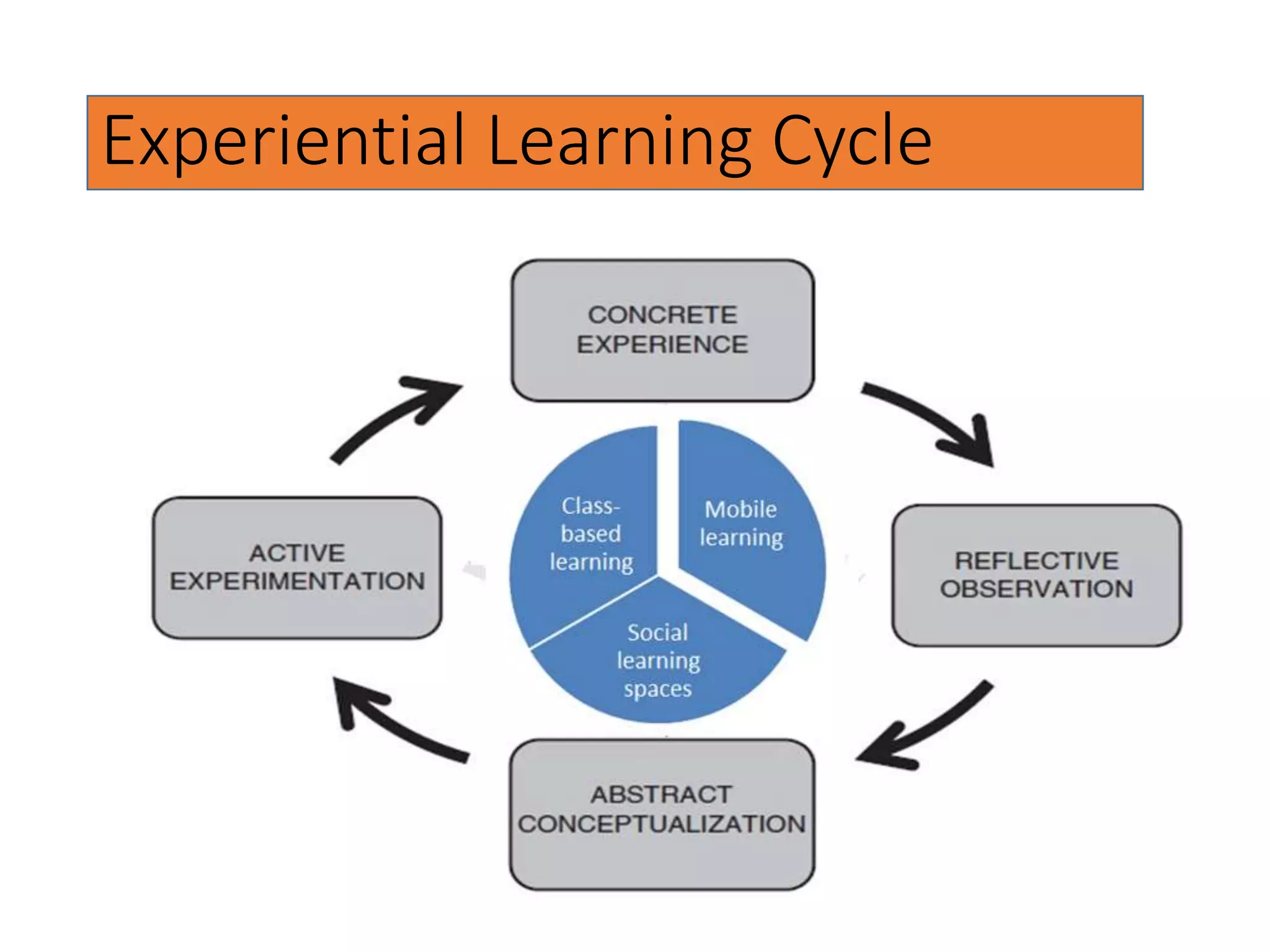
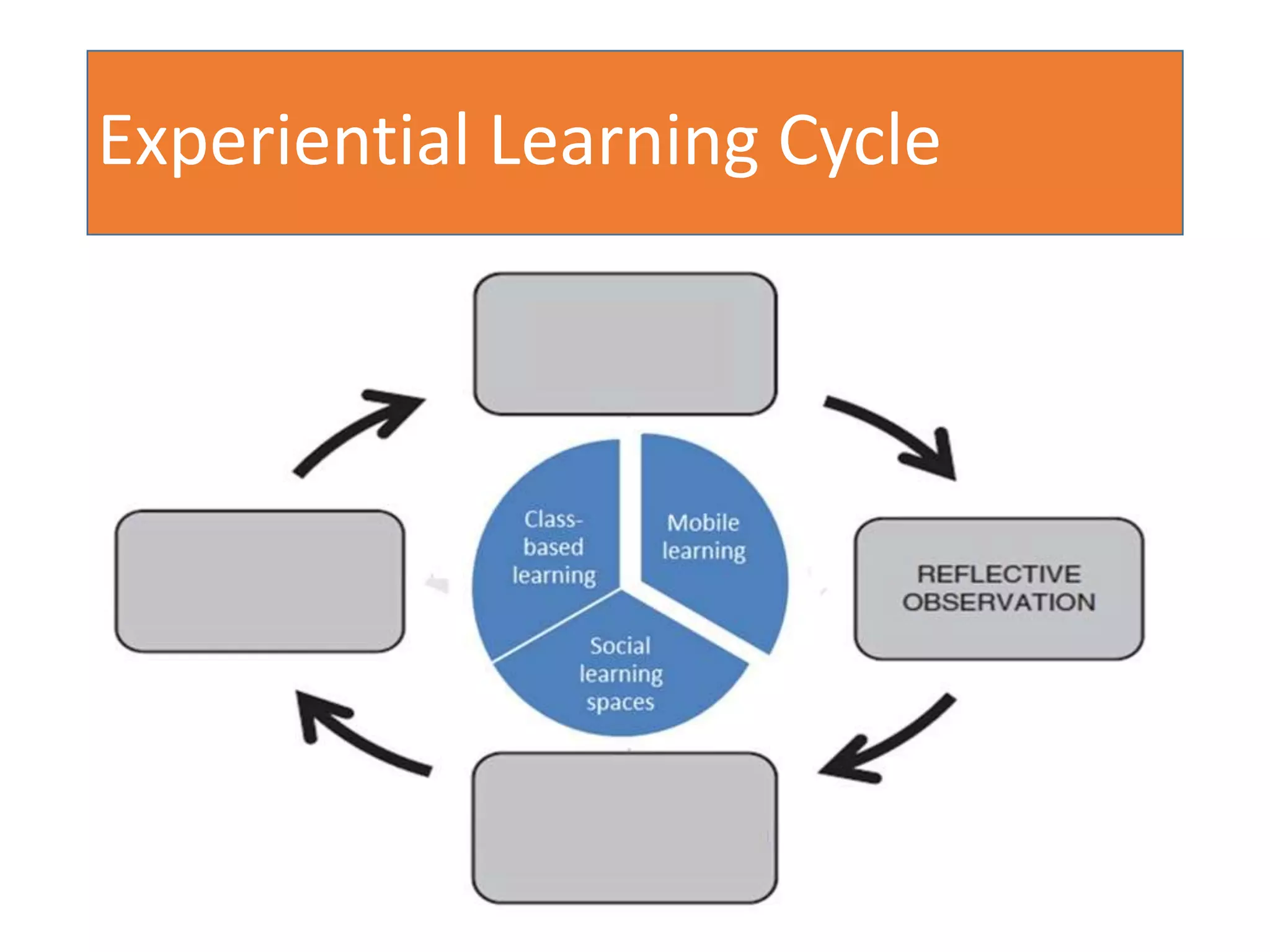
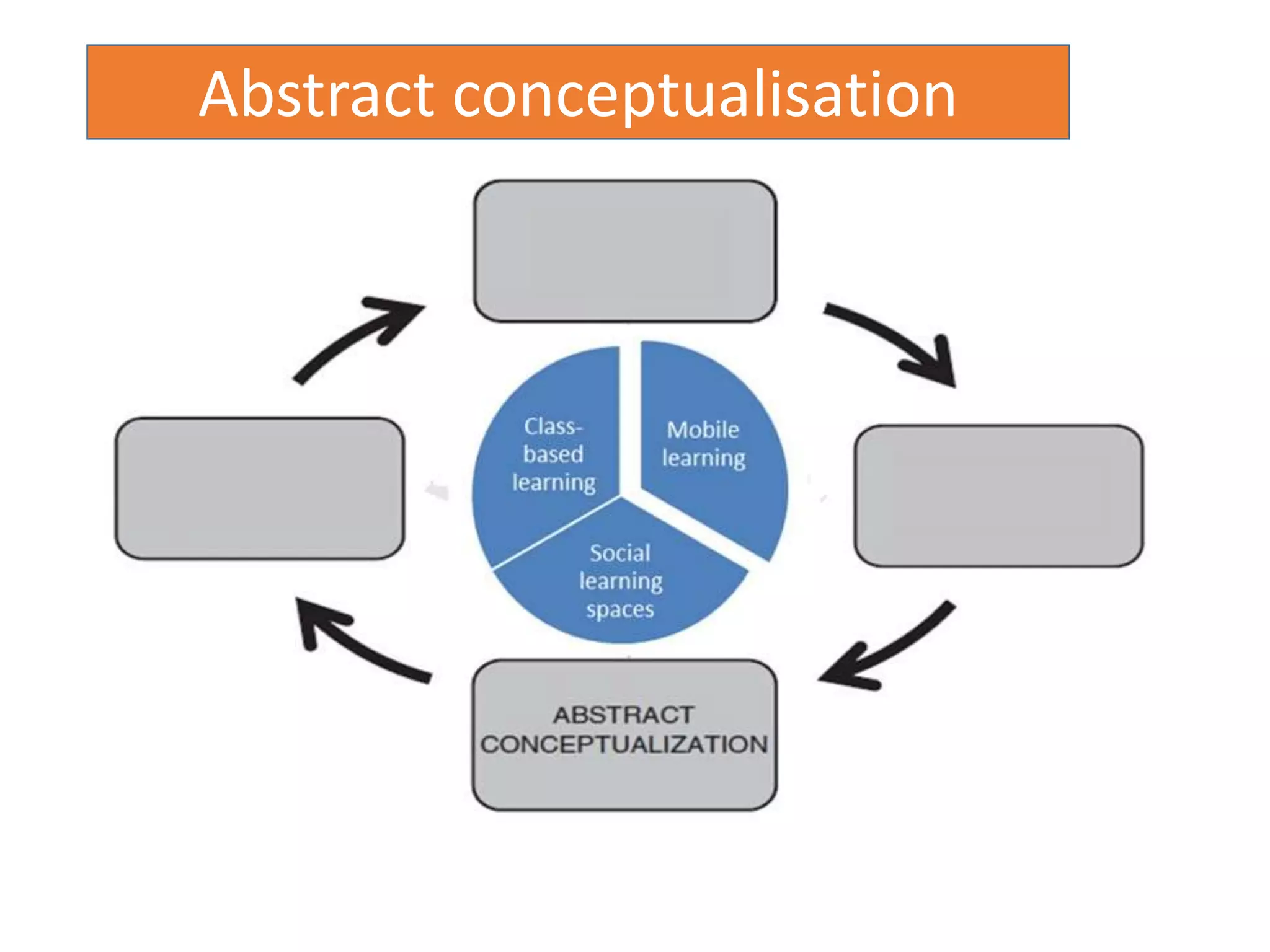
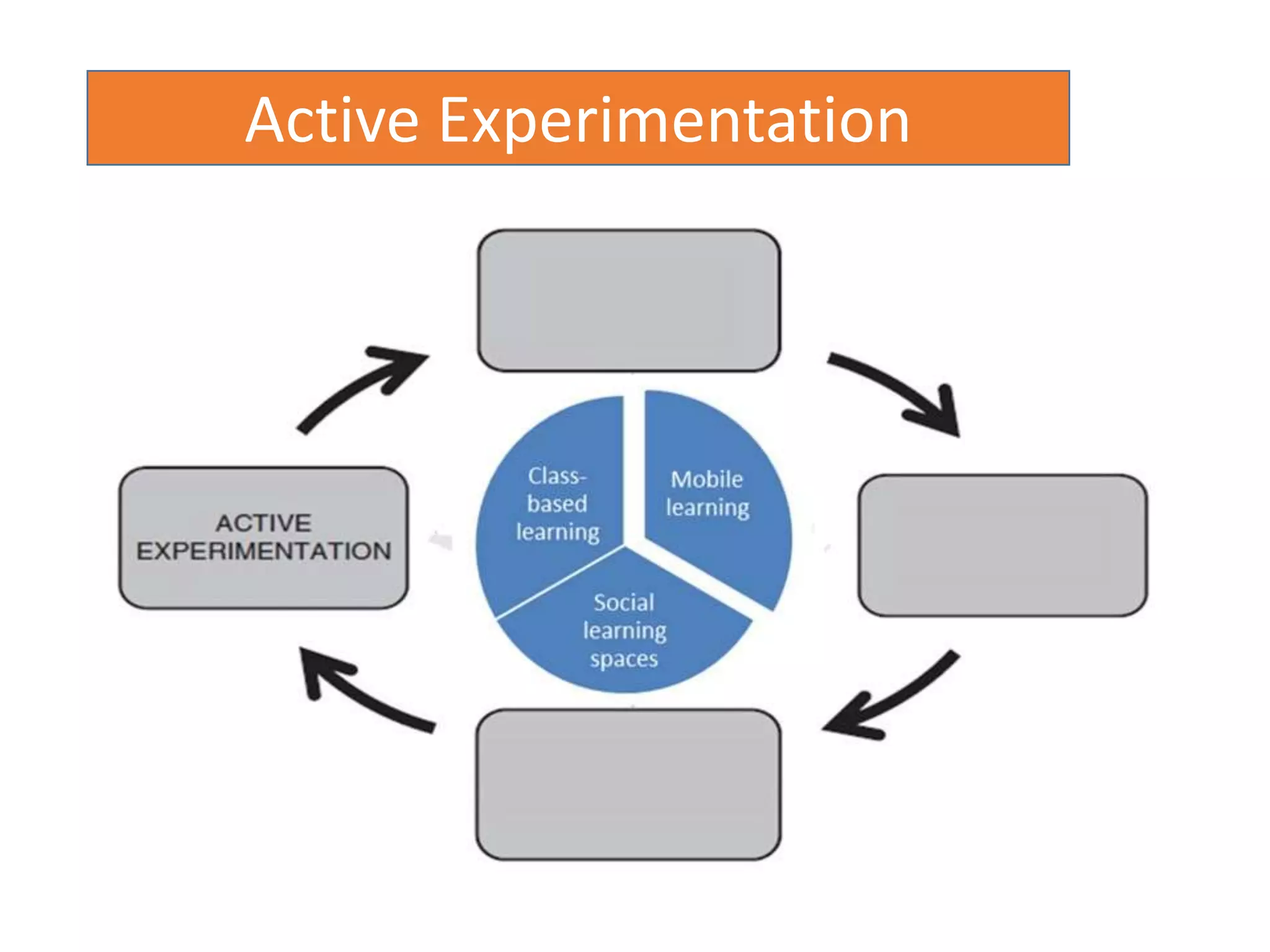
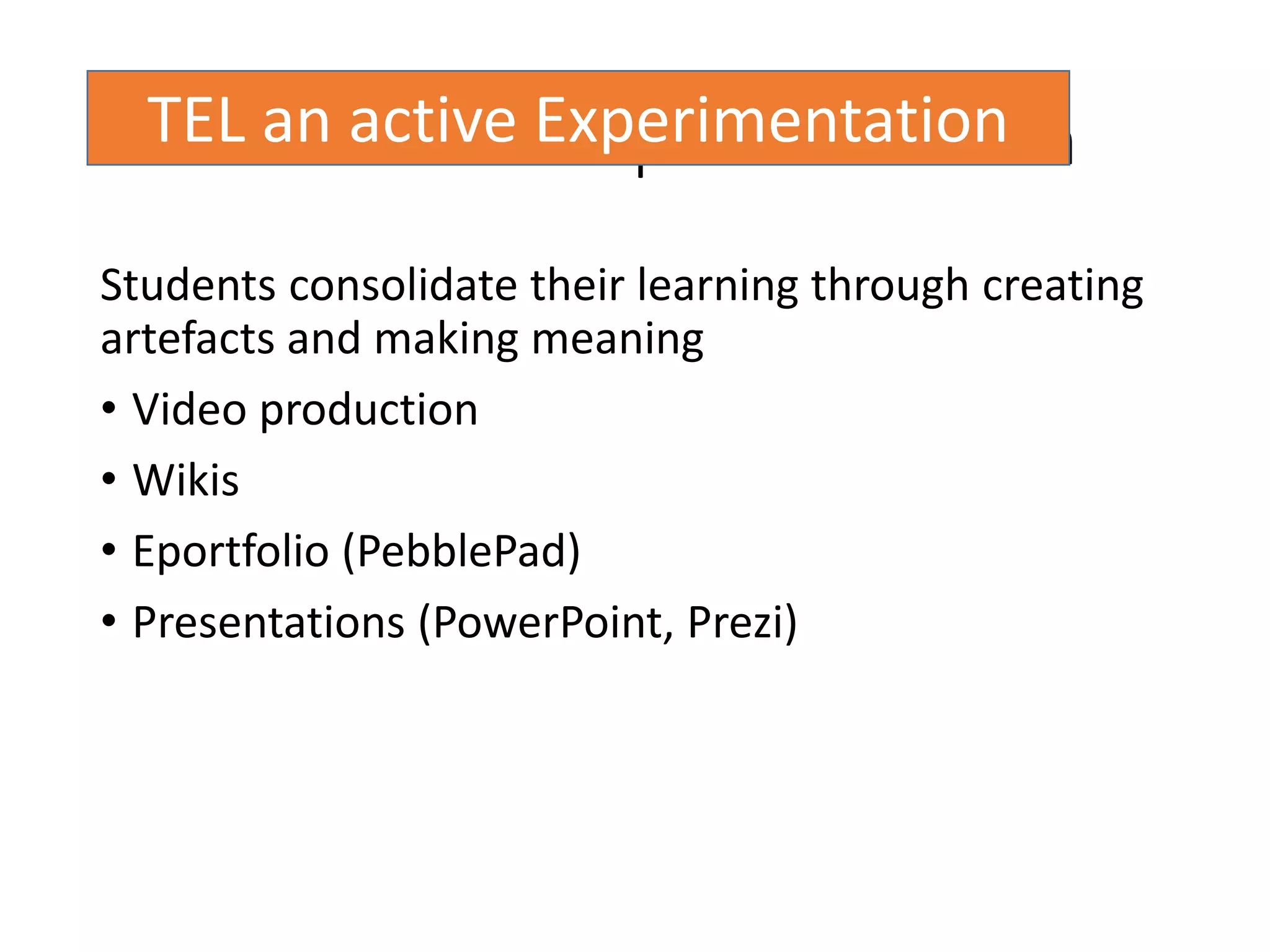
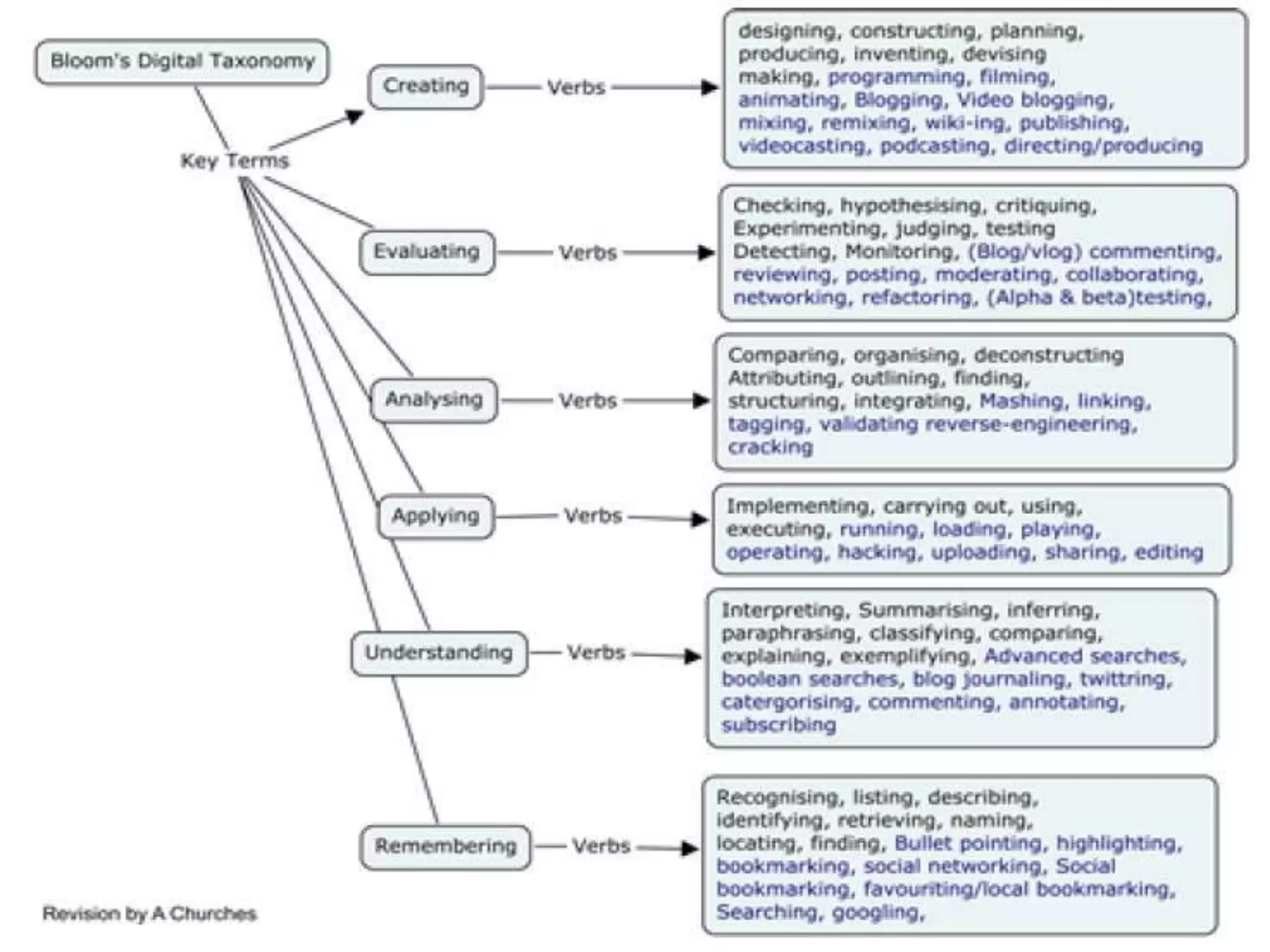
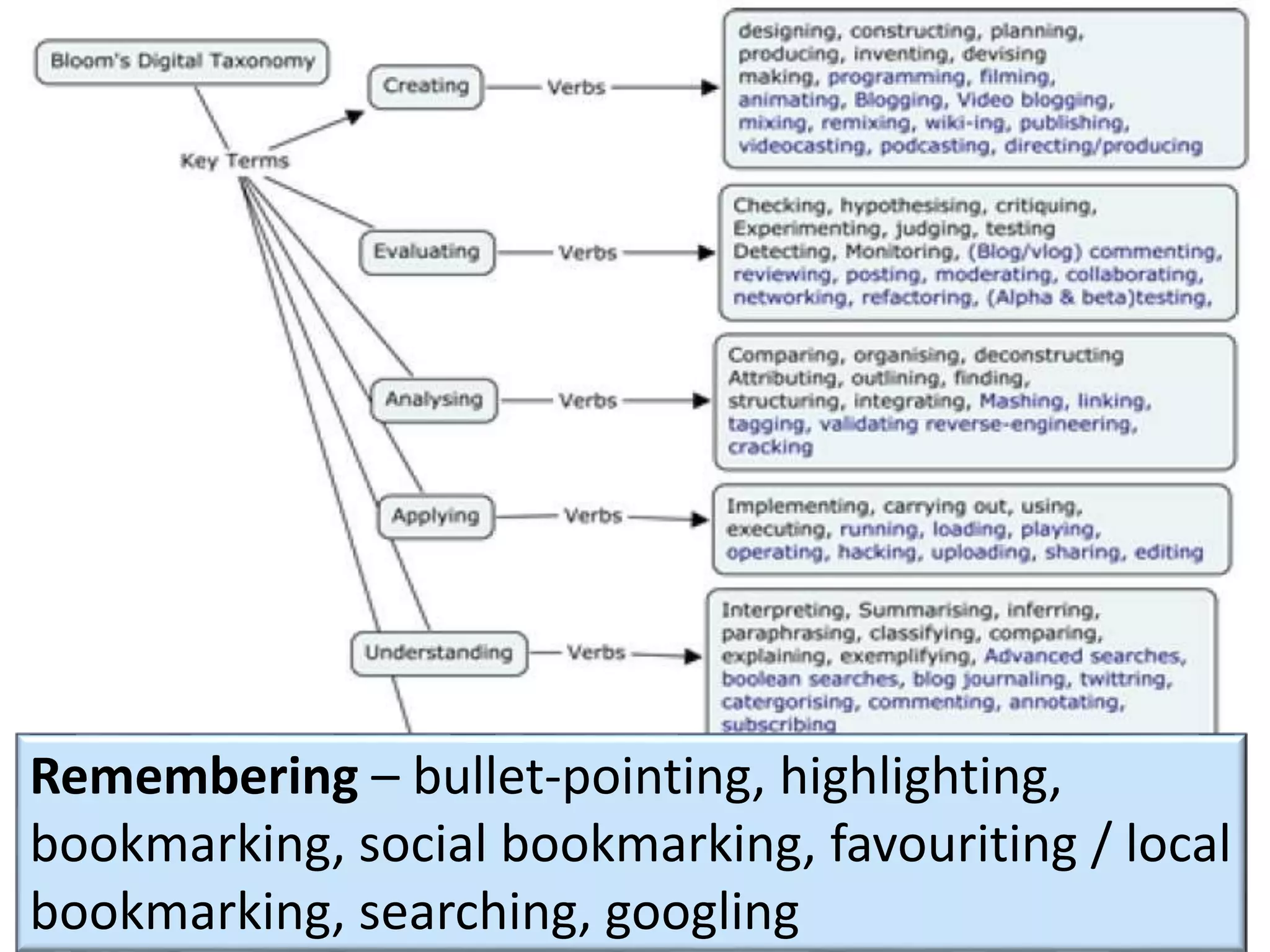
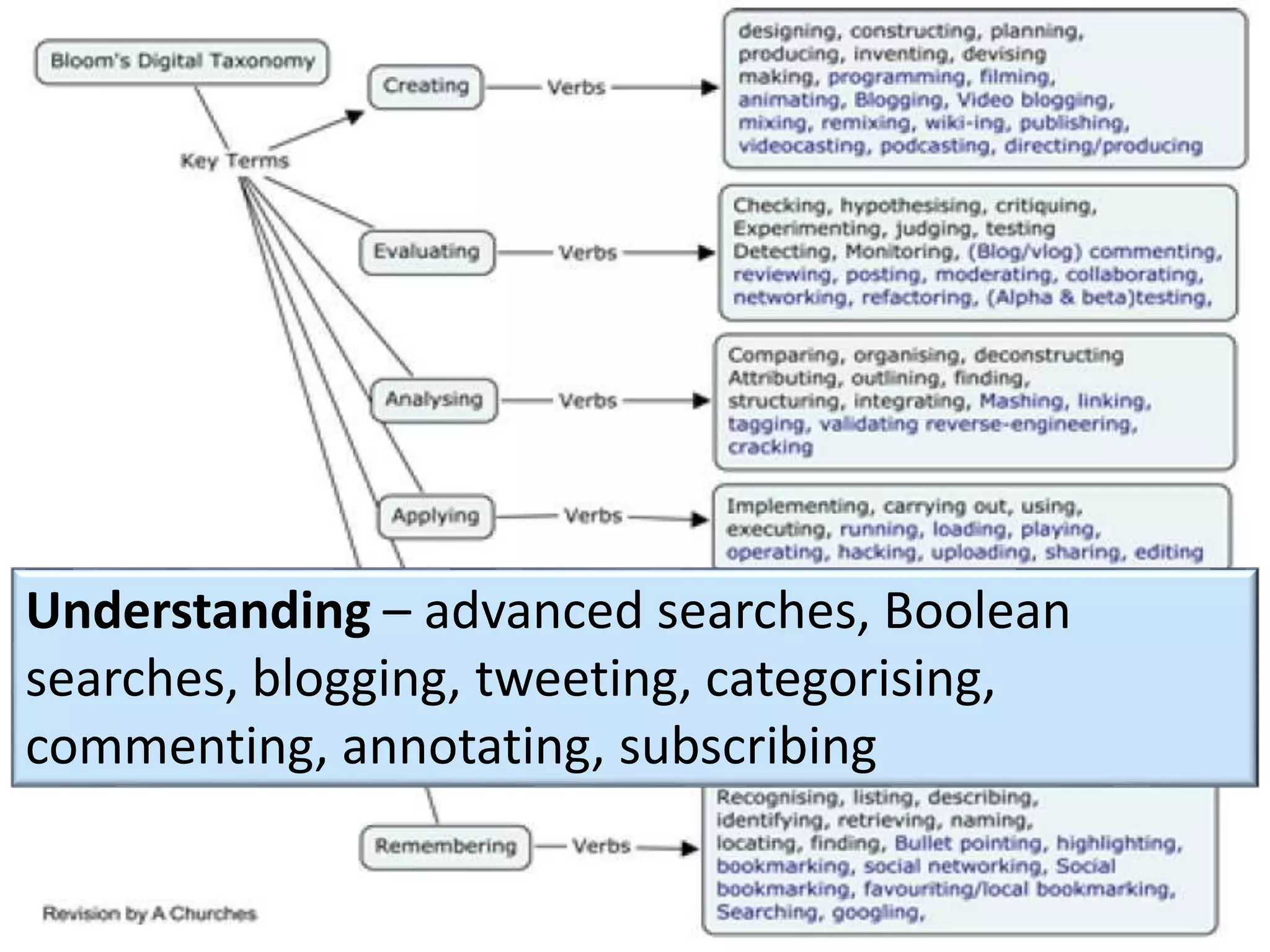
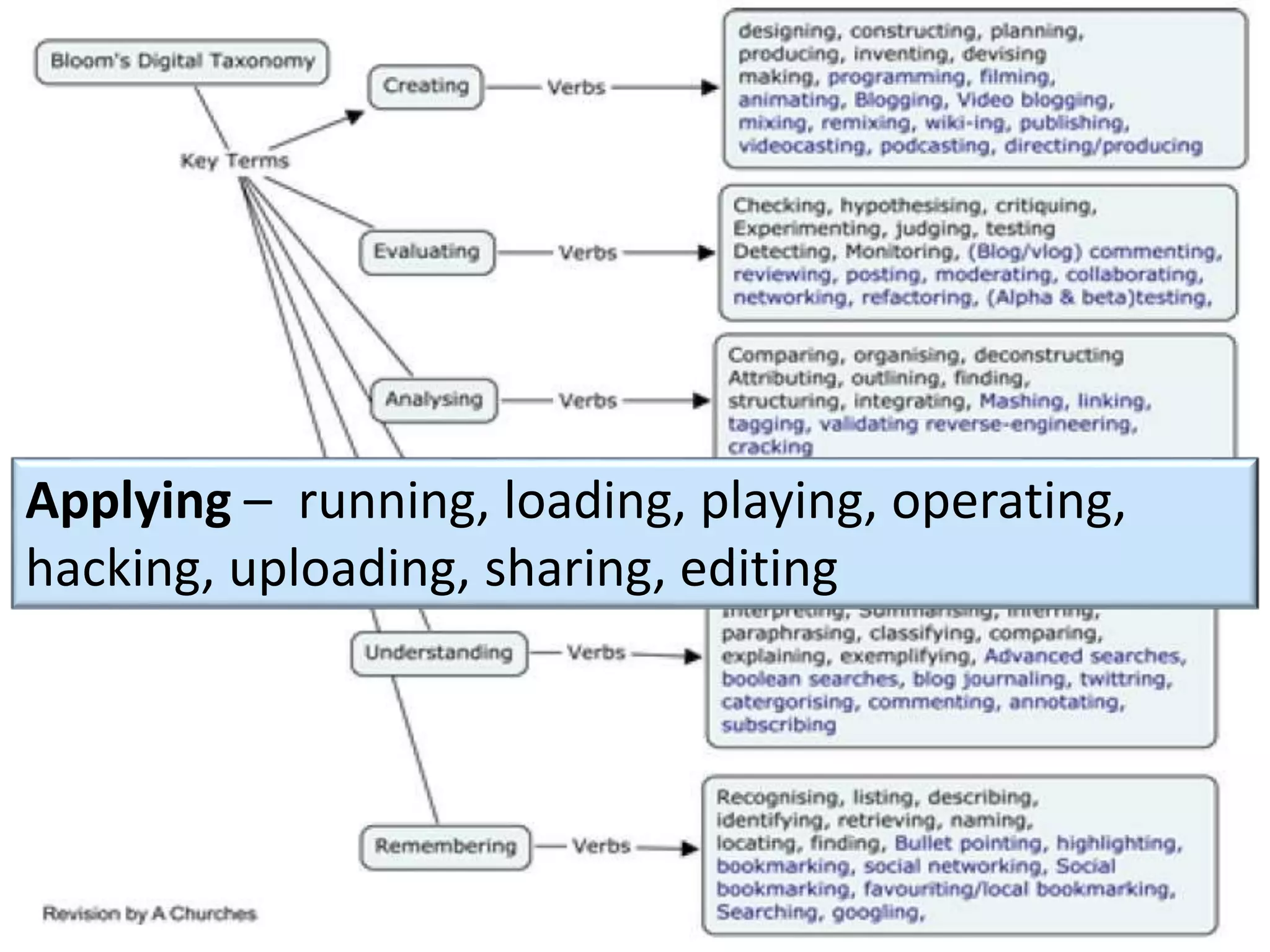
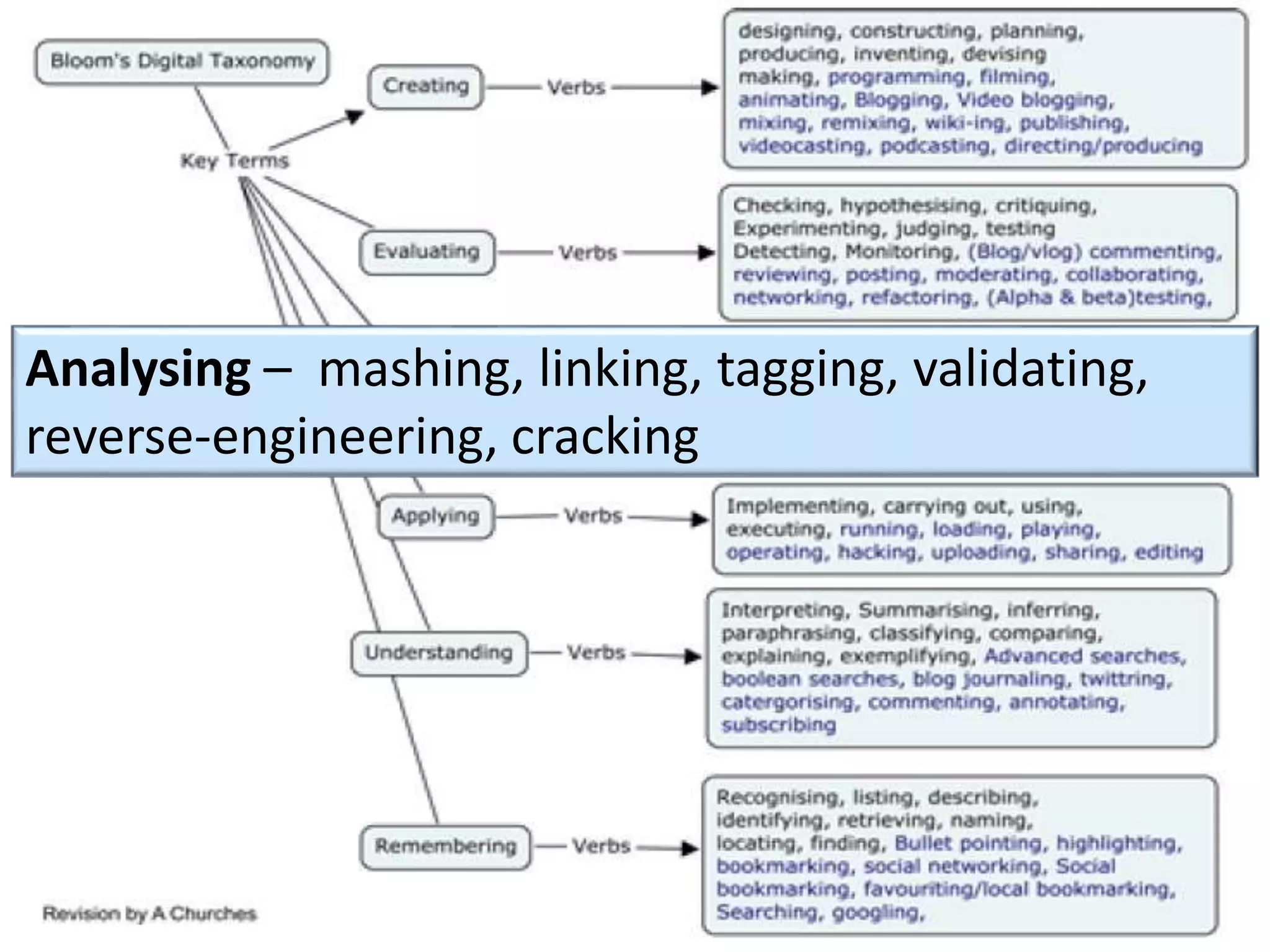
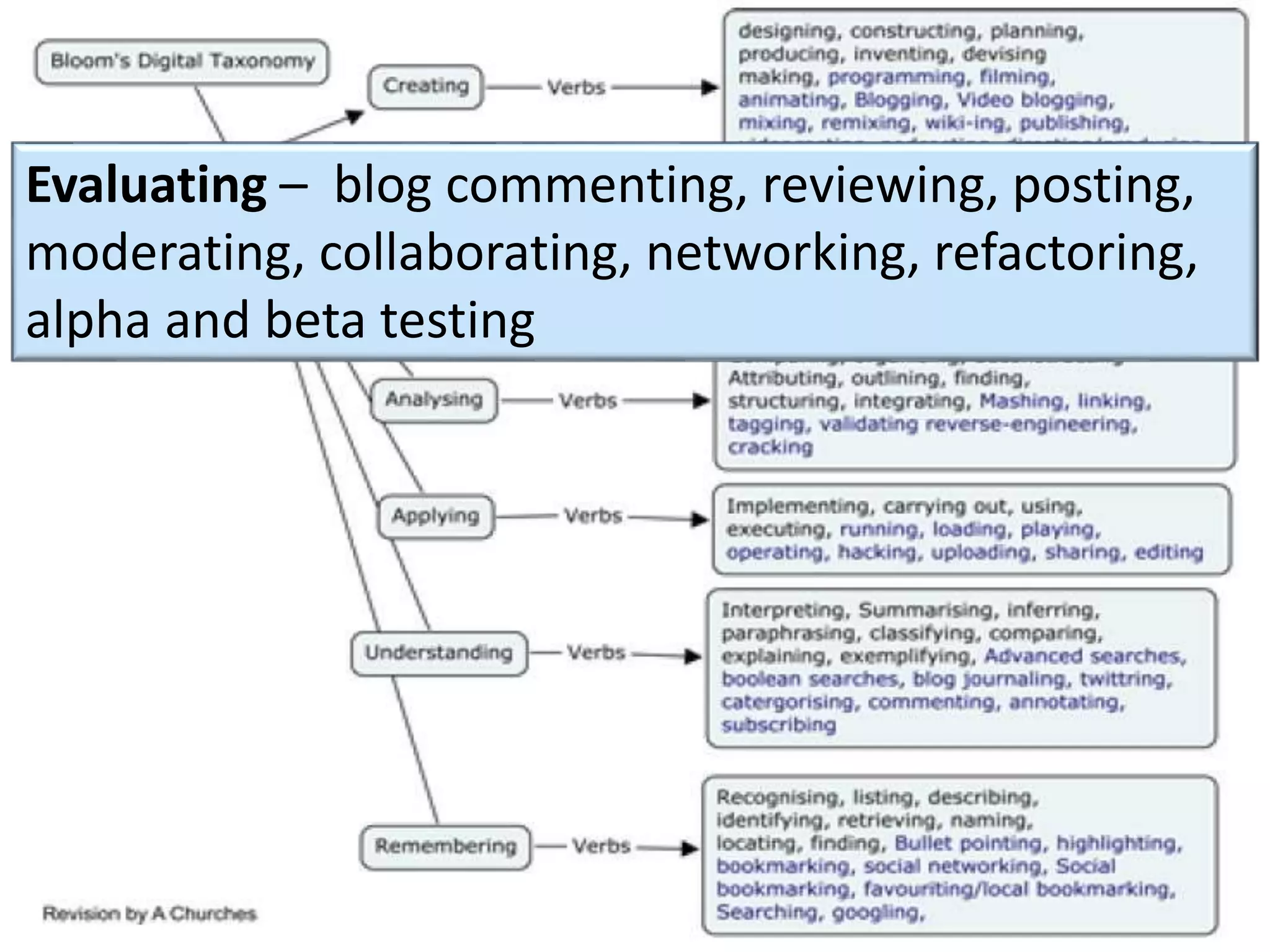
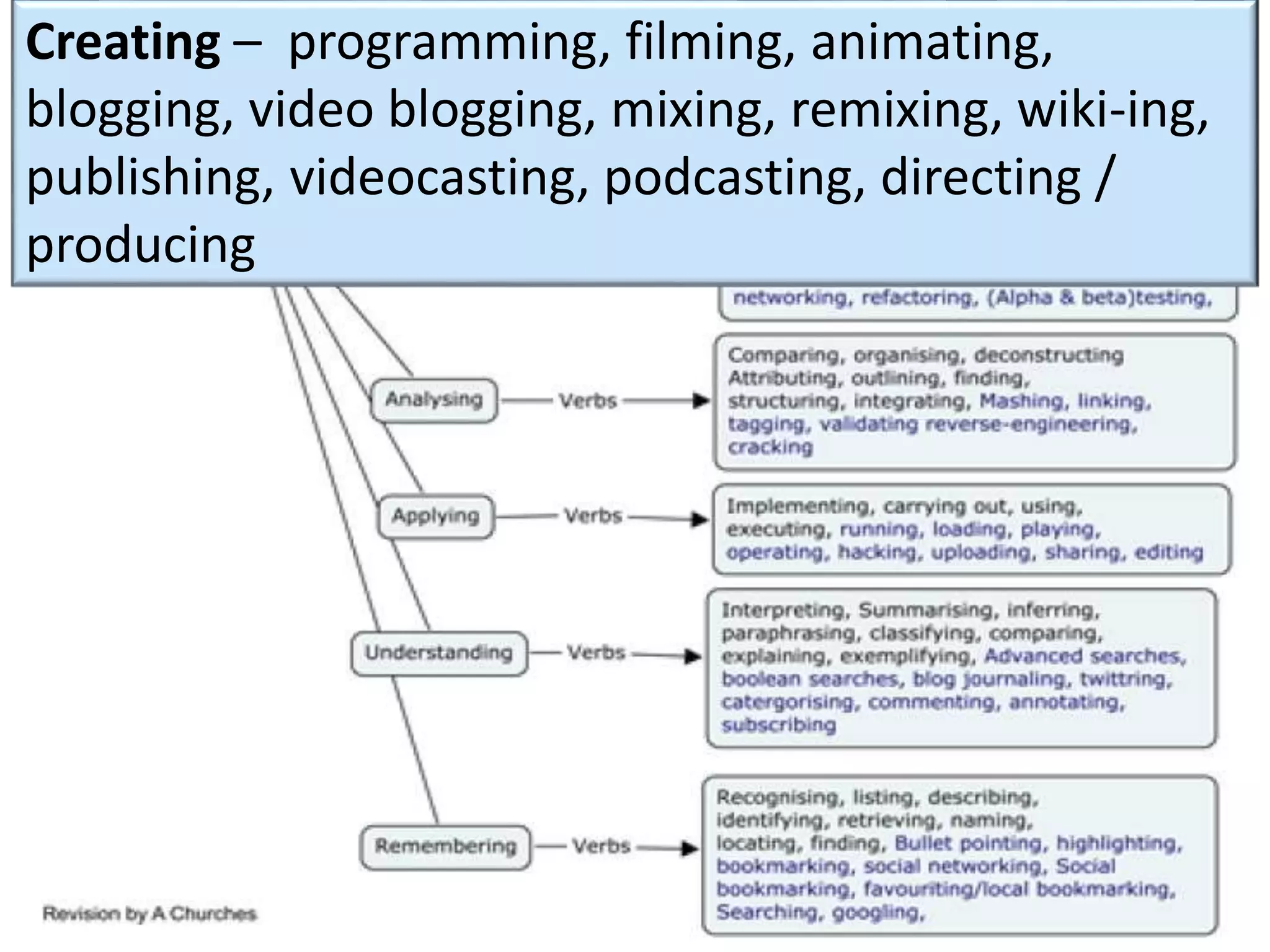
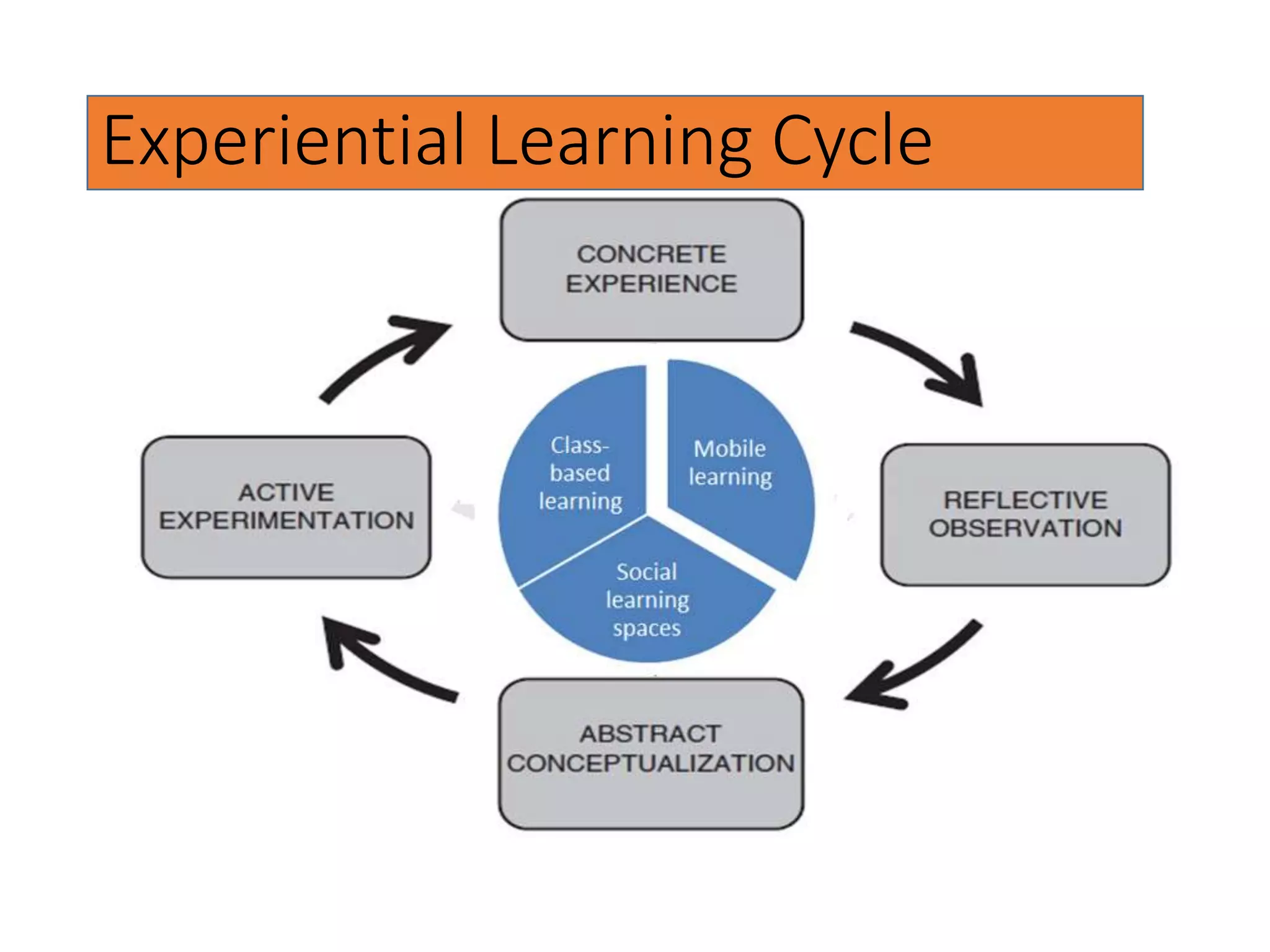
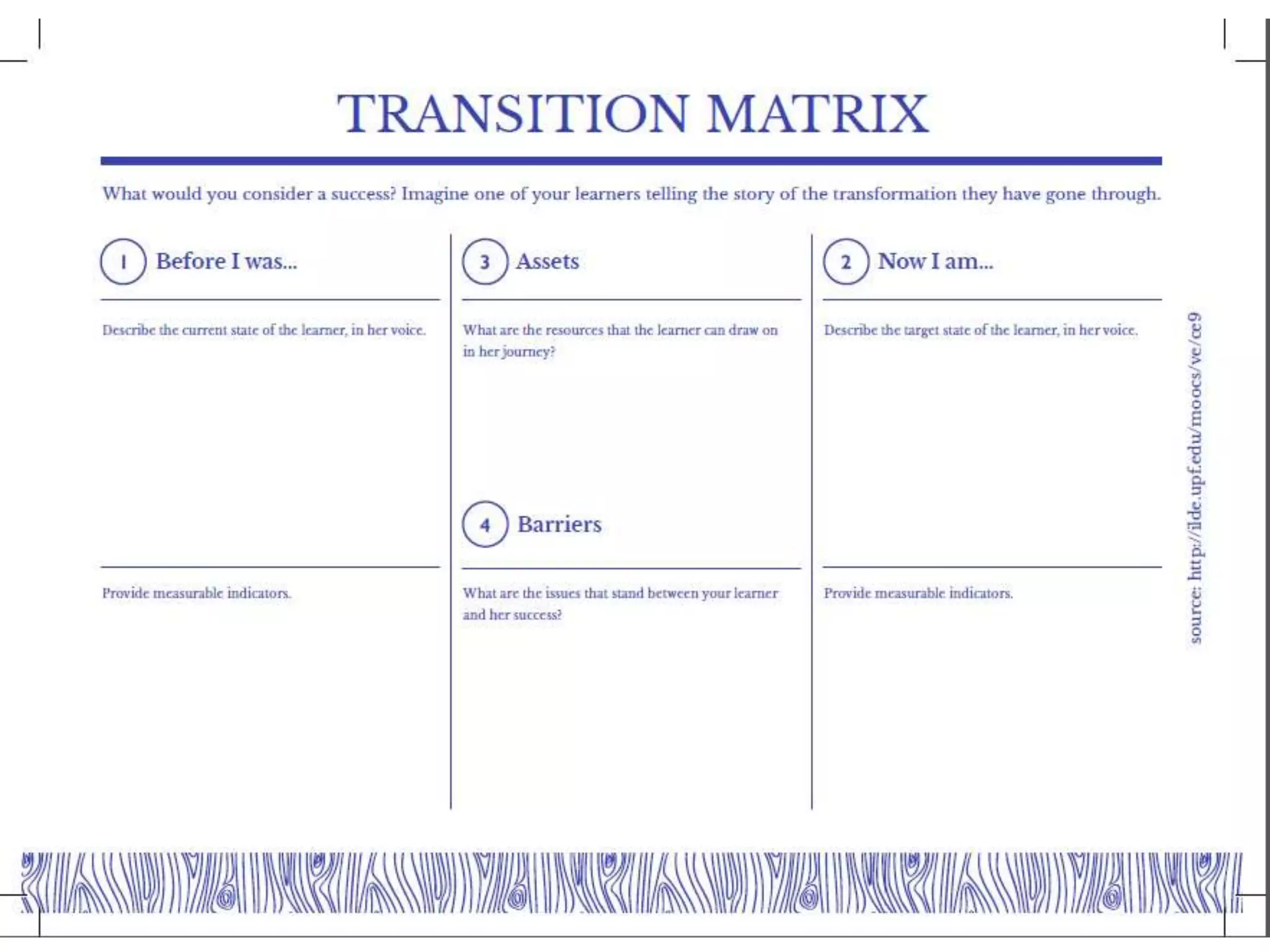
This document discusses designing activities for online learning. It outlines five models of learning design: teaching approaches, experiential learning cycle, 5 stages model, and supporting online interaction. The experiential learning cycle places student activities at the core and forms a cycle of concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation. Technology can support each stage, through simulations, videos, discussion boards, podcasts, and student-created artifacts. When designing activities, instructors should consider student preferences, demand for technology, and supporting reflection, conceptualization, and experimentation.