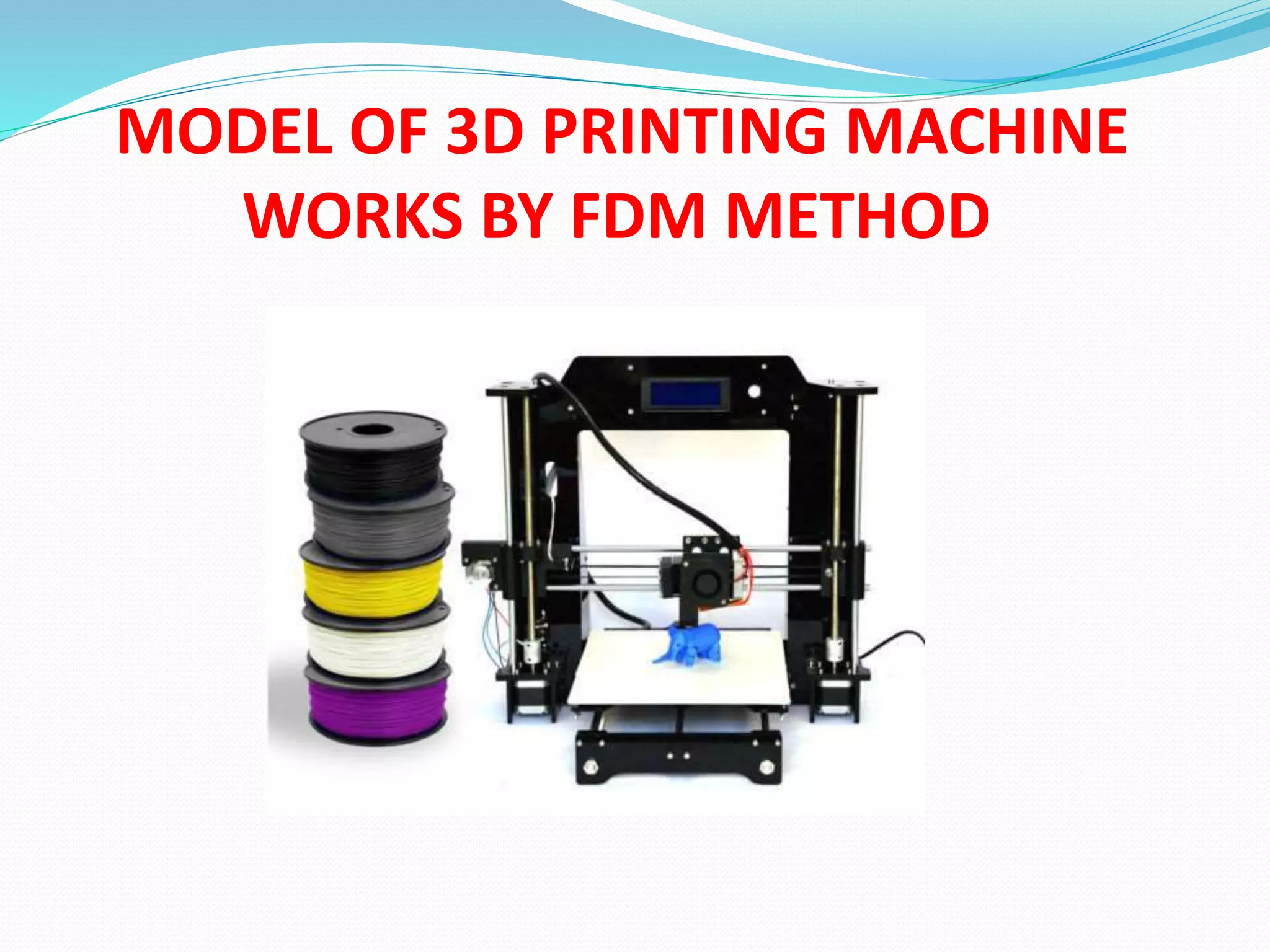
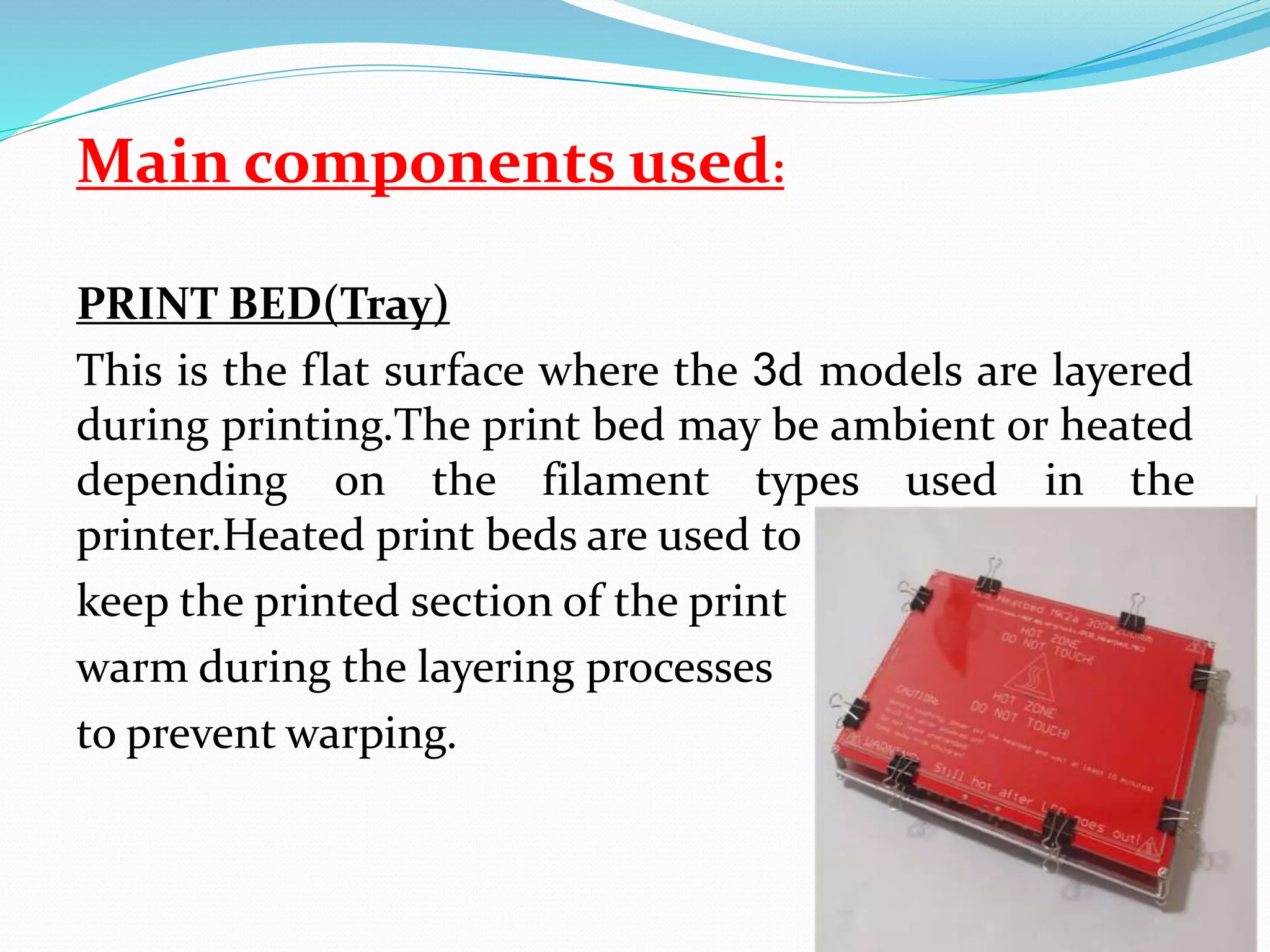
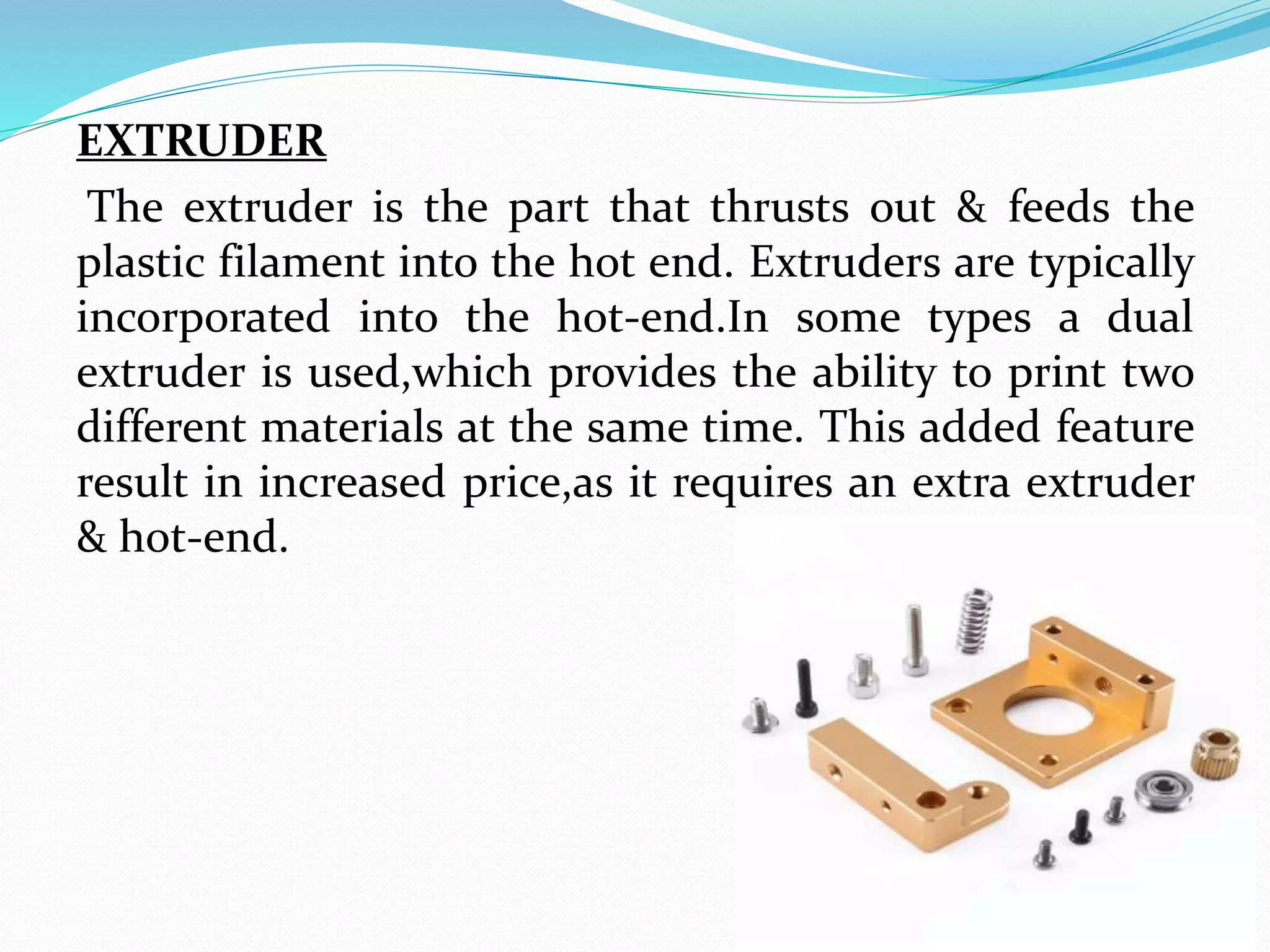
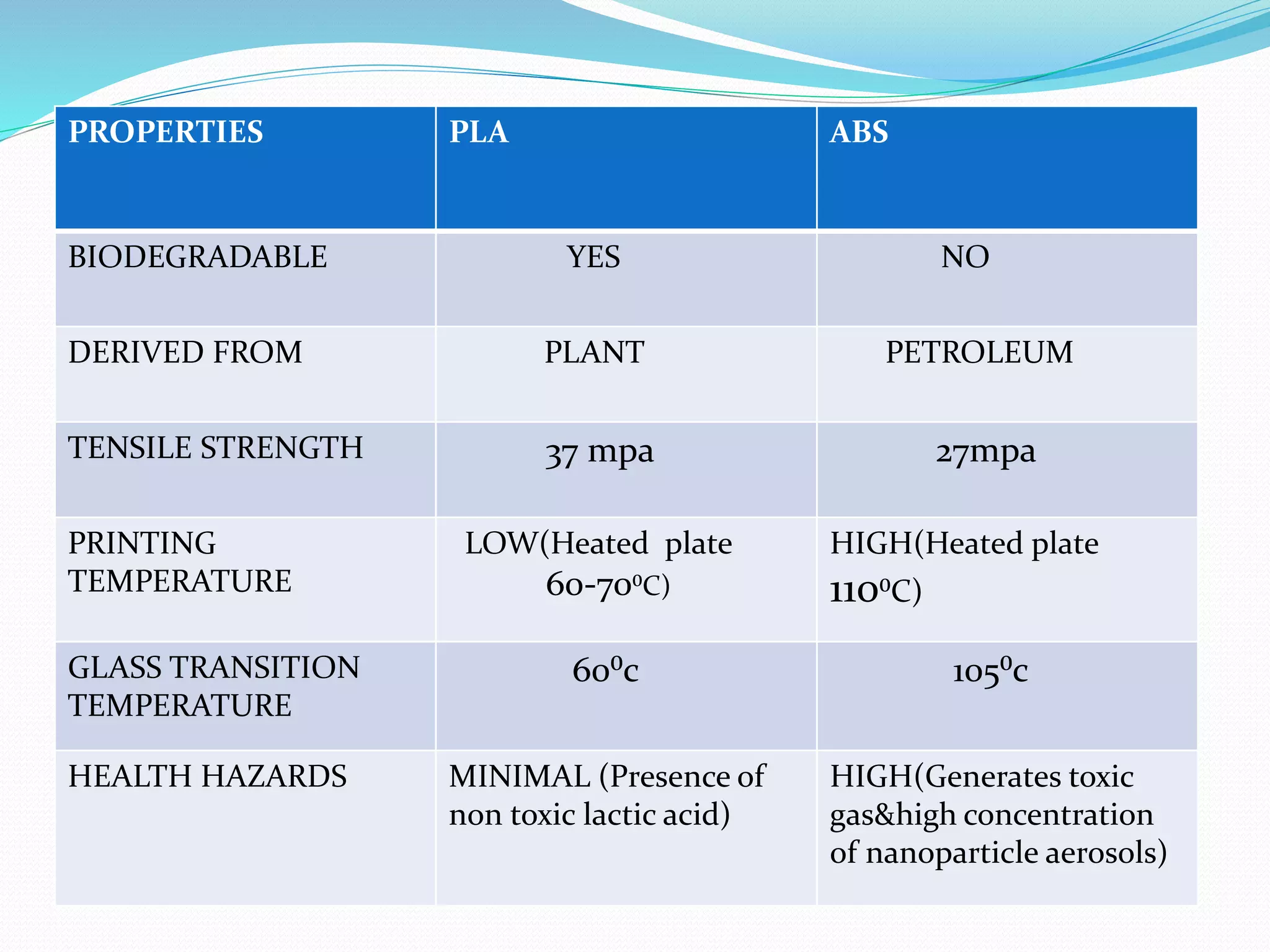
This document discusses the design and fabrication of a 3D printing machine. It provides details on the history of 3D printing, the basic process which involves layer-by-layer deposition of material, and the key components of a 3D printer including the print bed, hot end, extruder, and filament. The document outlines the progress made on building the 3D printer, describes Fused Deposition Modeling as the method used, and discusses advantages like reduced costs and limitations such as limited print size. Applications are mentioned in fields like architecture, medicine, aerospace, and optics.