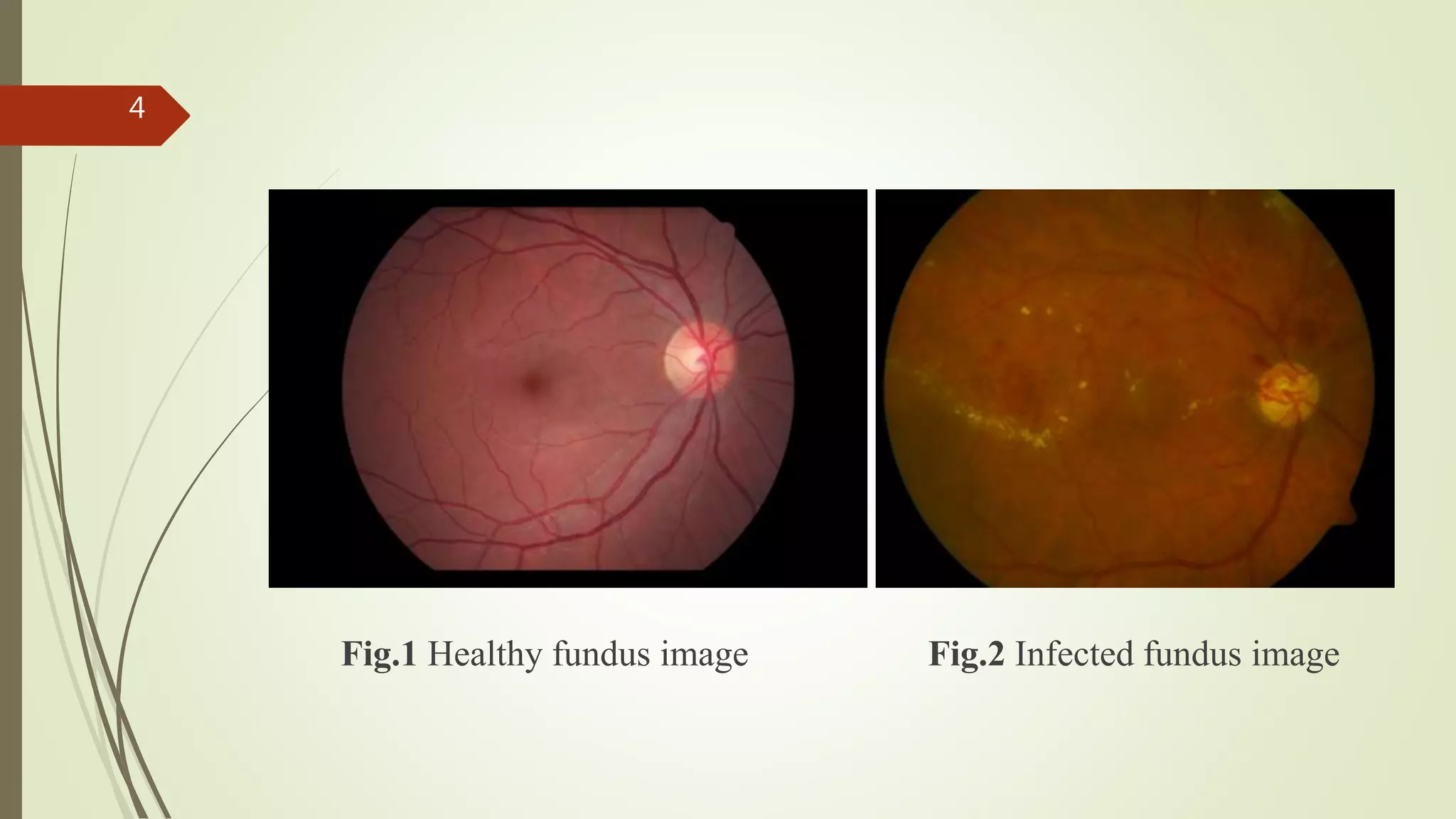
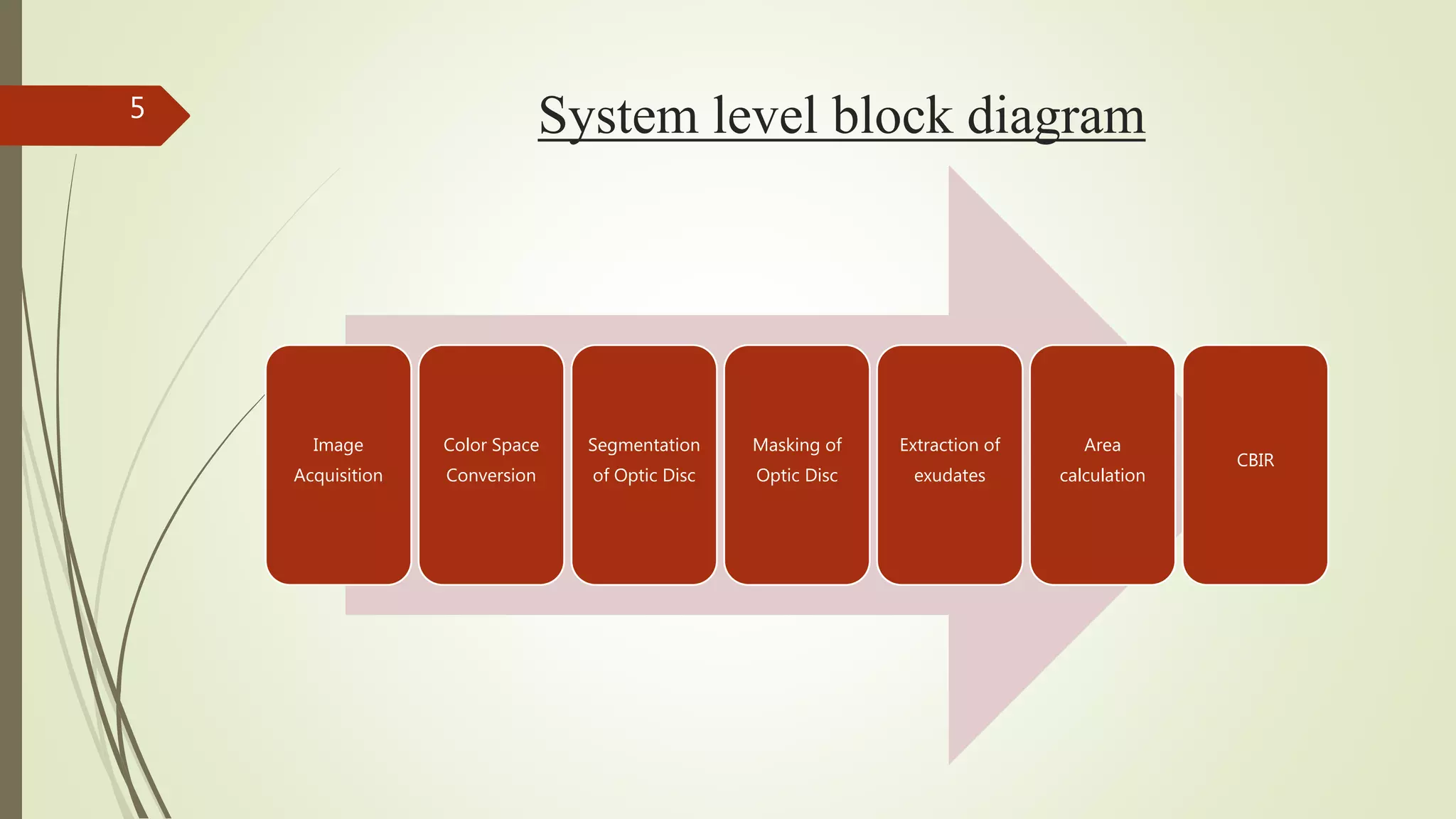
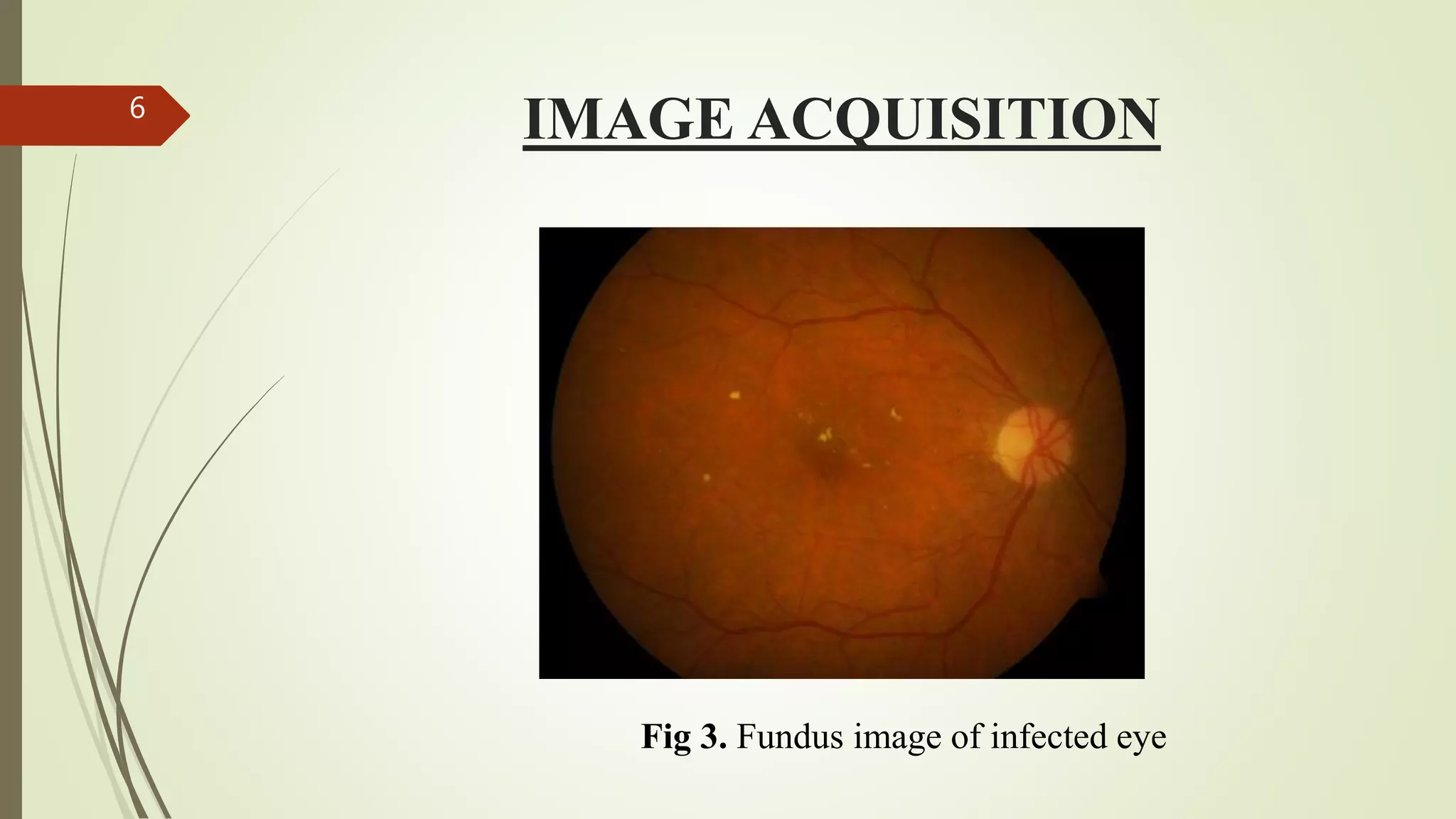
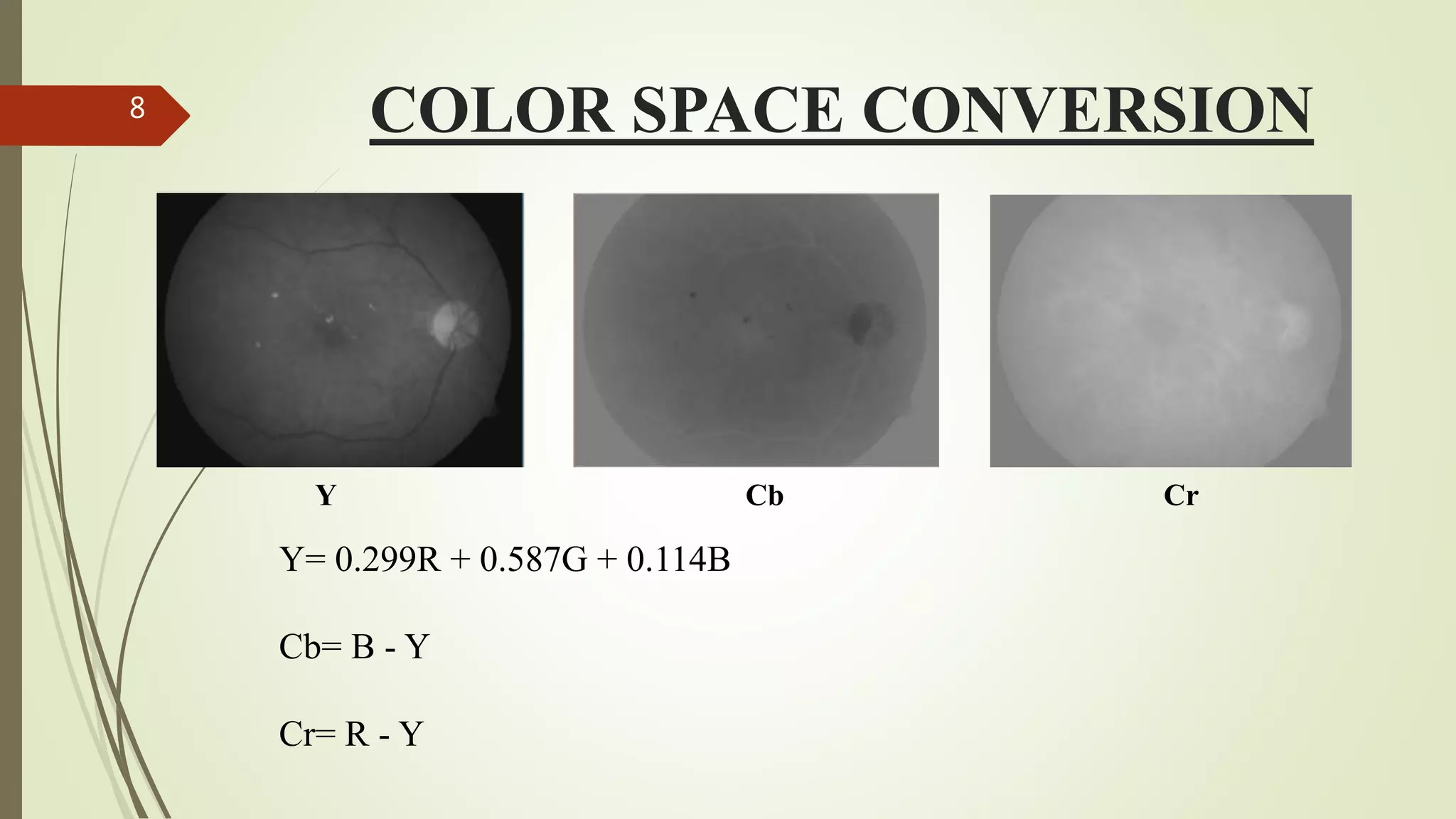
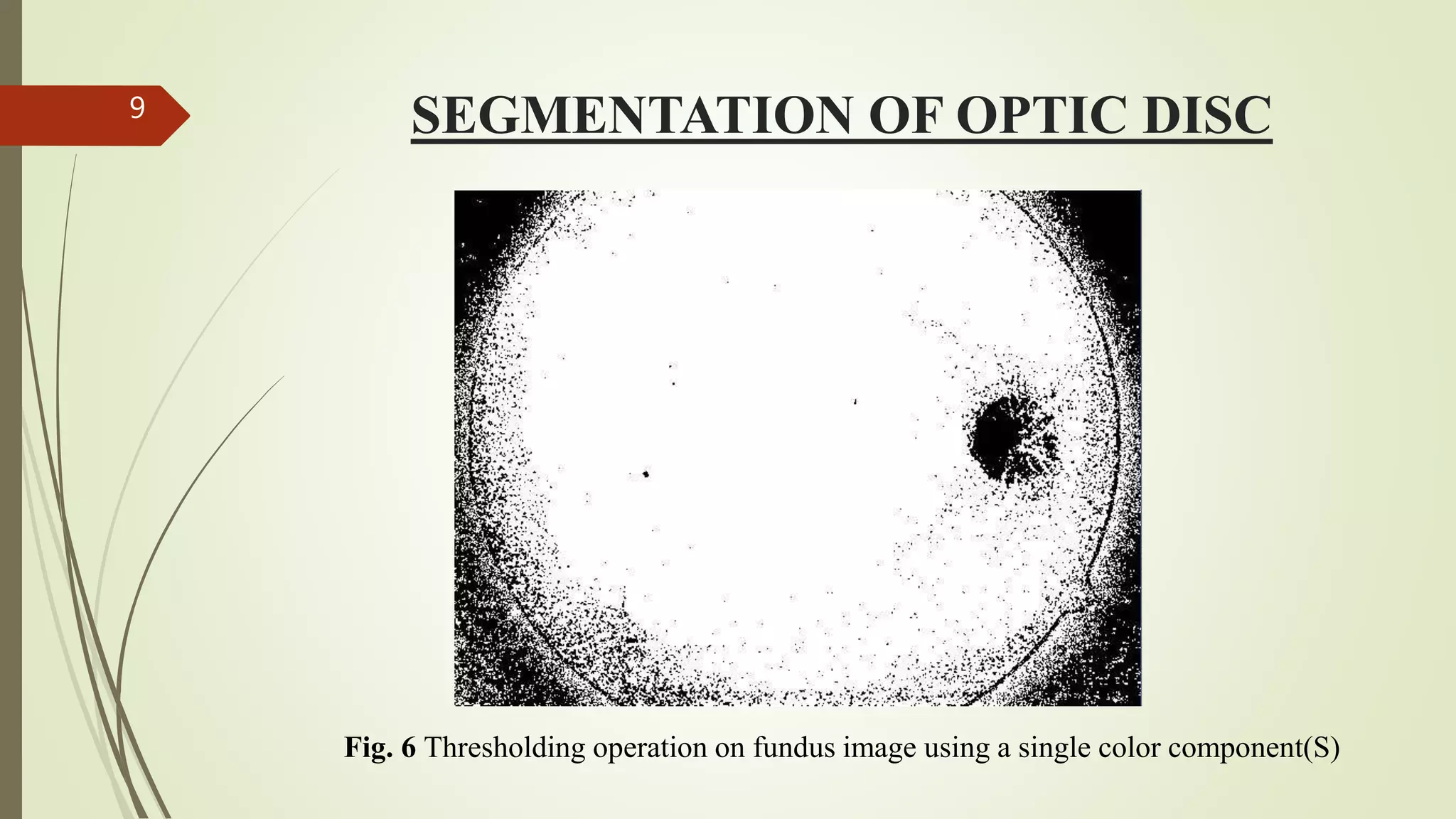
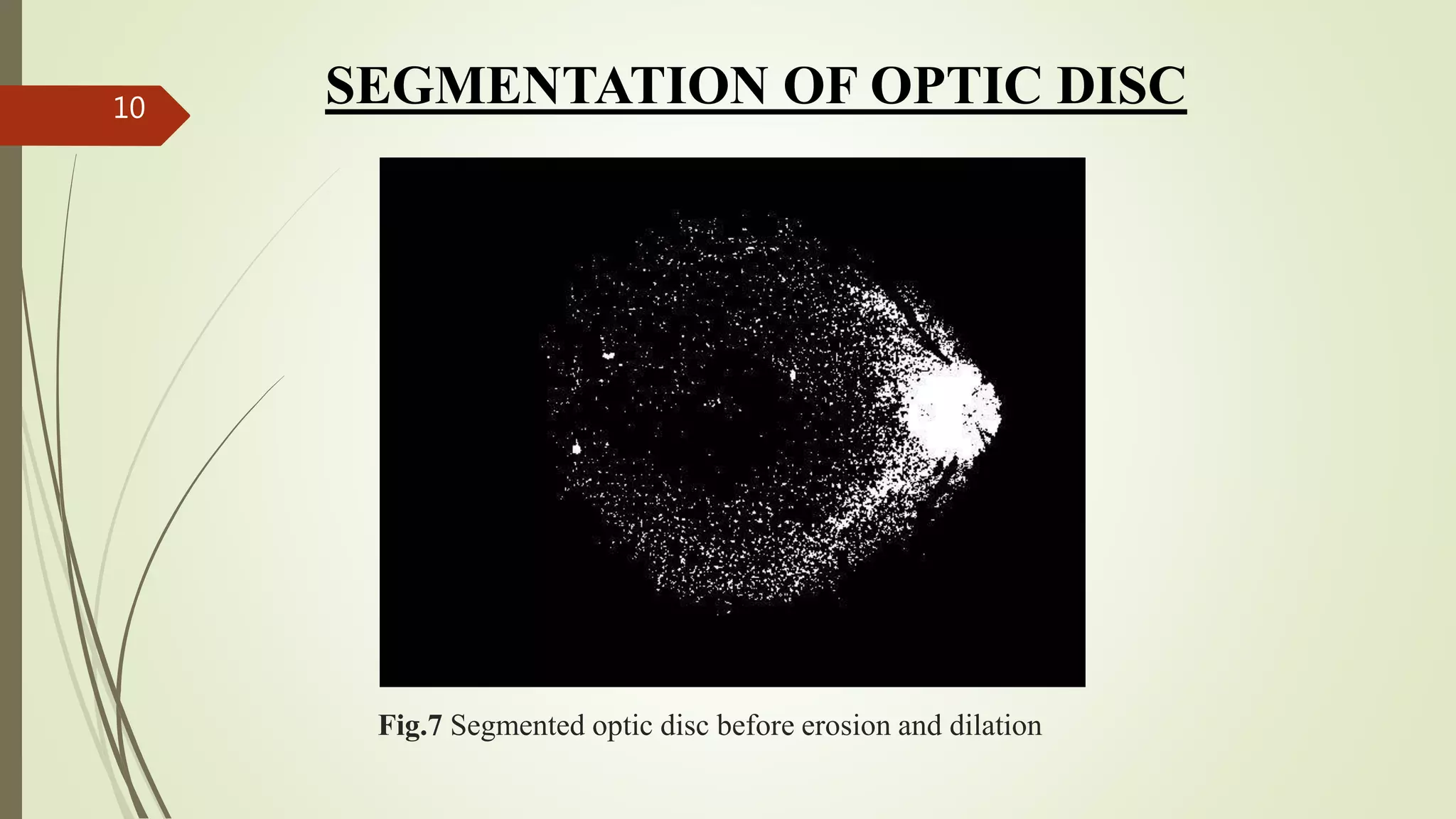
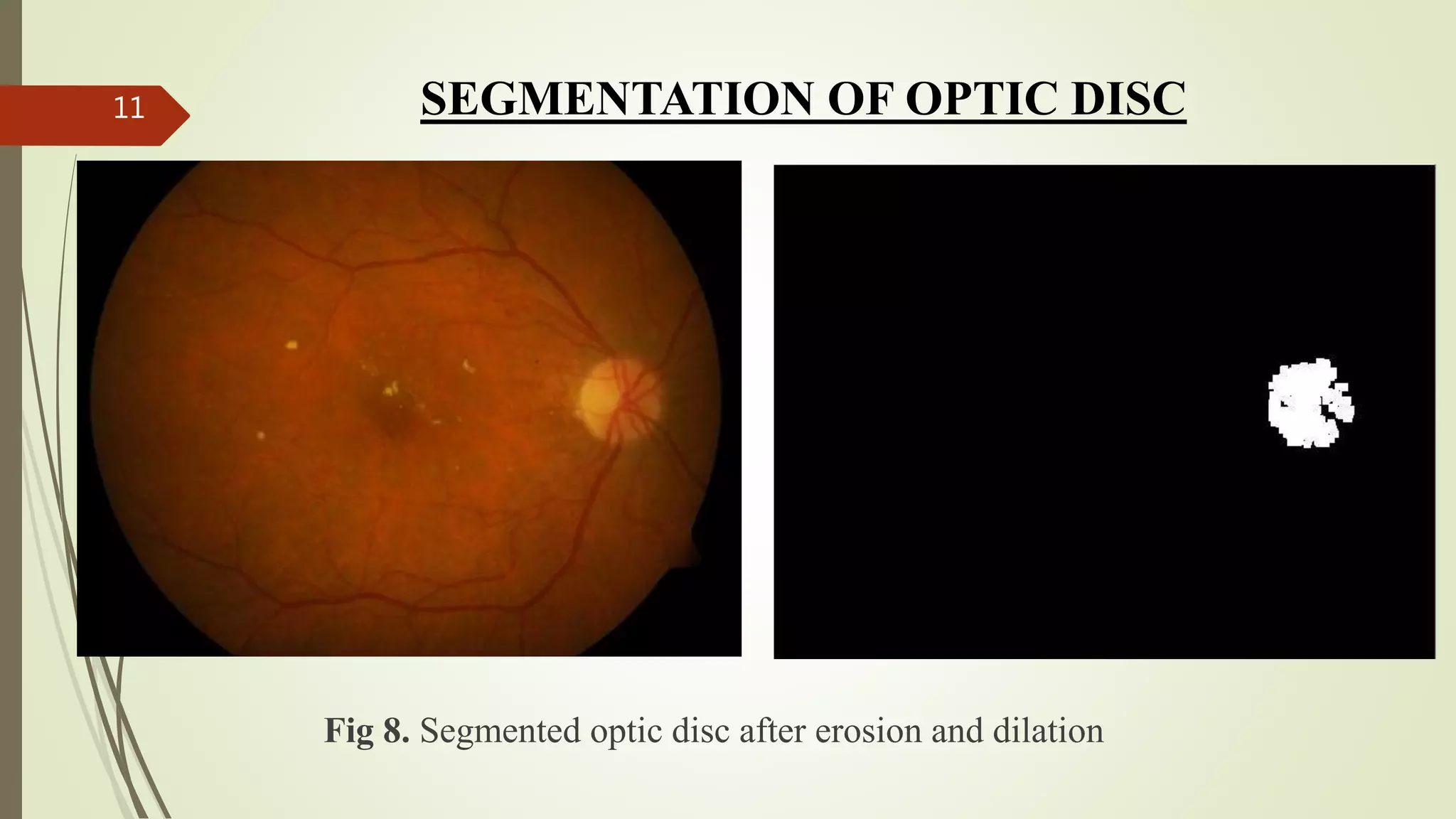
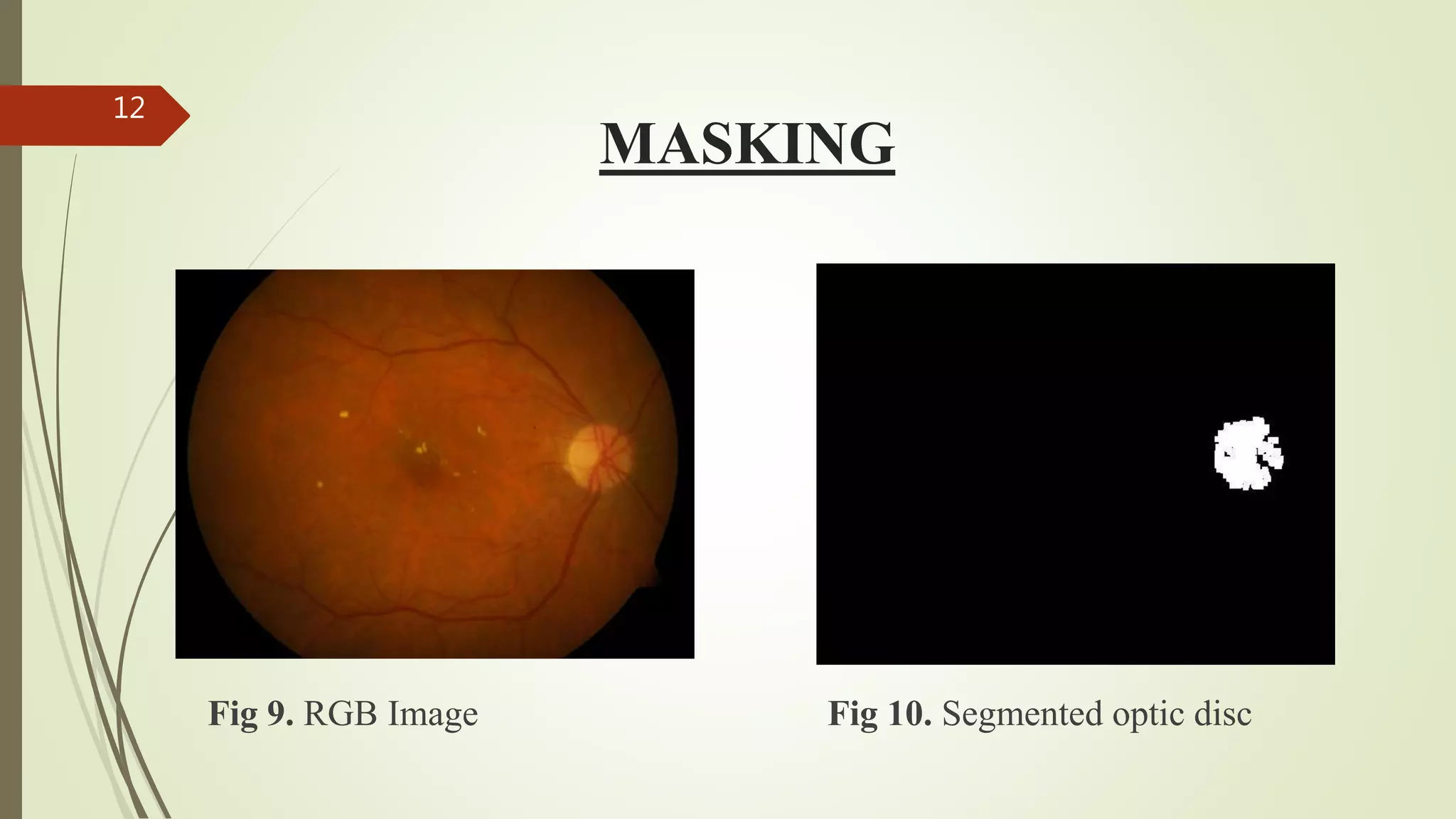
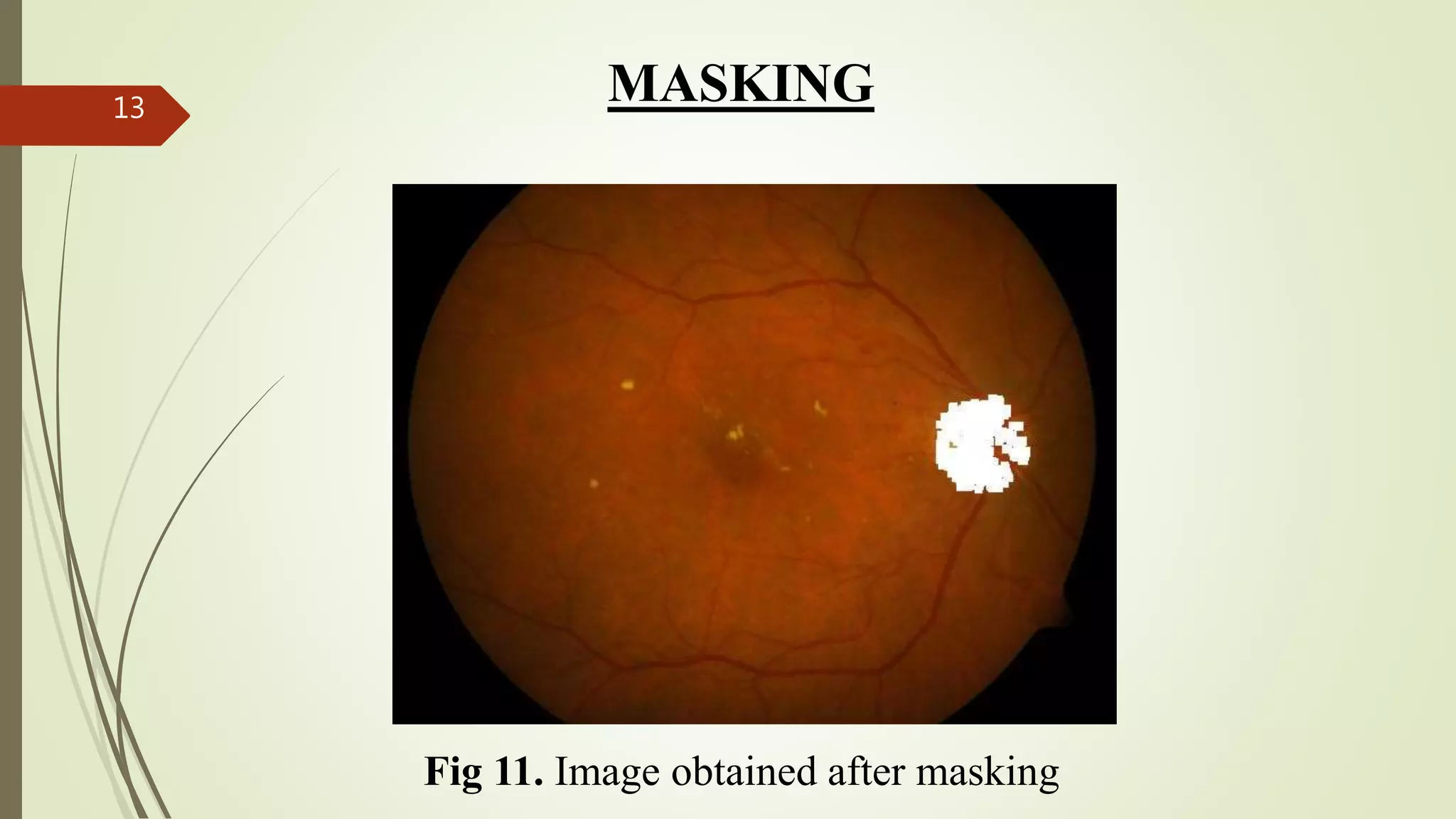
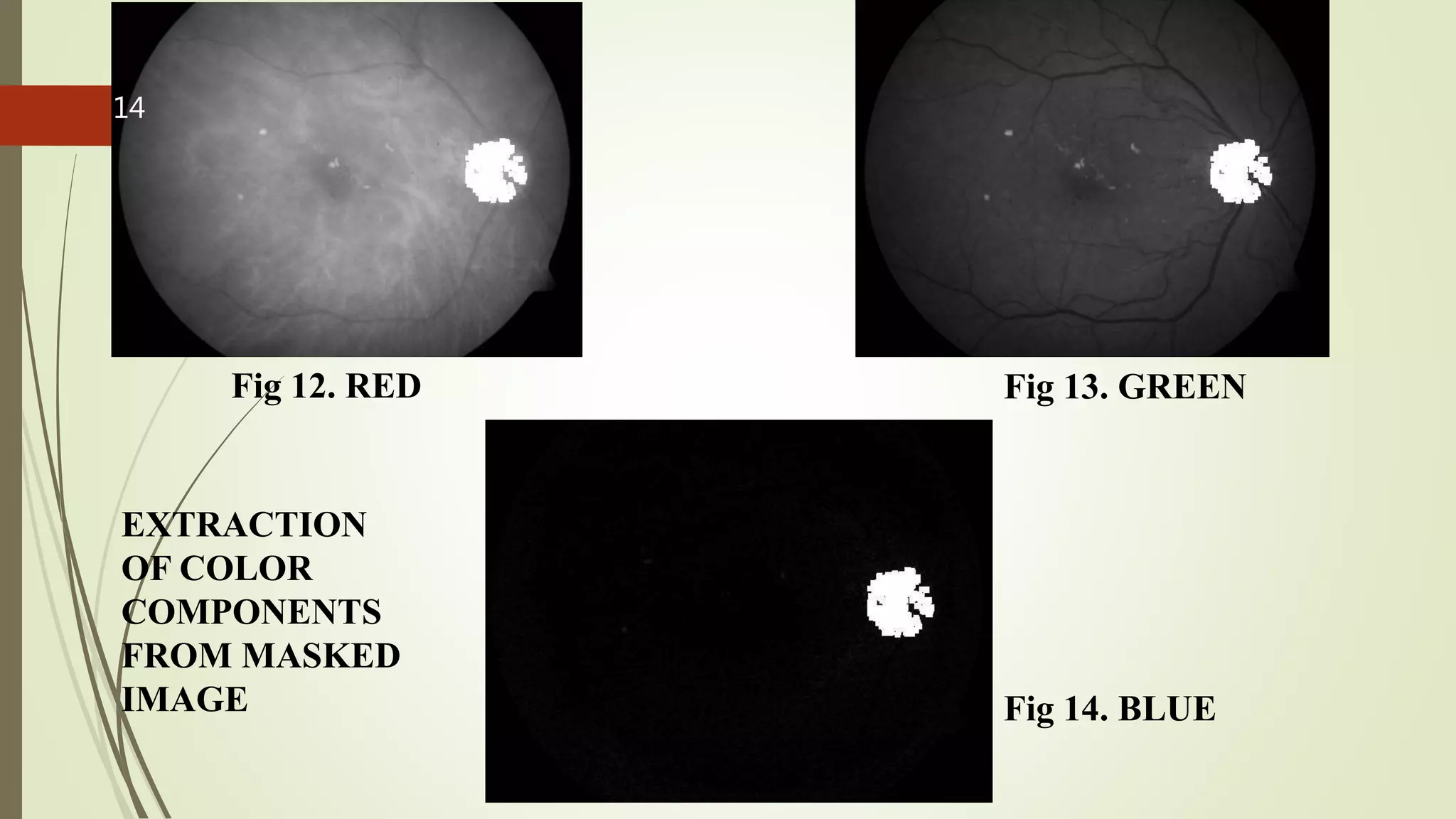
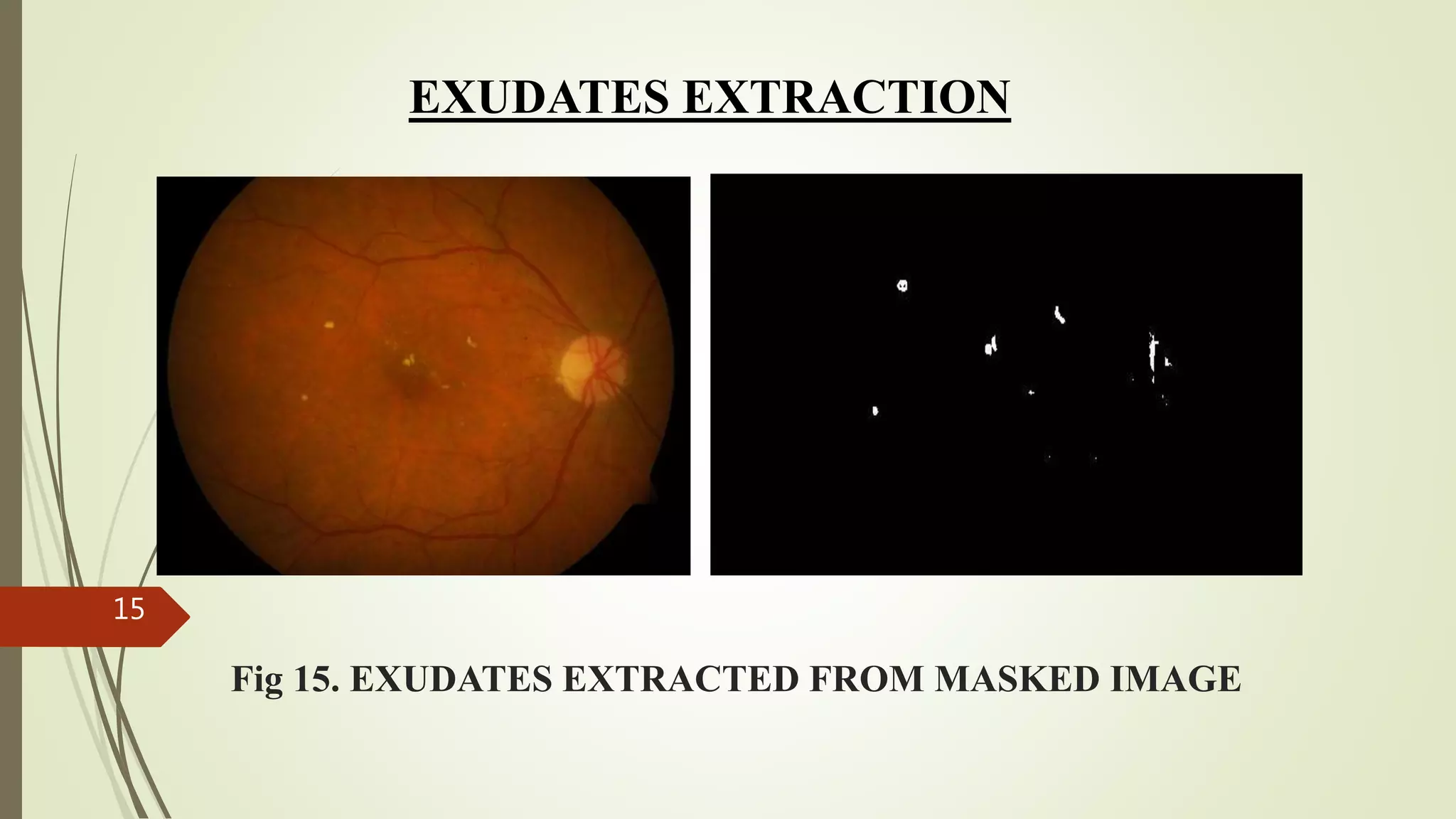
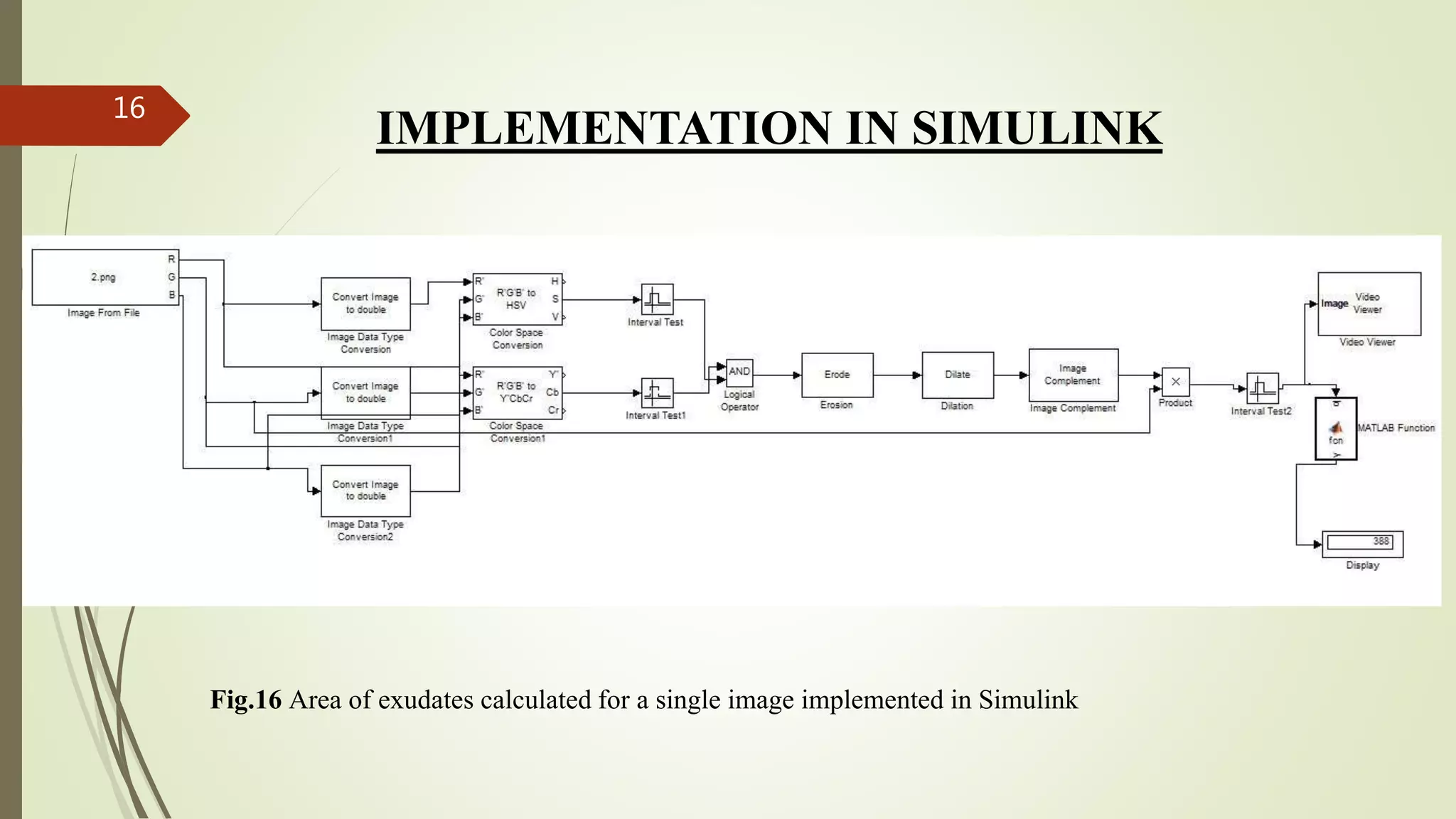
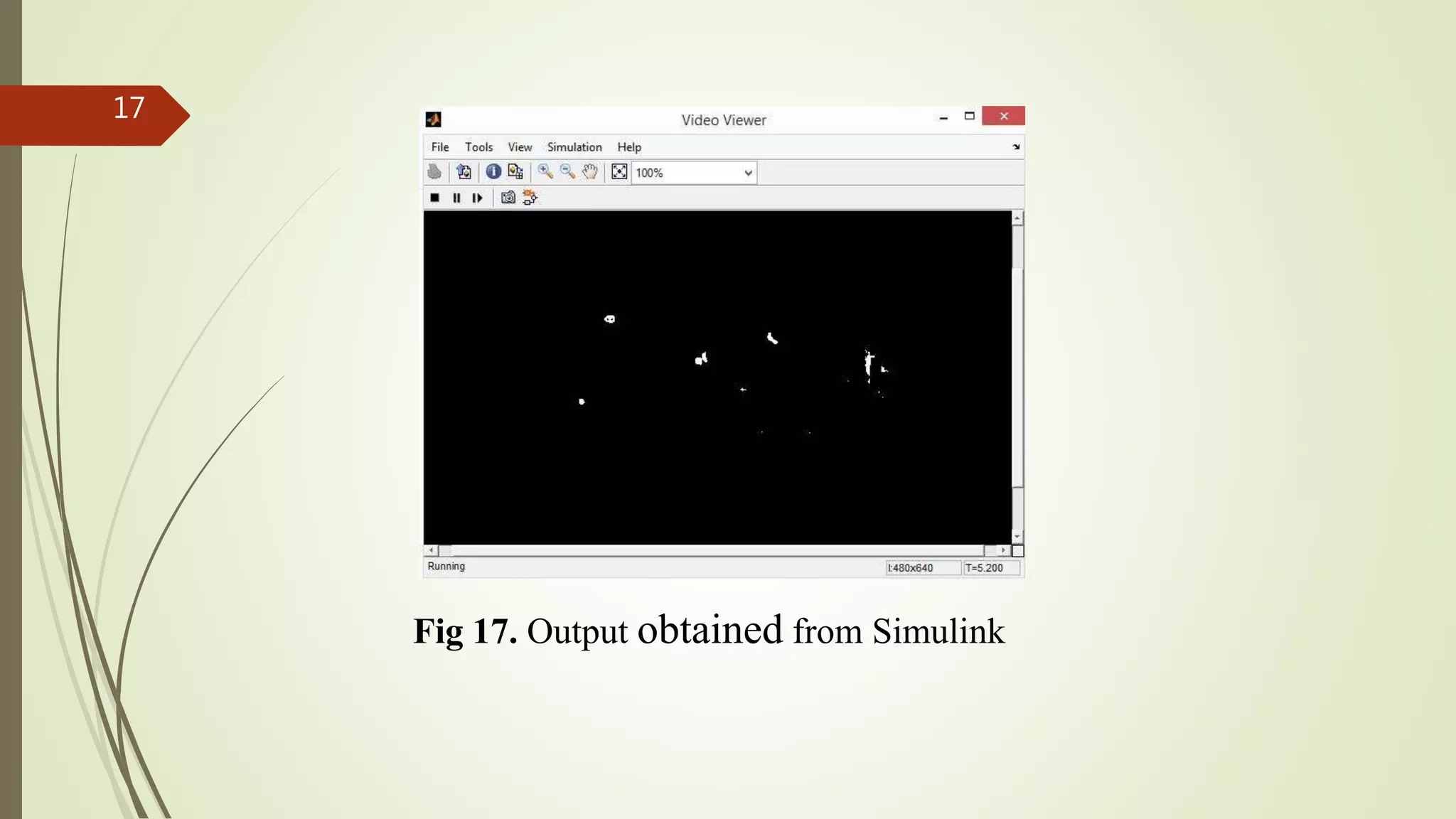
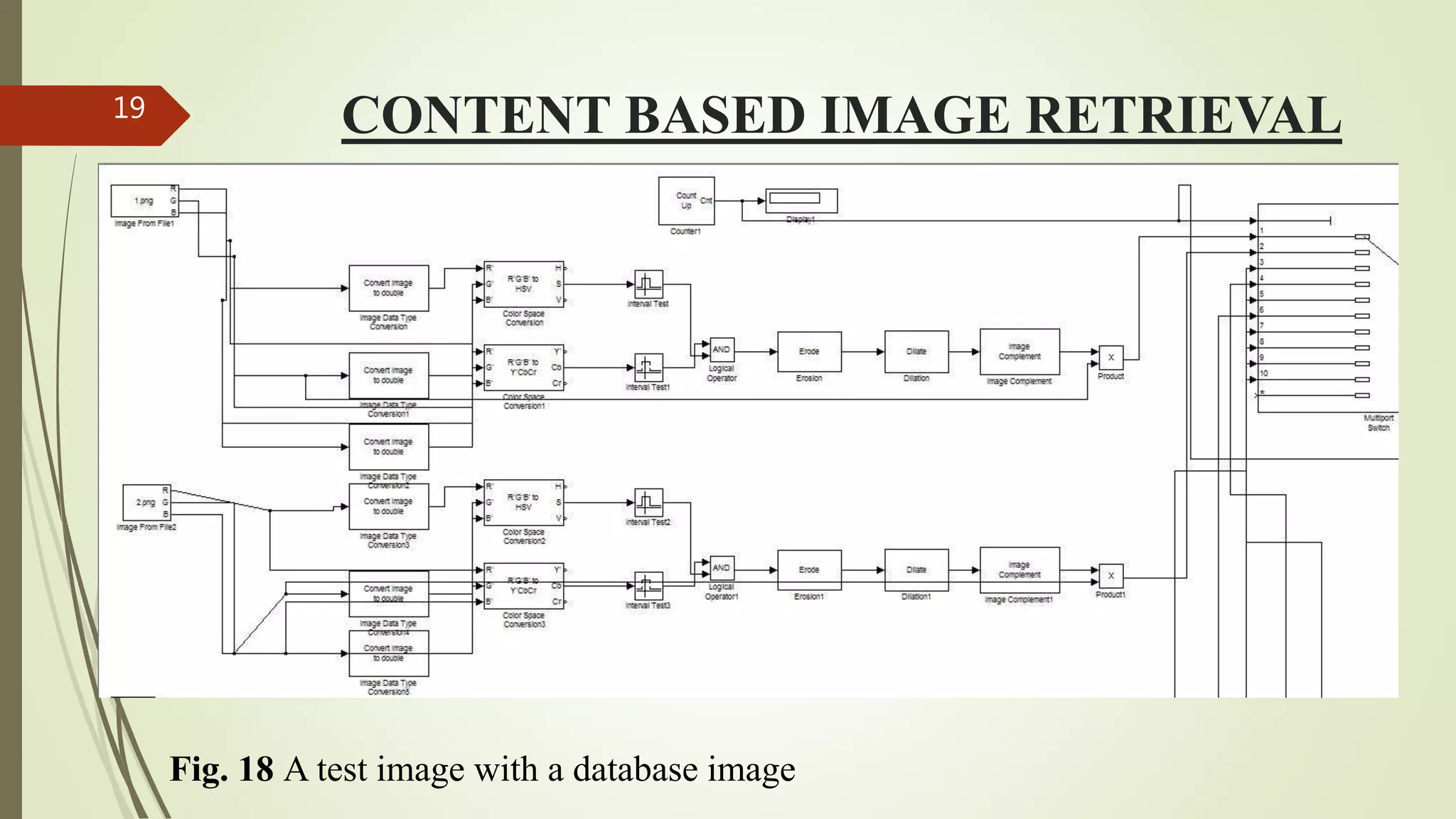
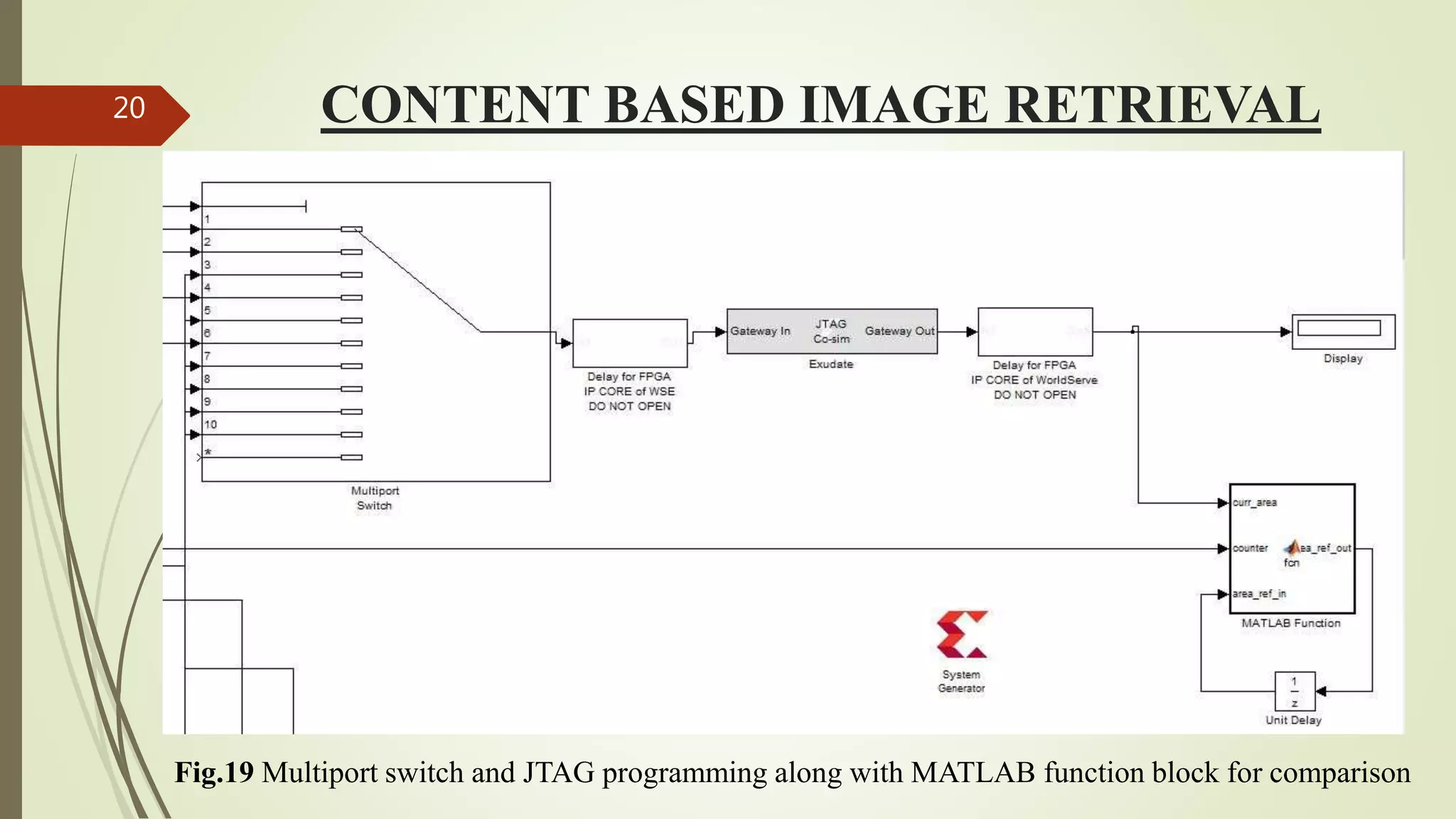
This document describes the design and development of an early optical disease recognition system using fundus imaging on an FPGA. The system aims to extract exudates from fundus images of eyes to detect diabetic retinopathy. It involves image acquisition, color space conversion, segmentation of the optic disc, masking of the optic disc, extraction of exudates, and area calculation of exudates. The system is implemented using Simulink and also allows for content-based image retrieval for comparison of test images to database images. Future work proposed includes better optic disc segmentation, displaying medication information, and developing handheld ophthalmoscopes.