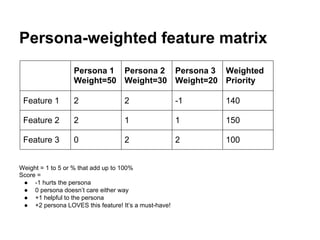
This document provides an overview of human-centered design principles and techniques for understanding users and their needs. It discusses conducting user research through methods like observation, interviews and personas. Personas involve creating profiles of representative users to develop empathy and keep the focus on the user. The document also discusses how to create user stories and maps based on personas to guide design. The goal is to apply a deep understanding of users to build successful products and services.