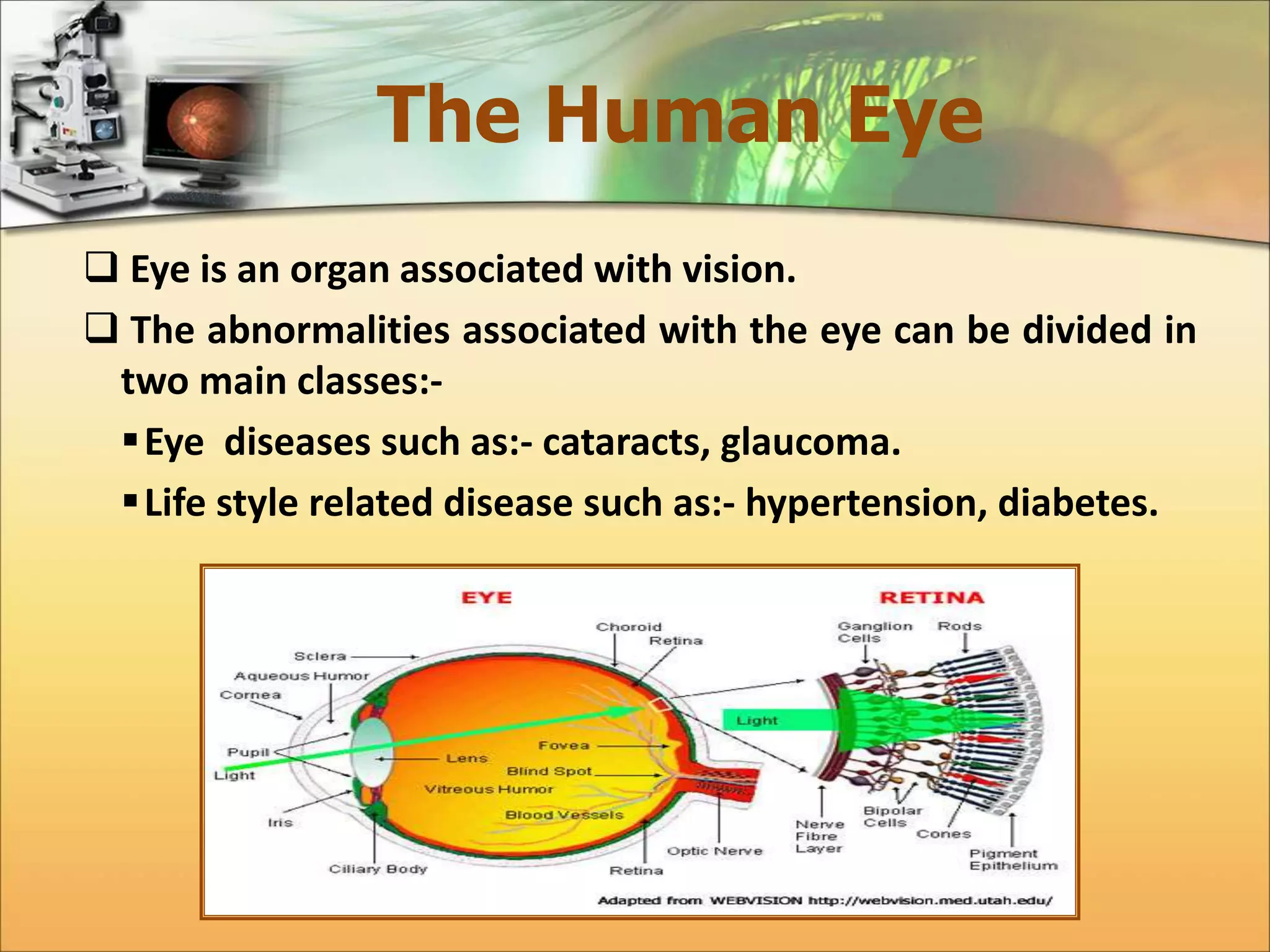
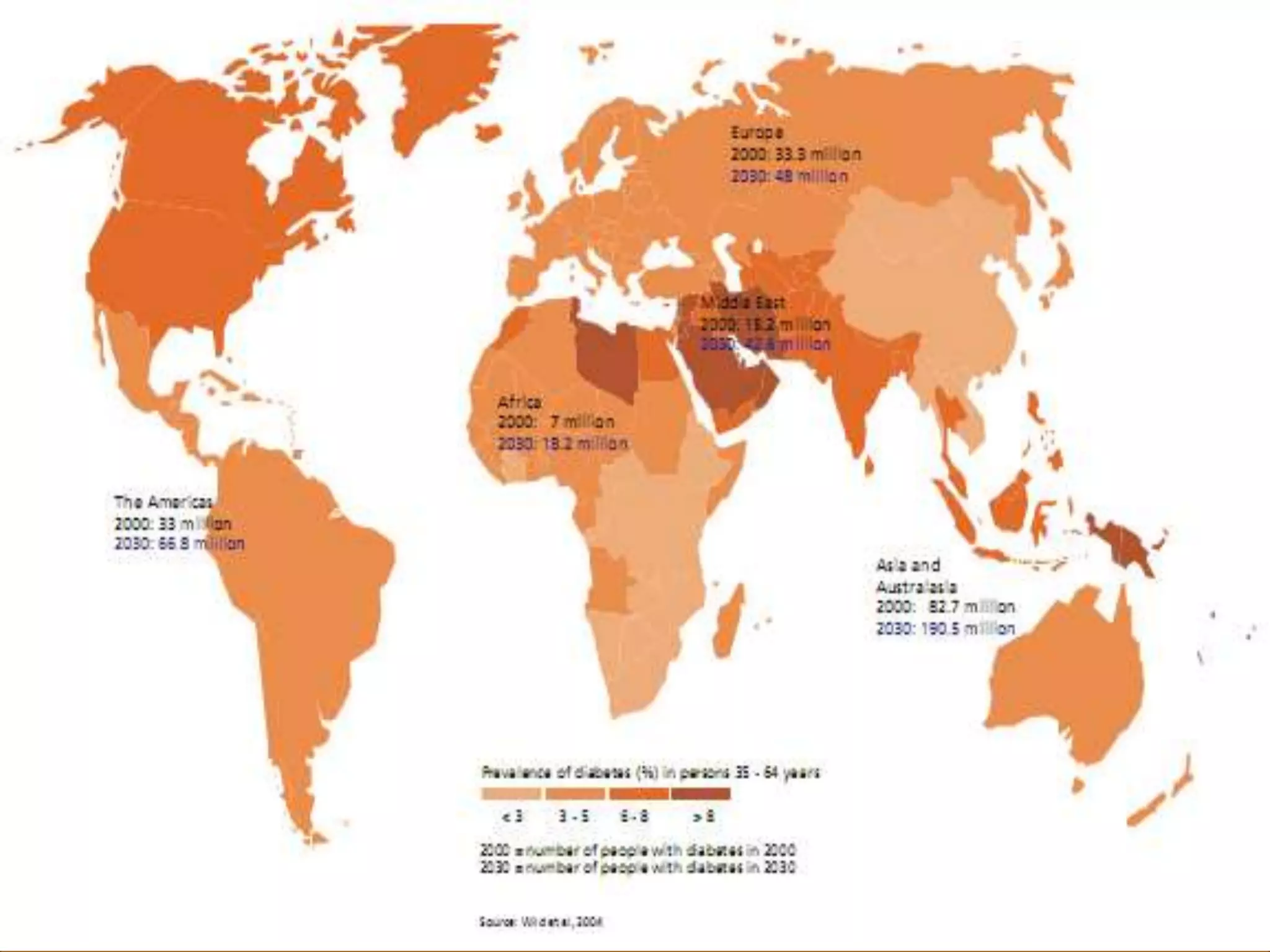
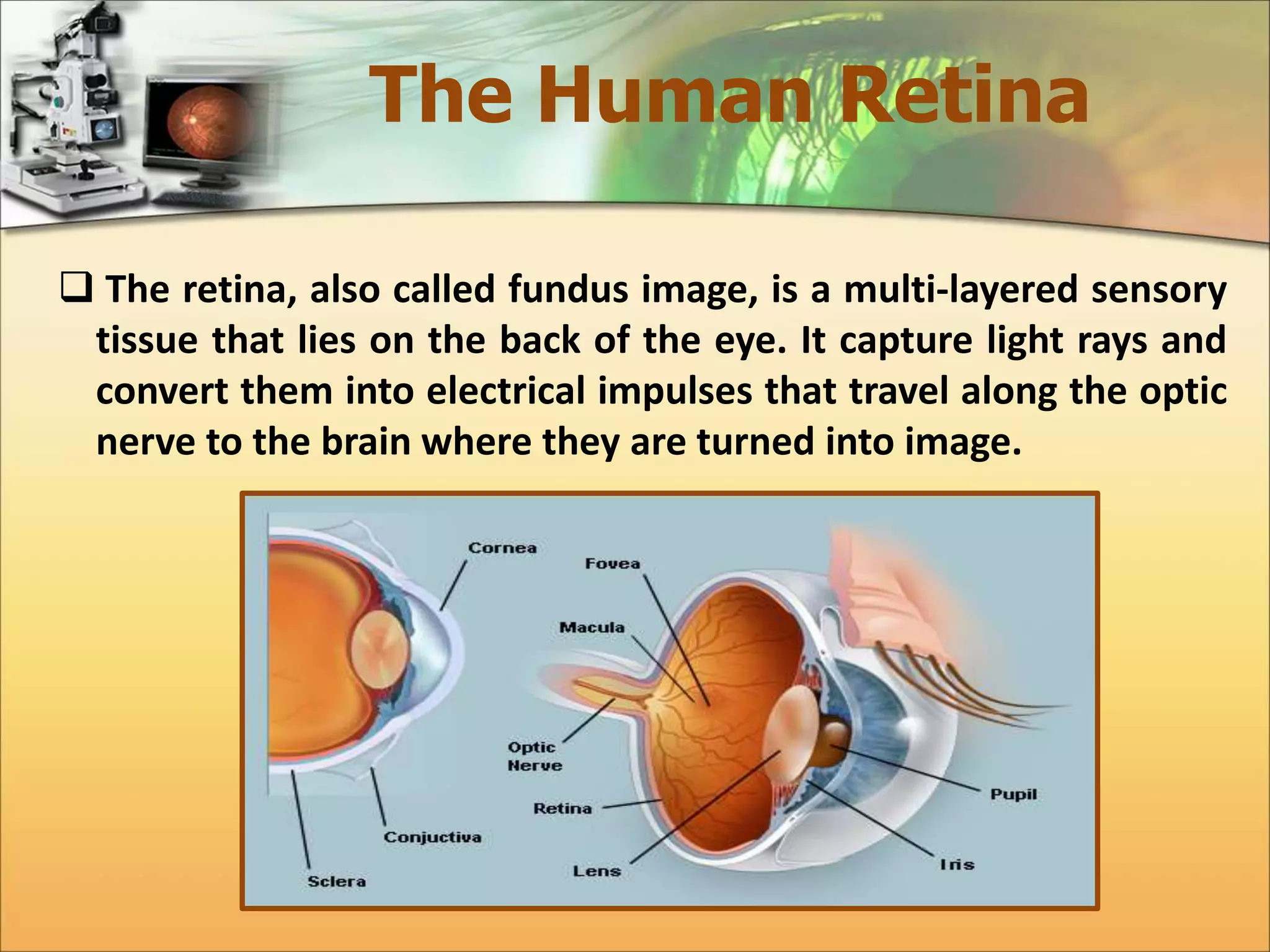
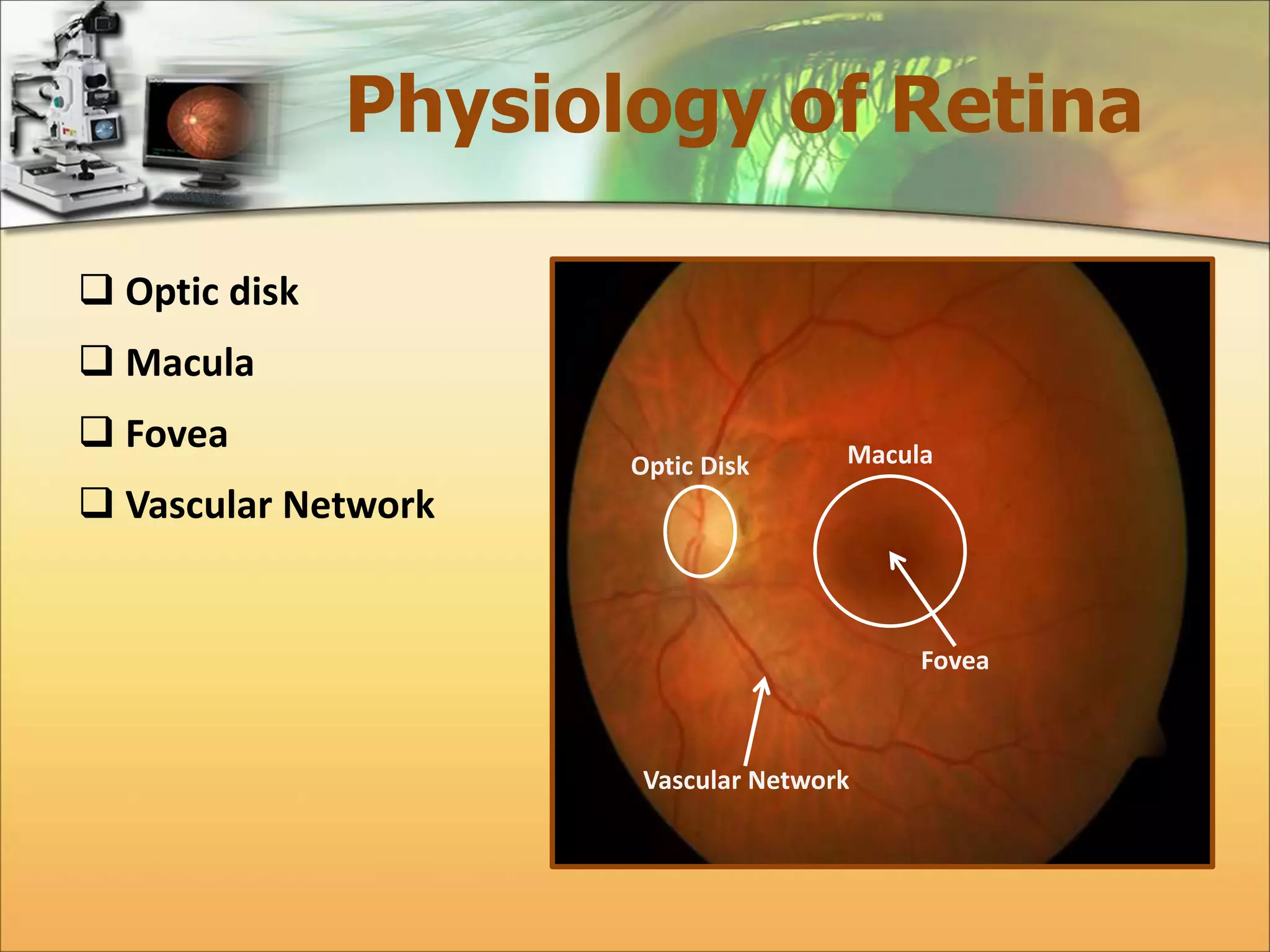
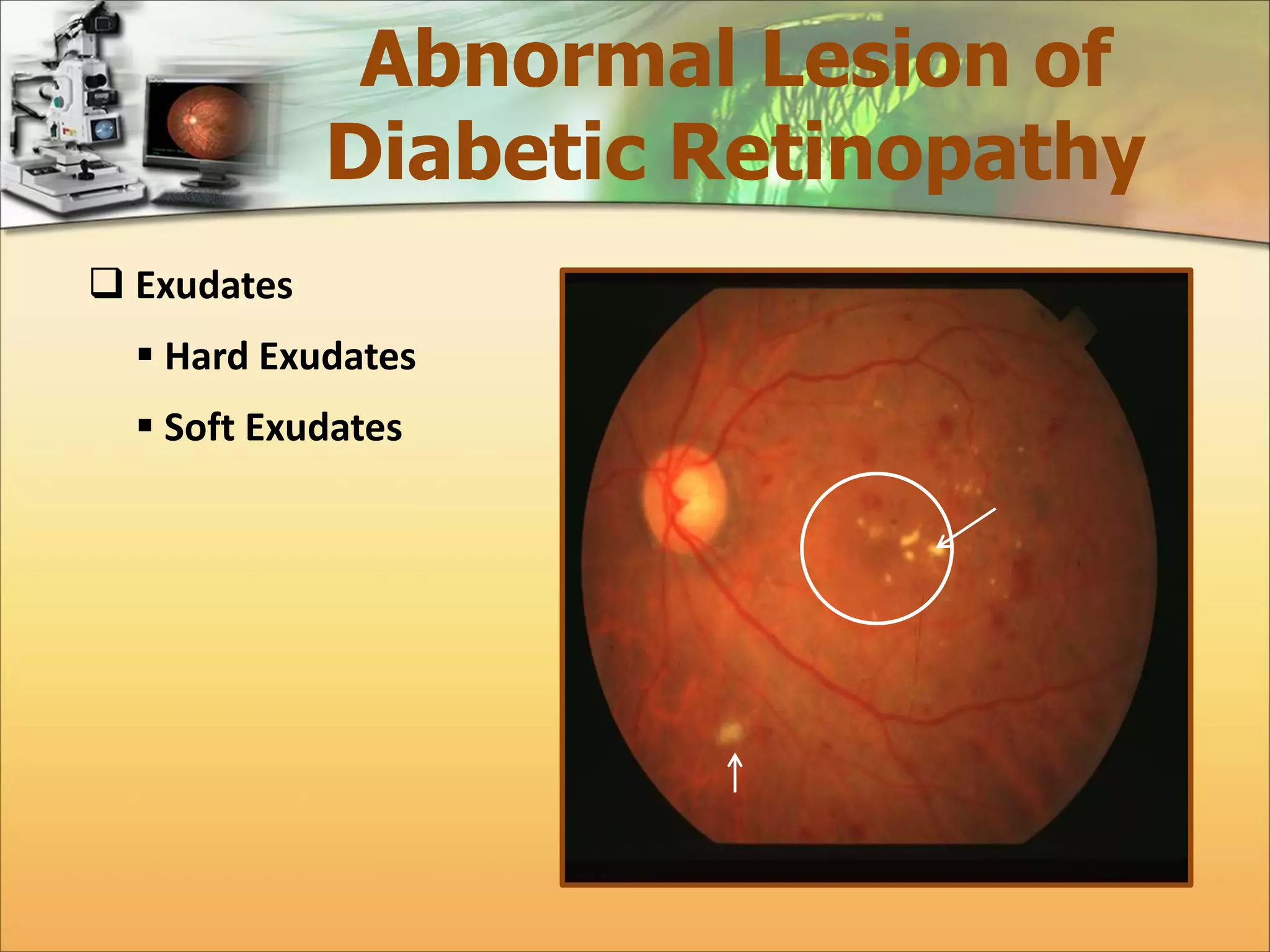
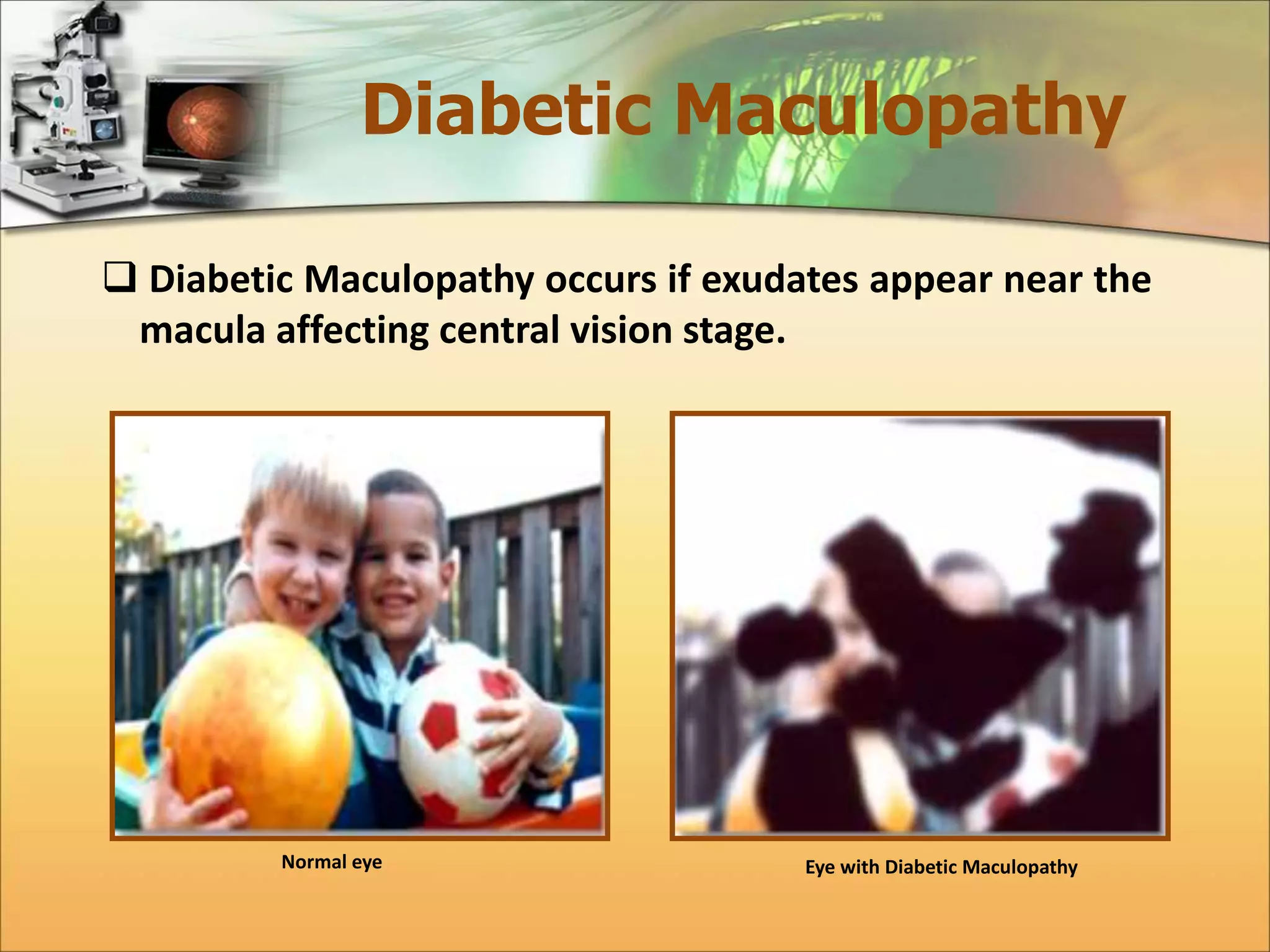
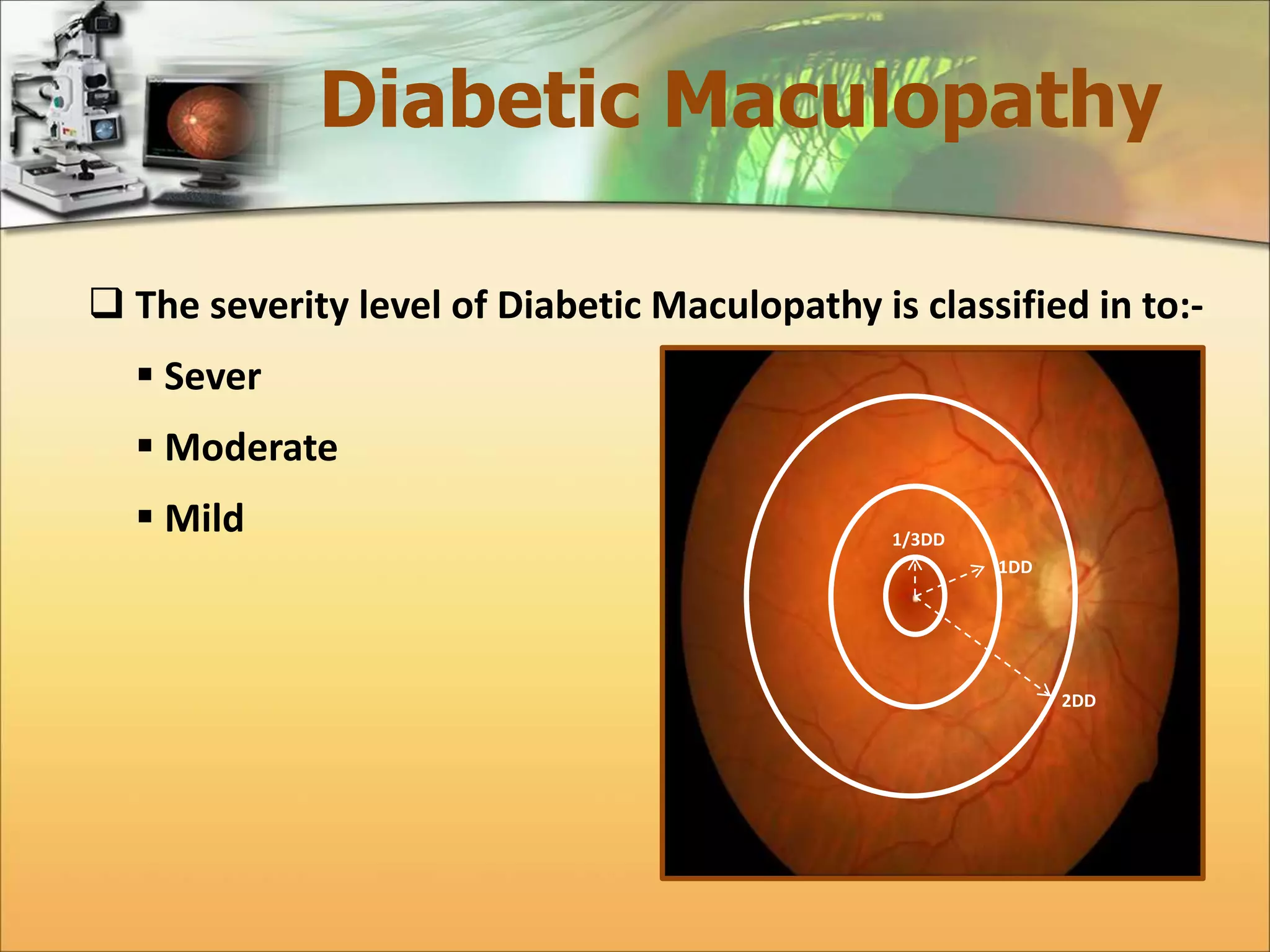
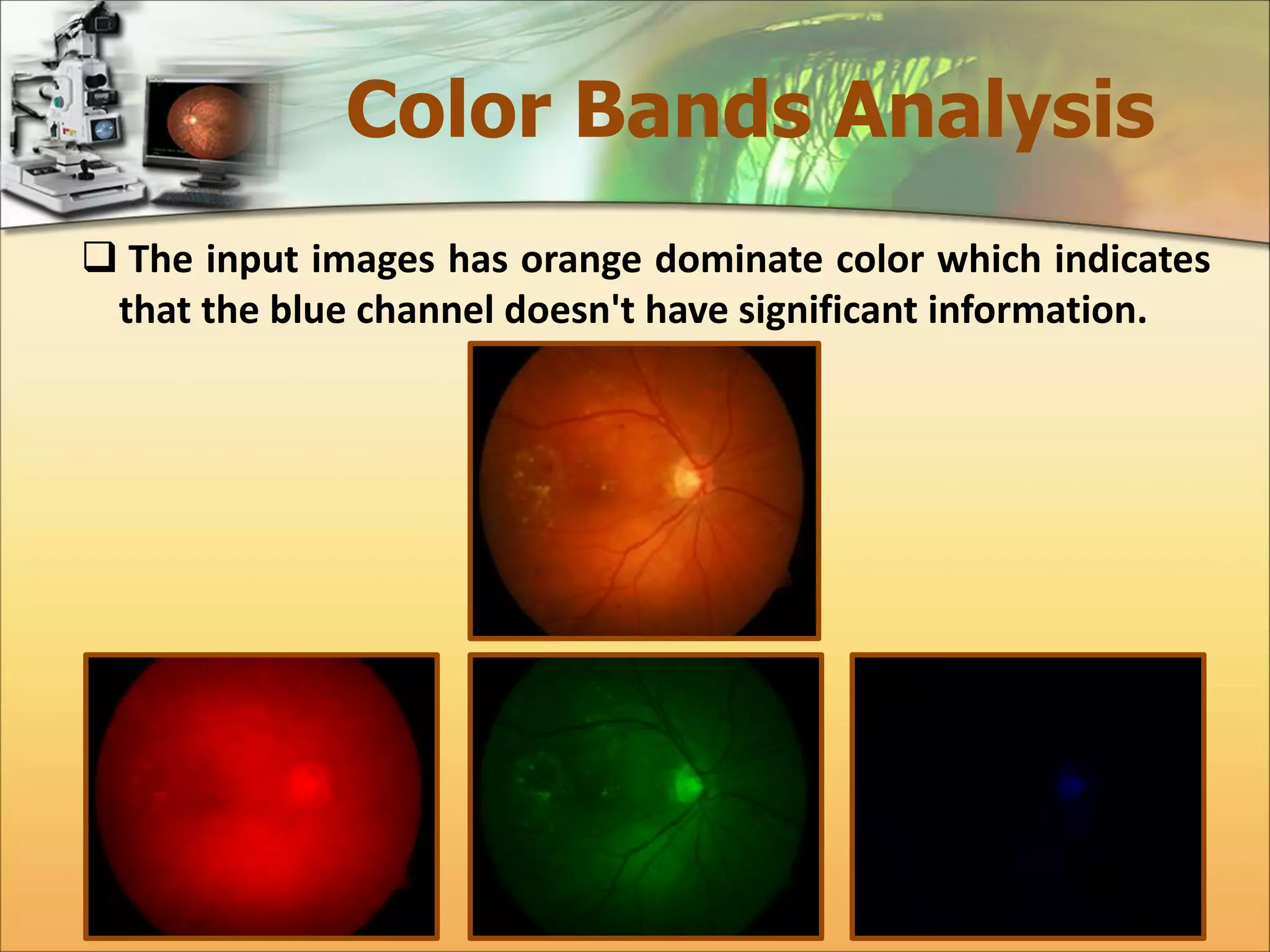
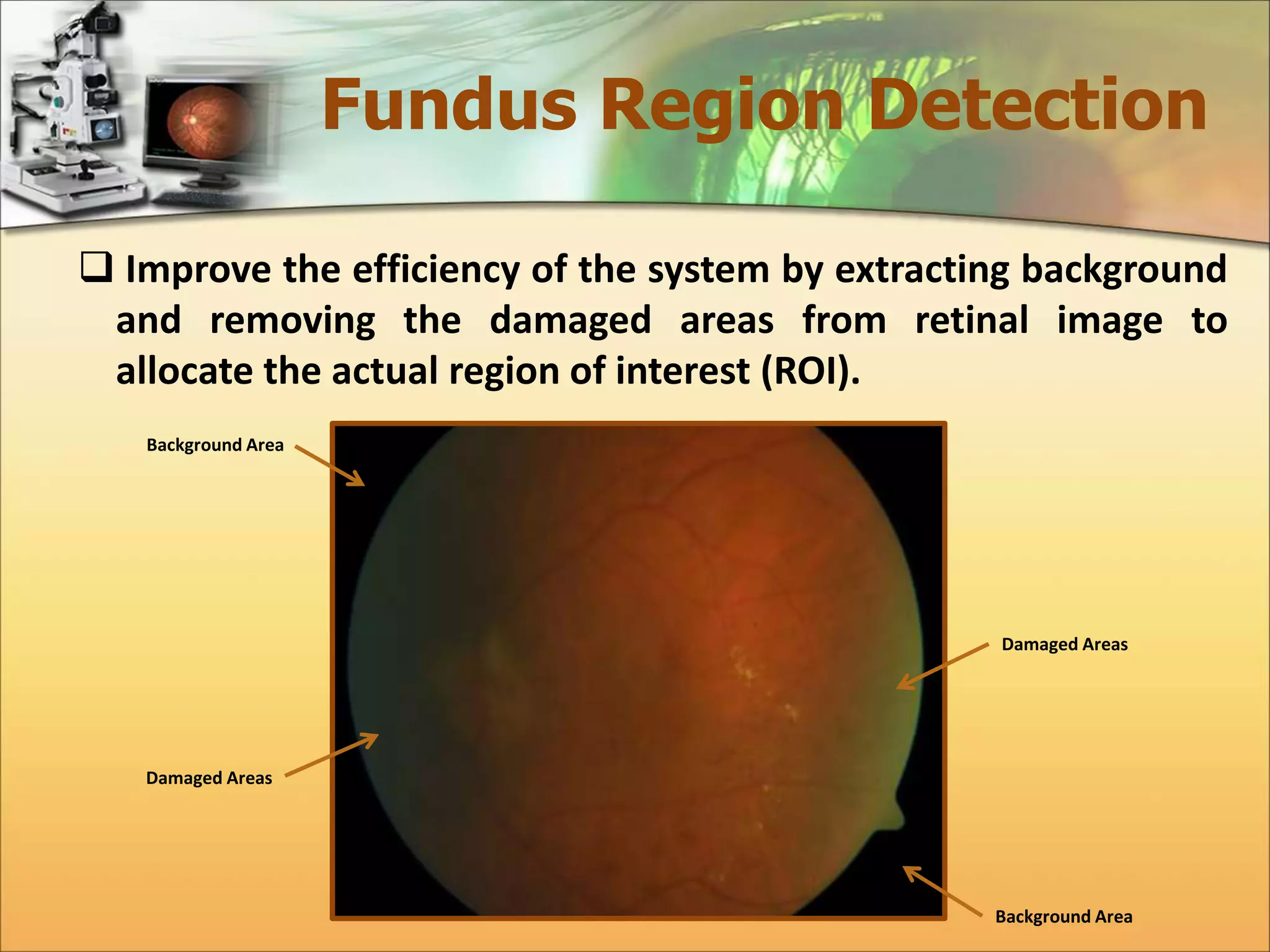
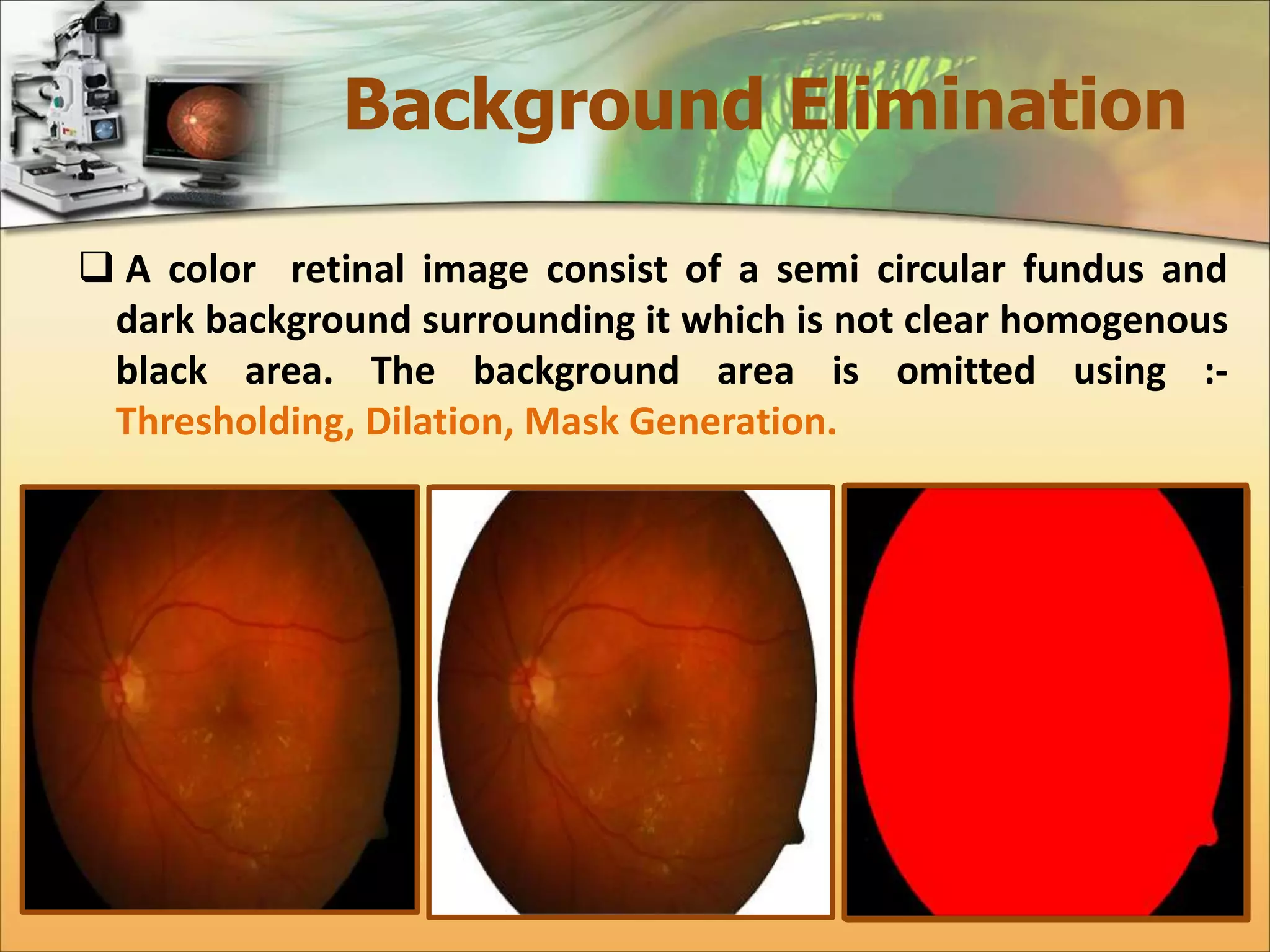
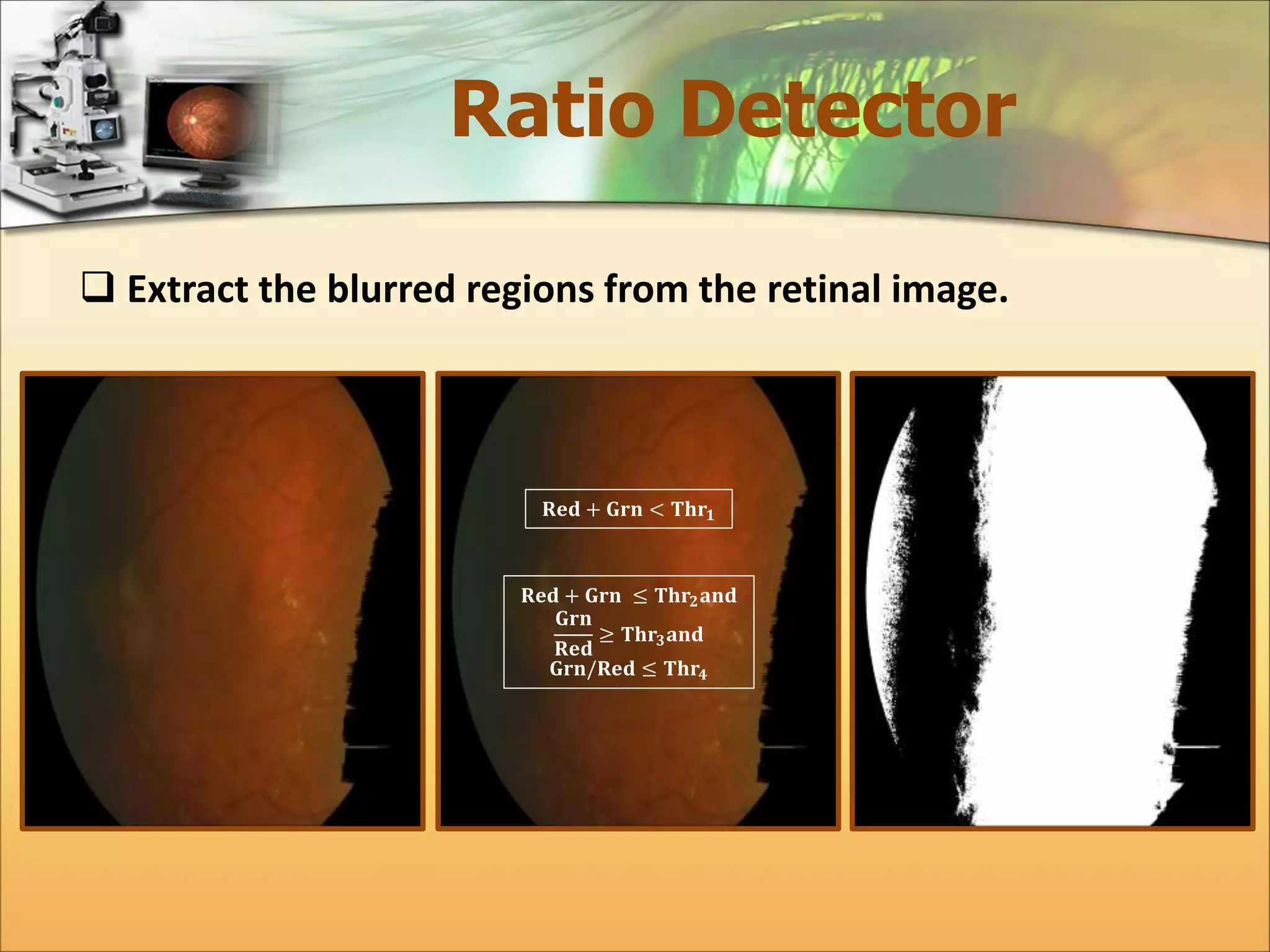
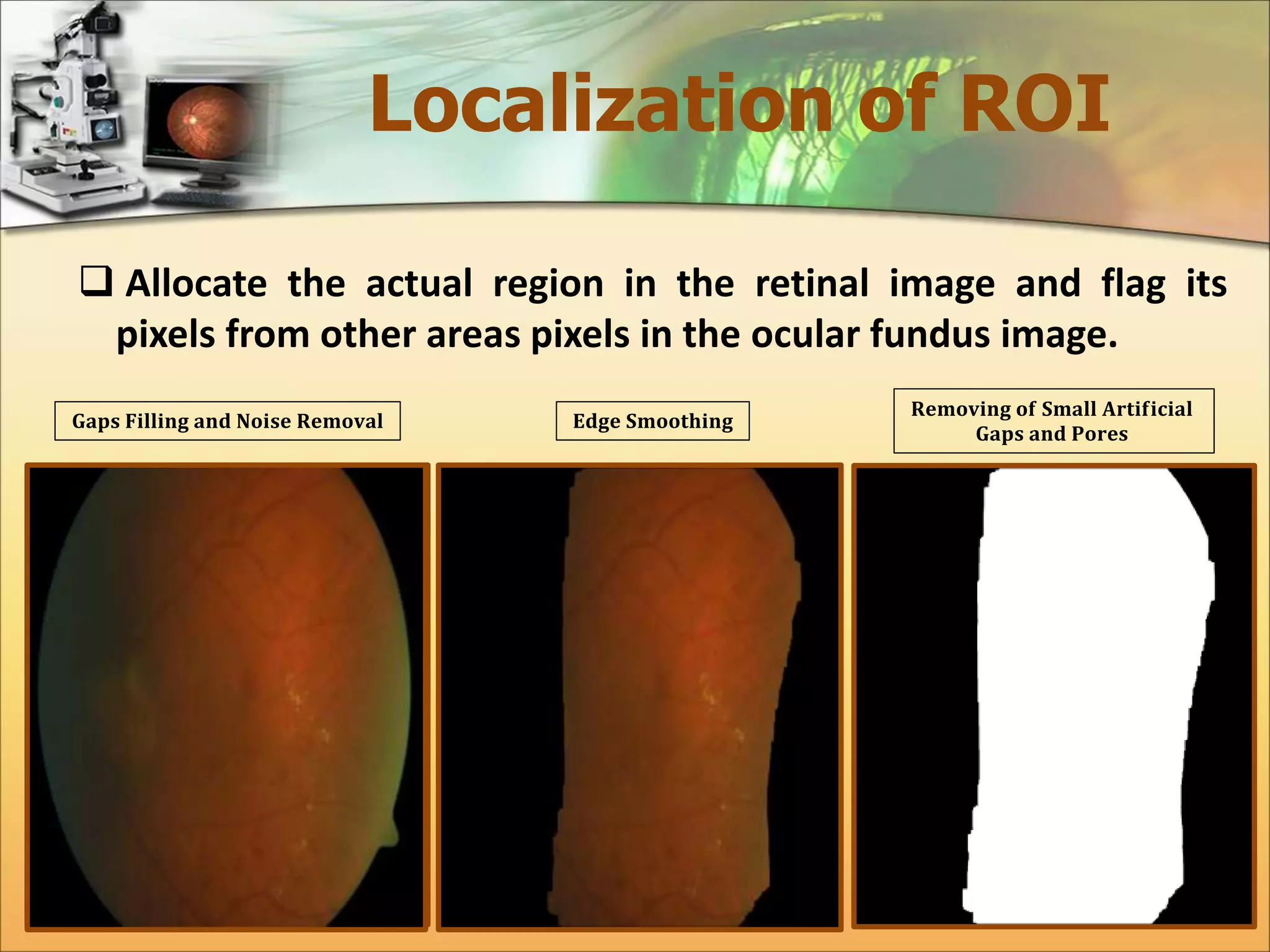
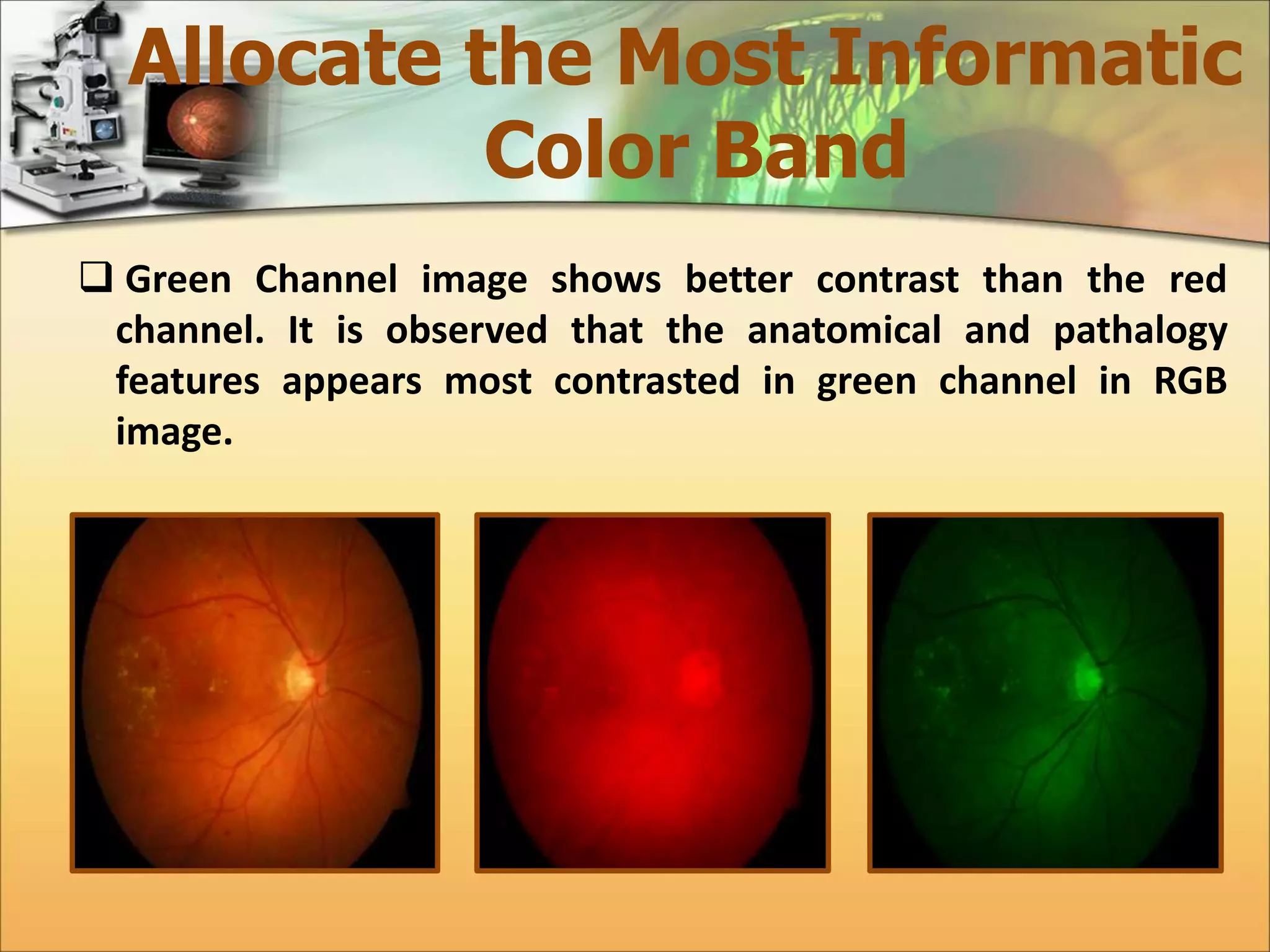
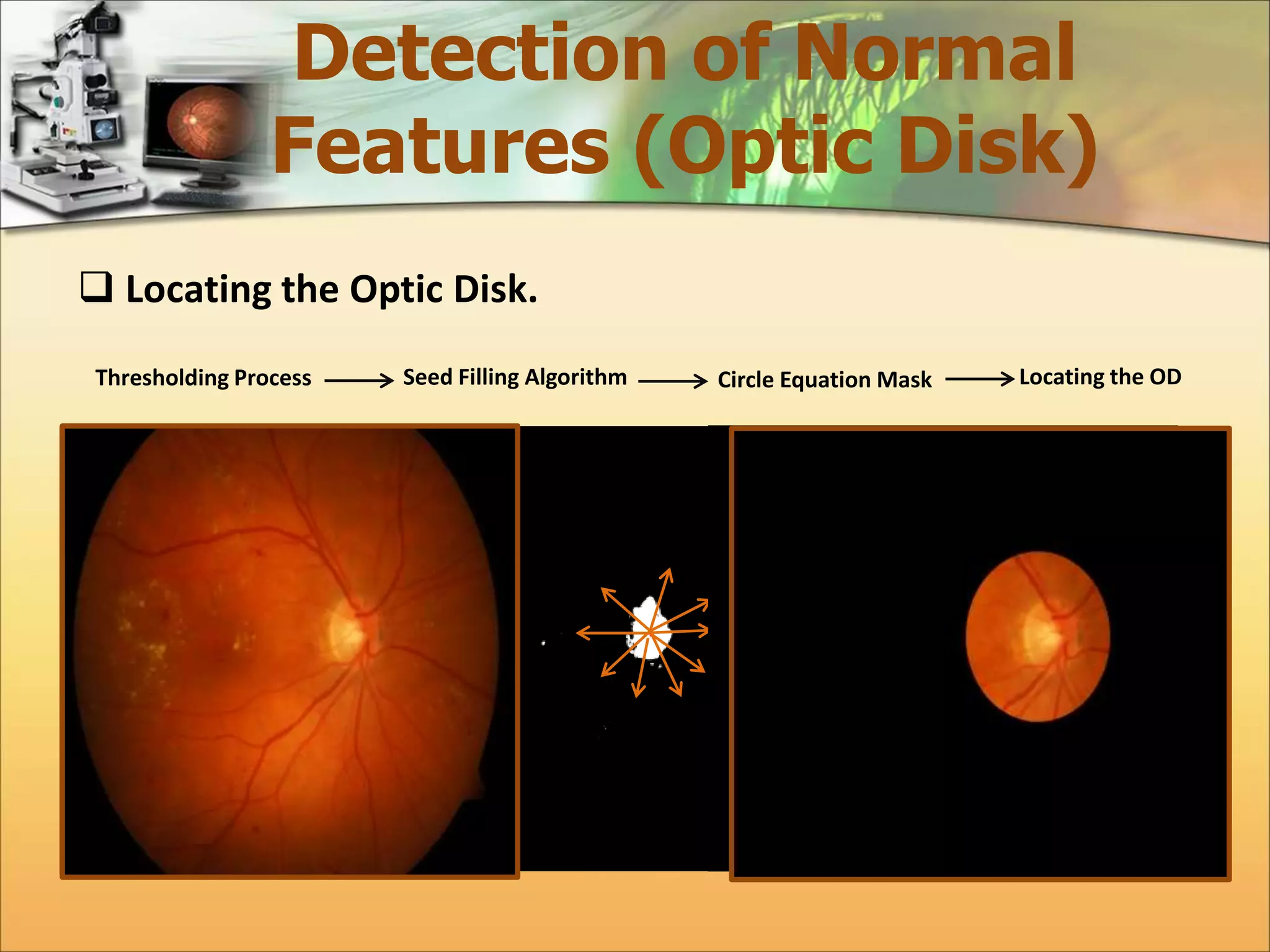
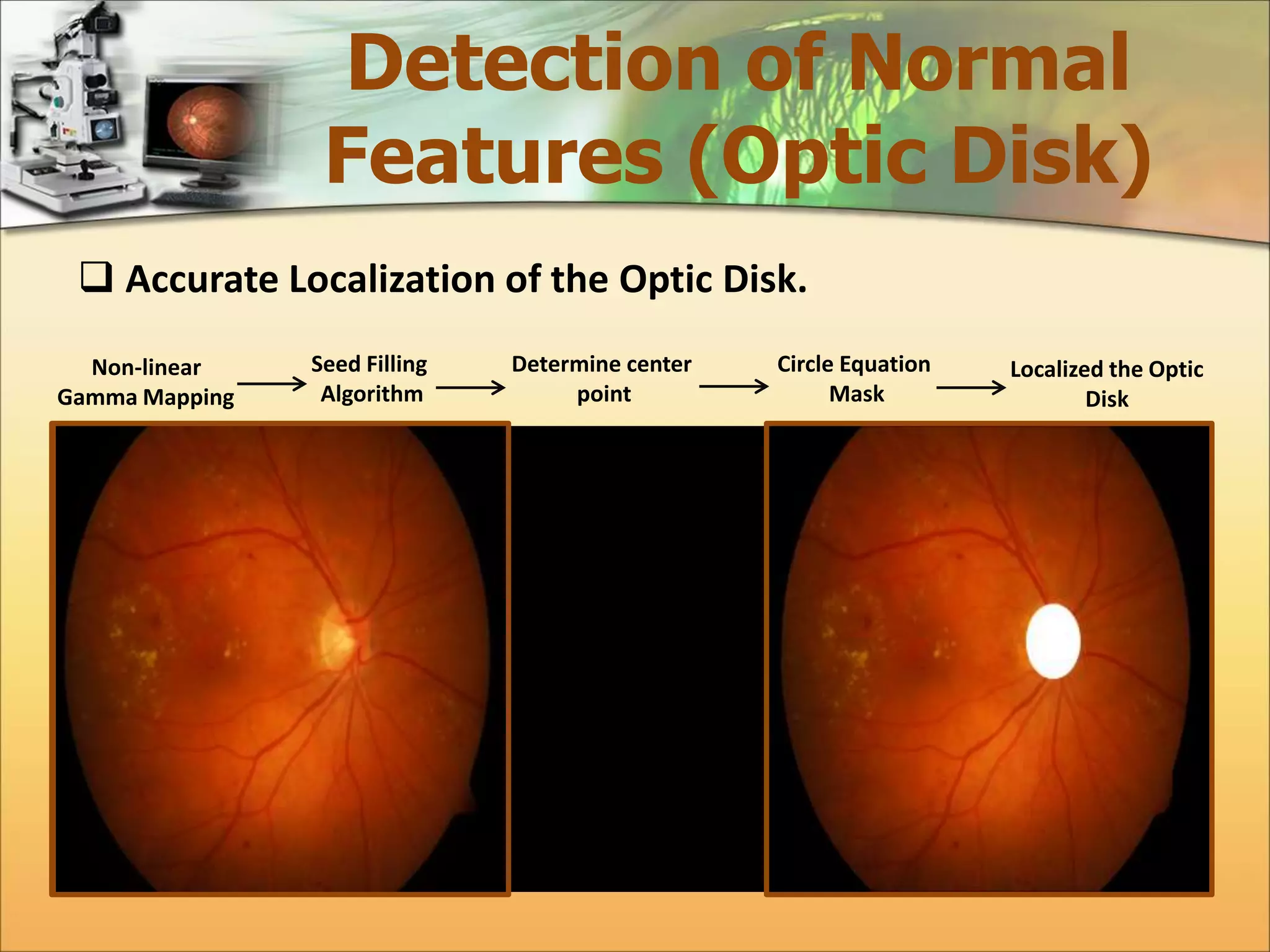
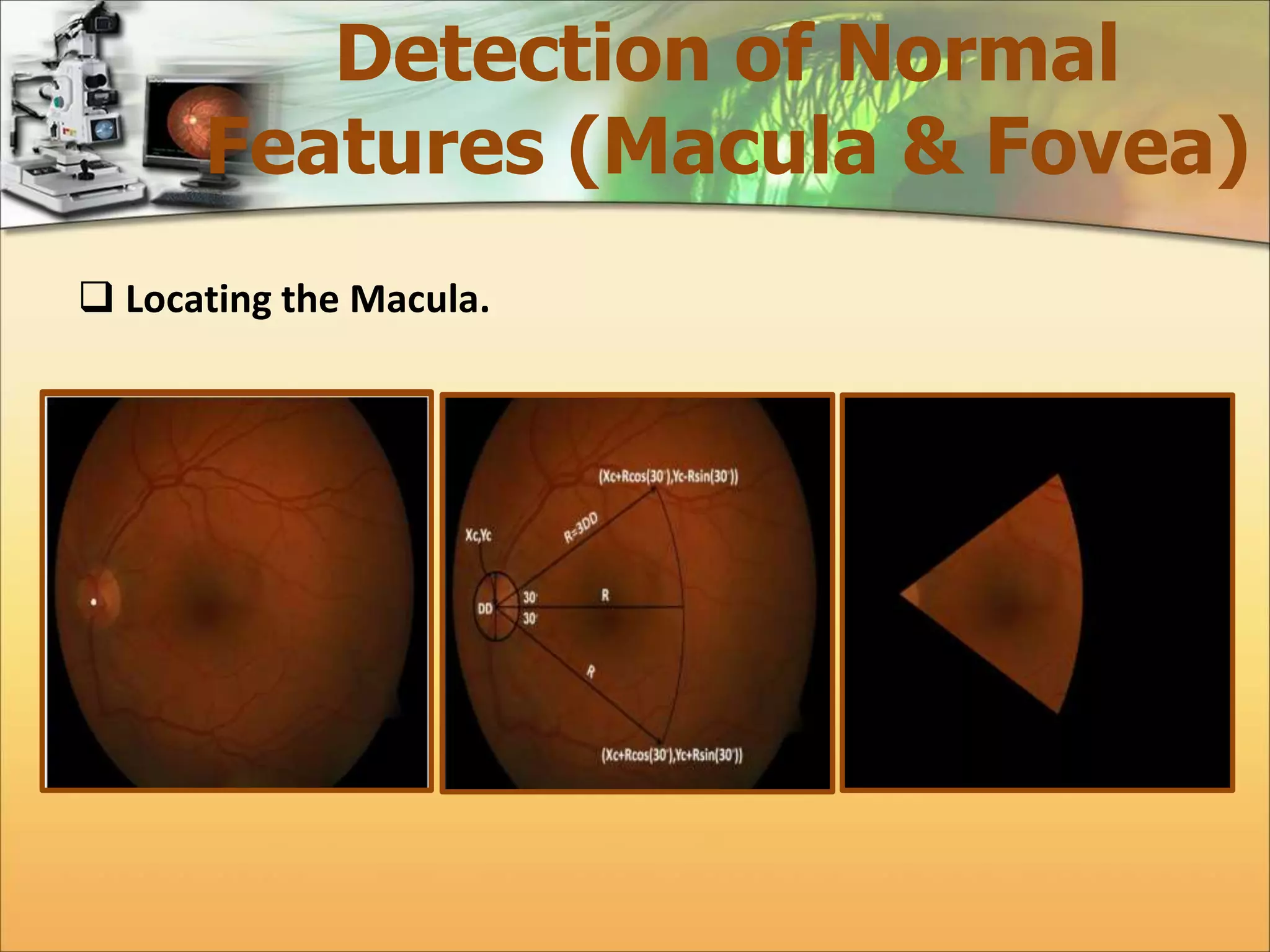
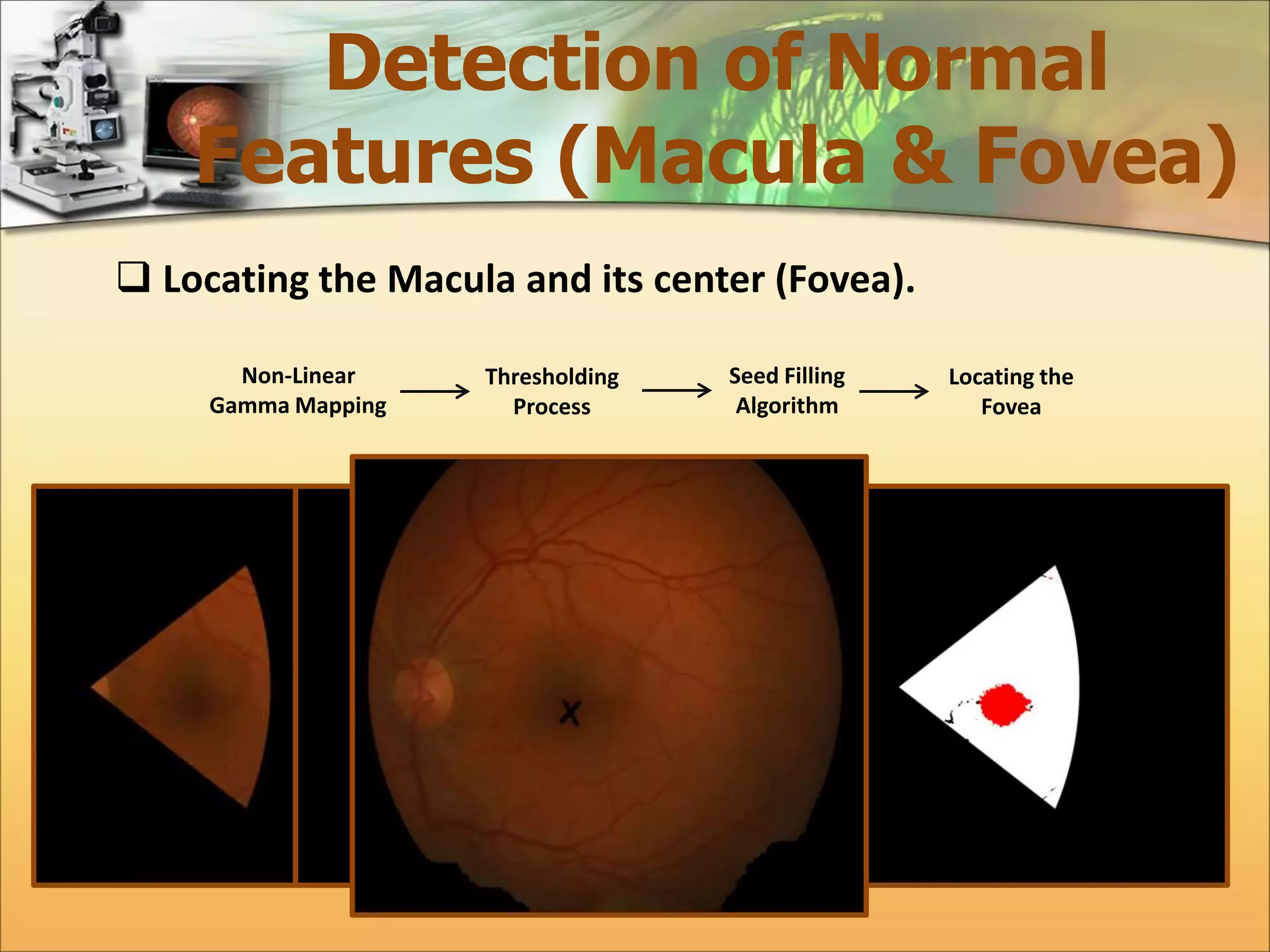
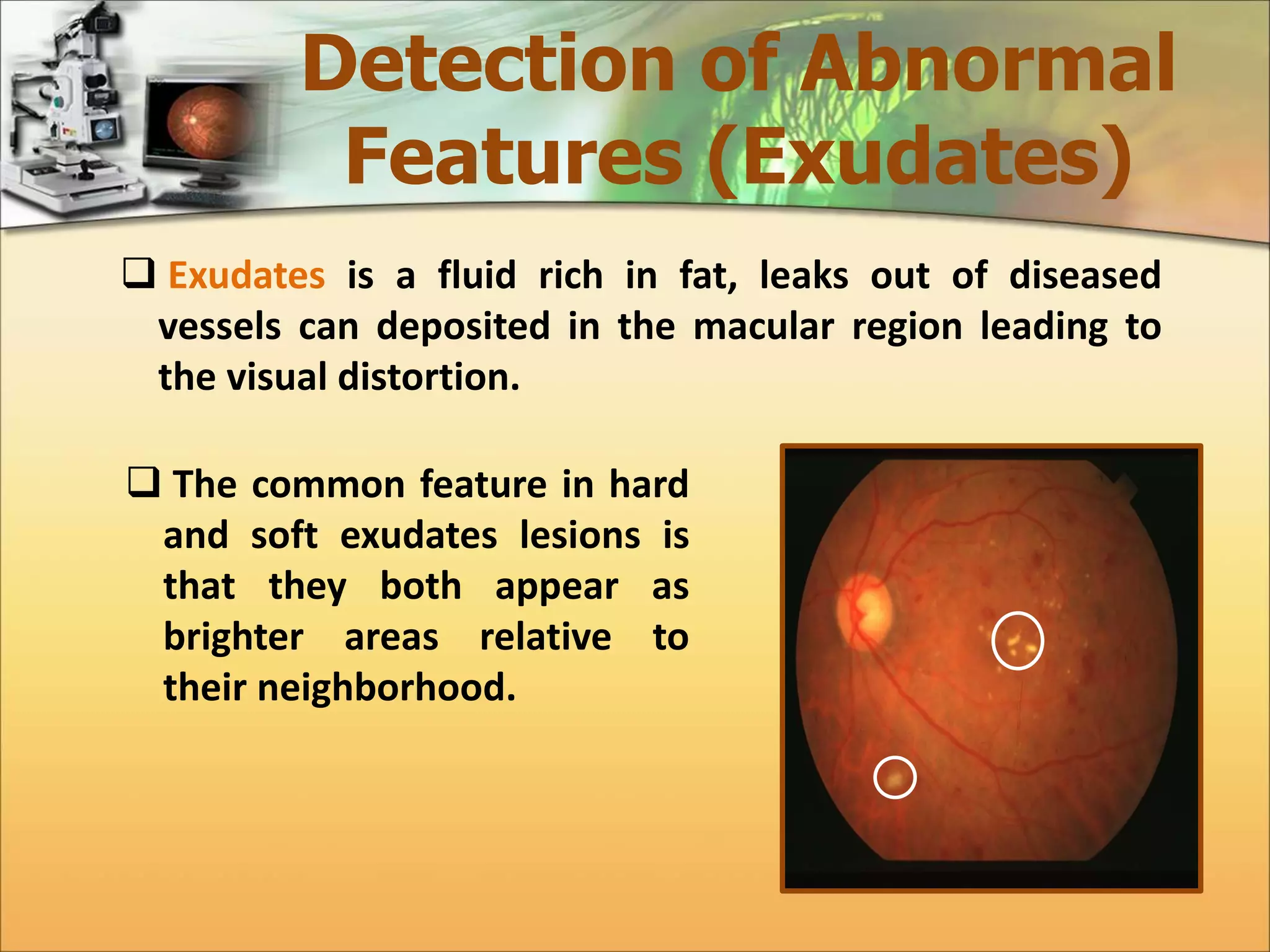
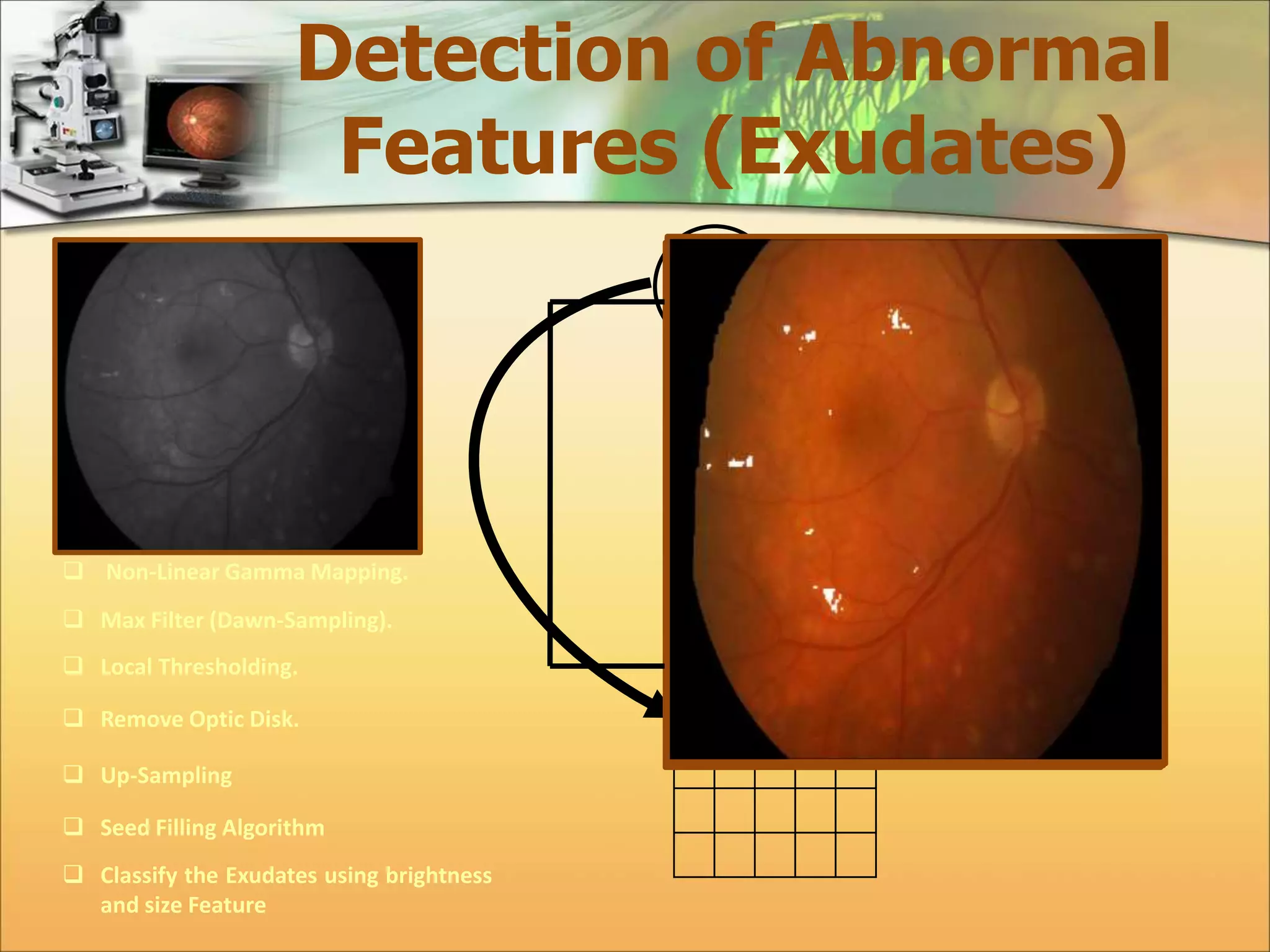
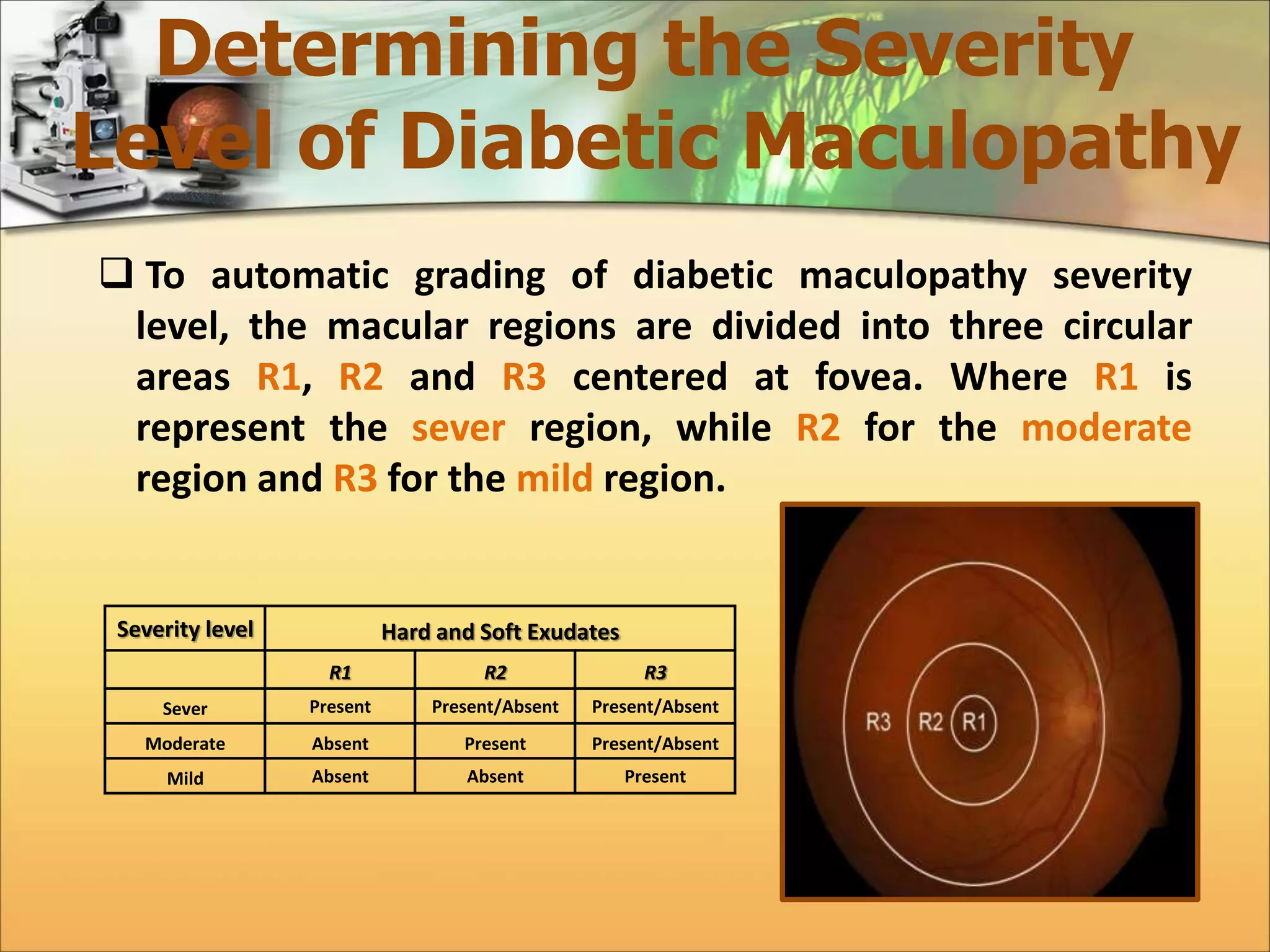
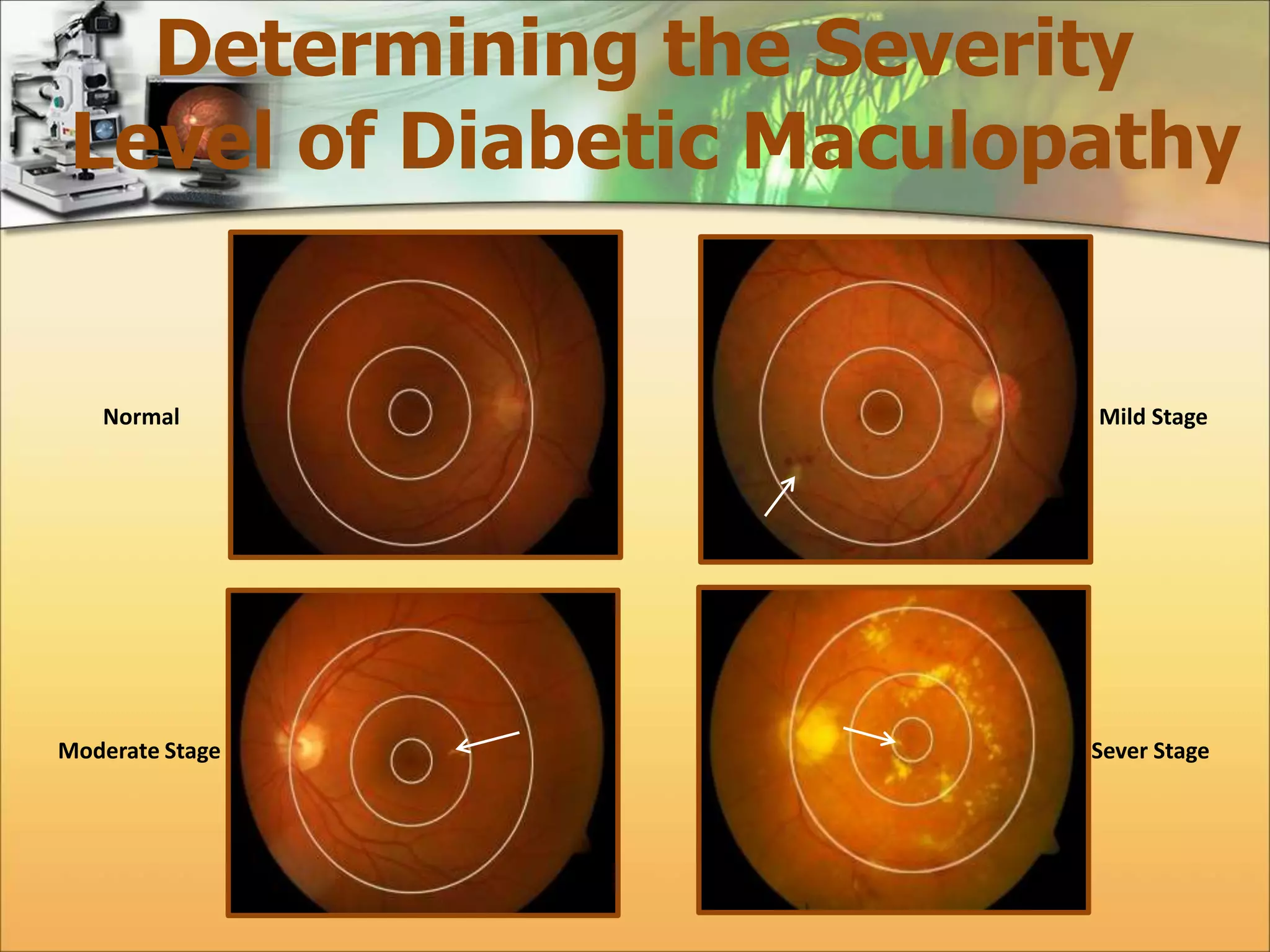
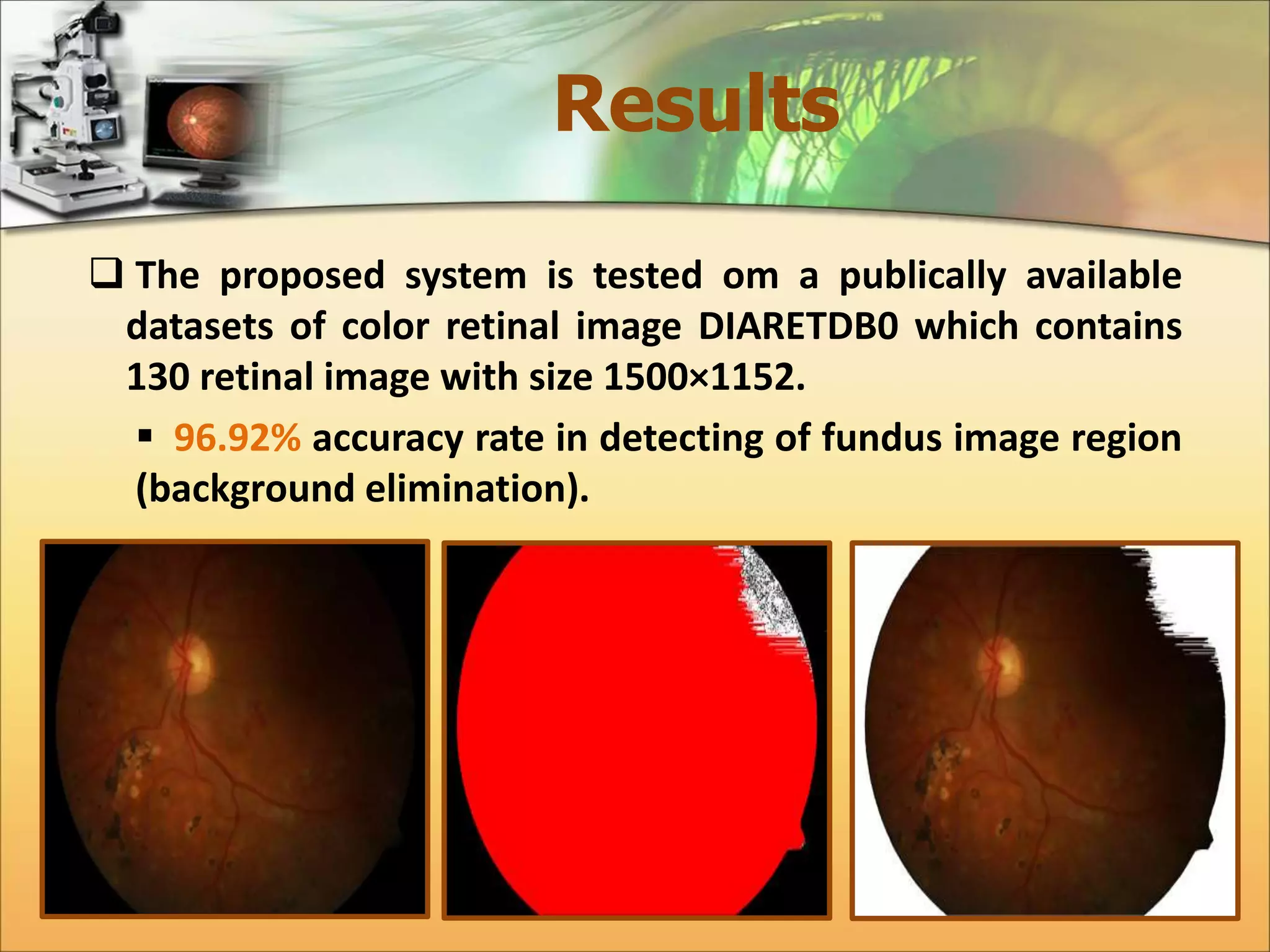
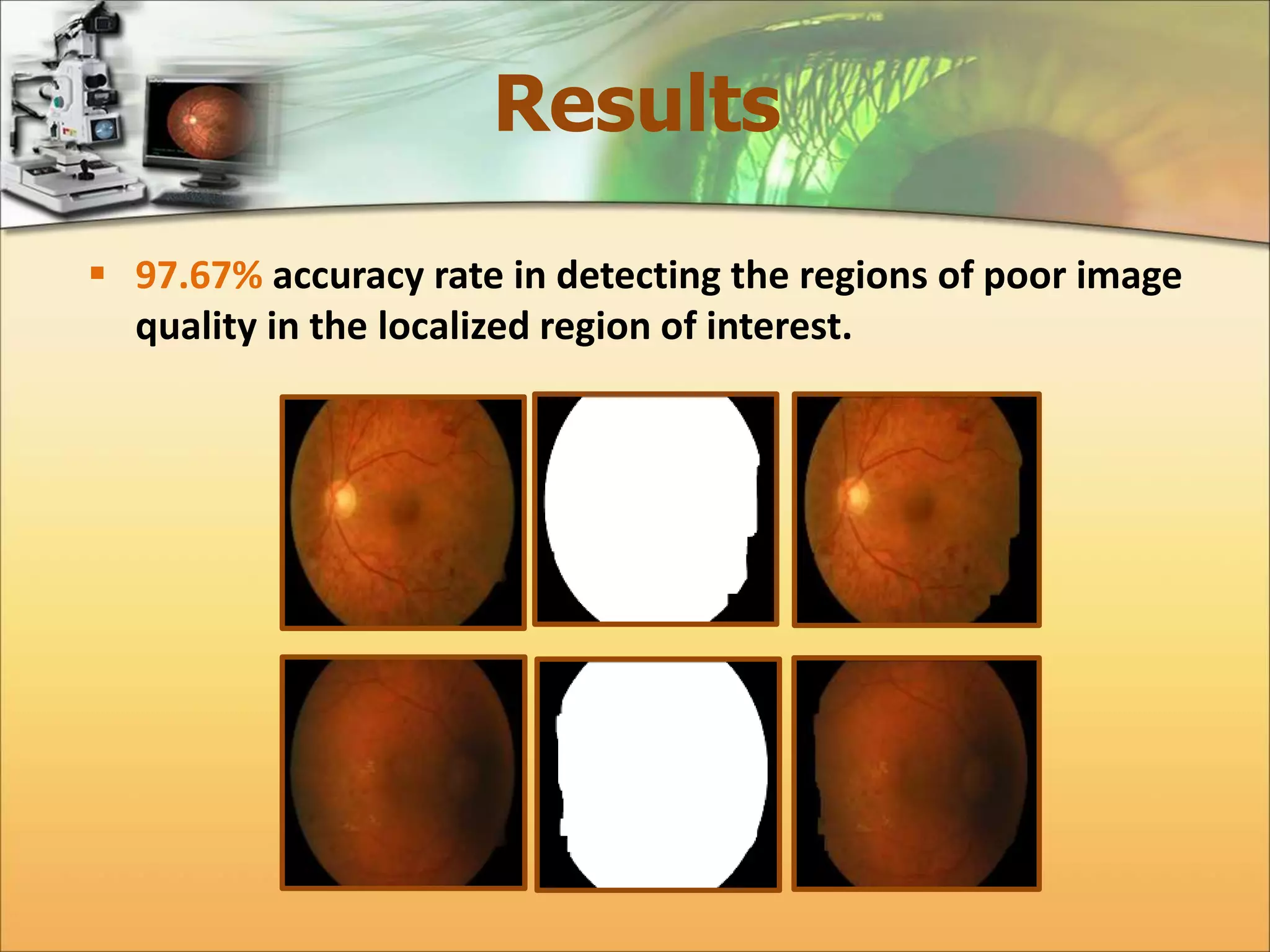
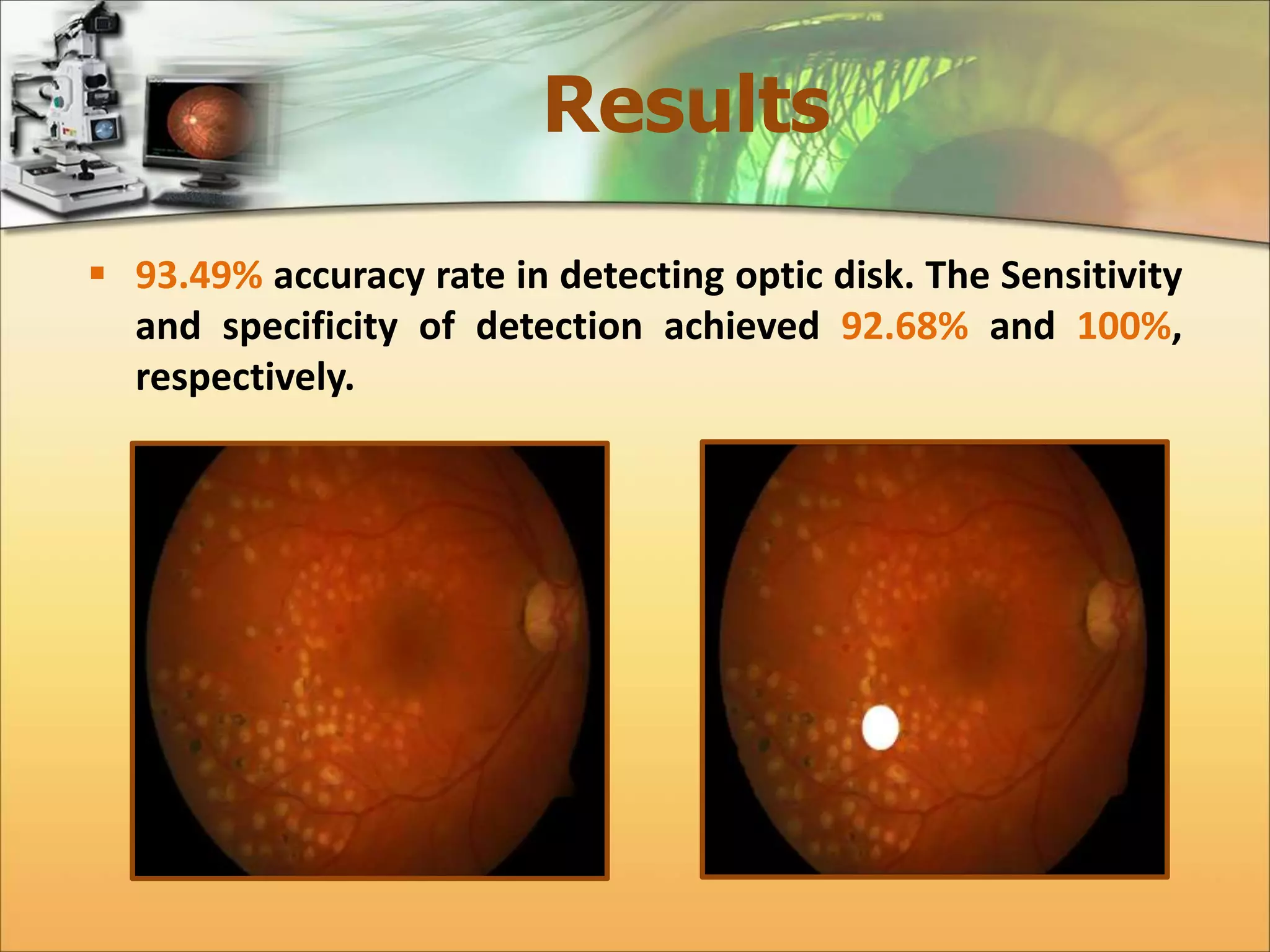
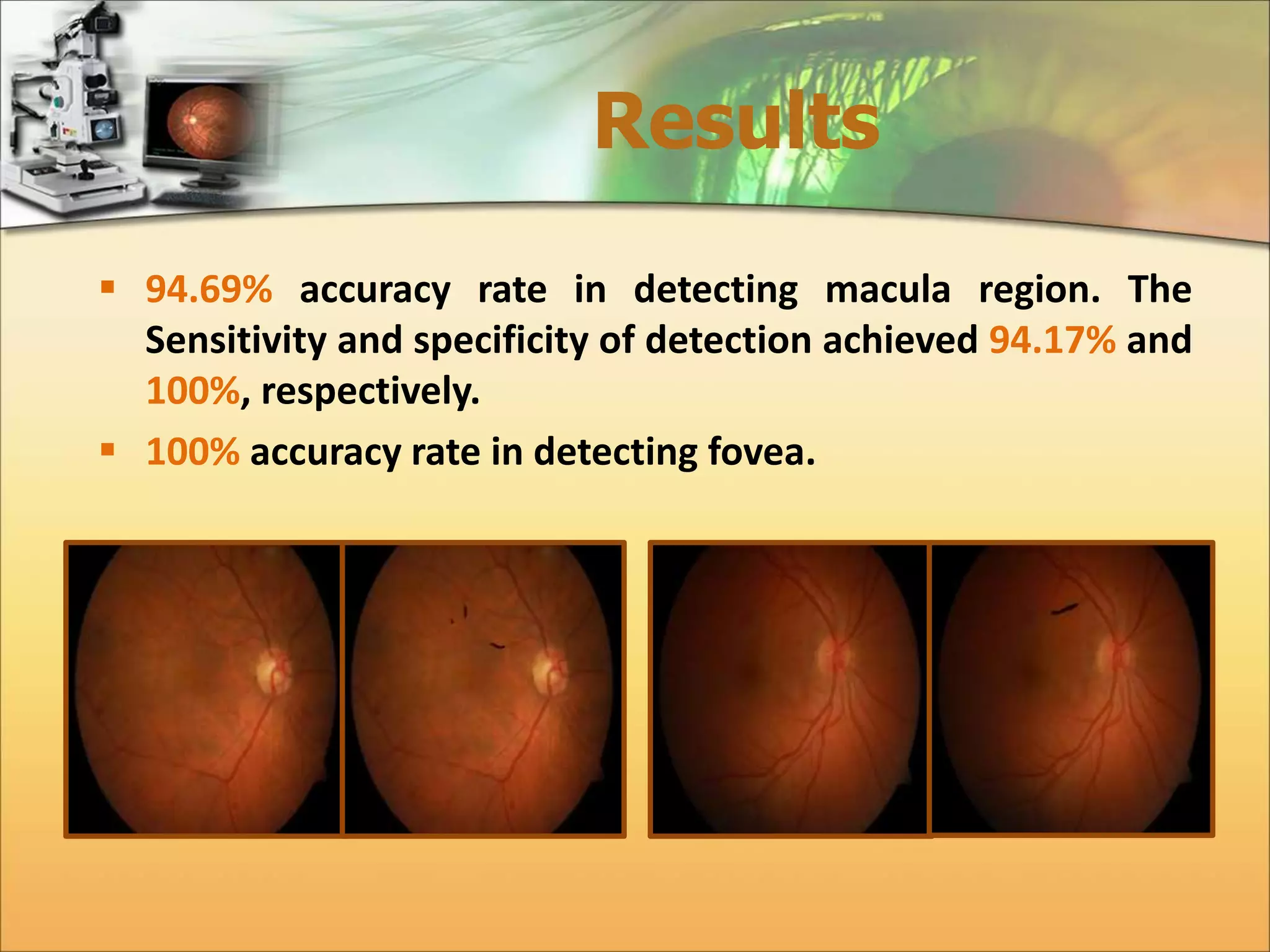
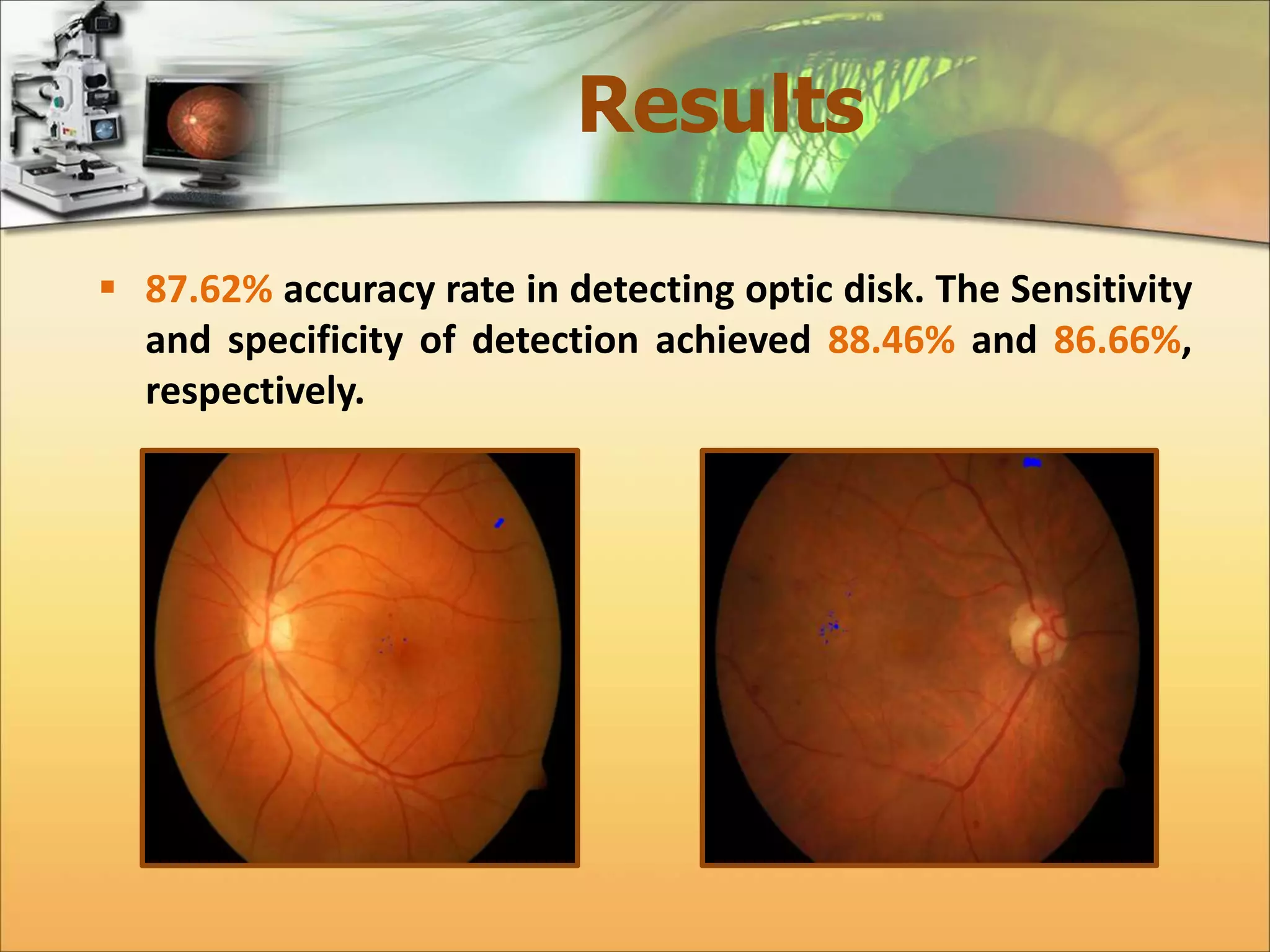
The document discusses the automatic detection of diabetic maculopathy from fundus images using image analysis techniques, highlighting the importance of identifying various retinal features. It details the methods for detecting both normal and abnormal features in retinal images, including the optic disk, macula, and exudates, as well as the severity classification of diabetic maculopathy. The proposed system demonstrates high accuracy rates in processing and analyzing retinal images, achieving significant performance in detecting various features related to diabetic retinopathy.