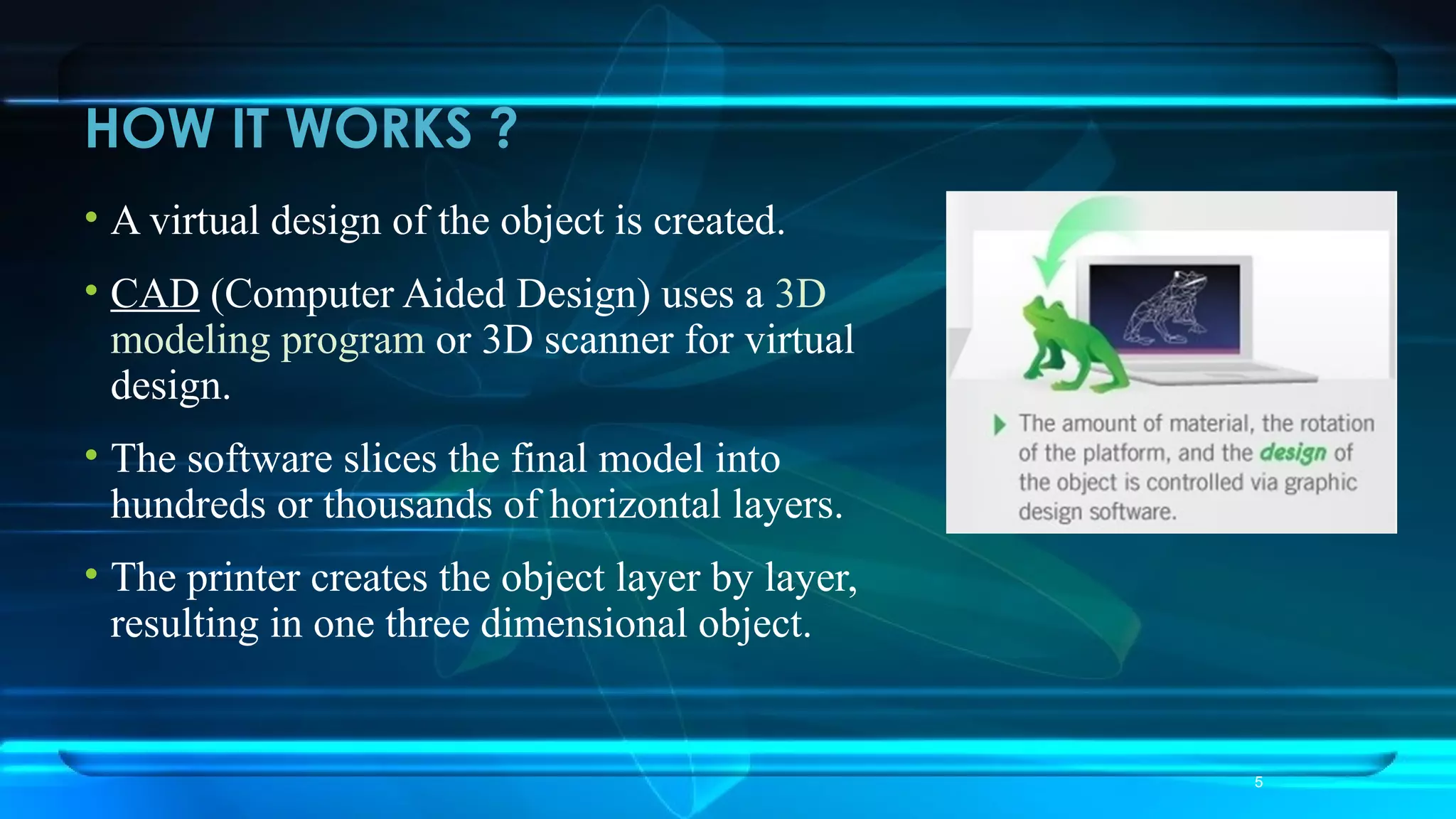
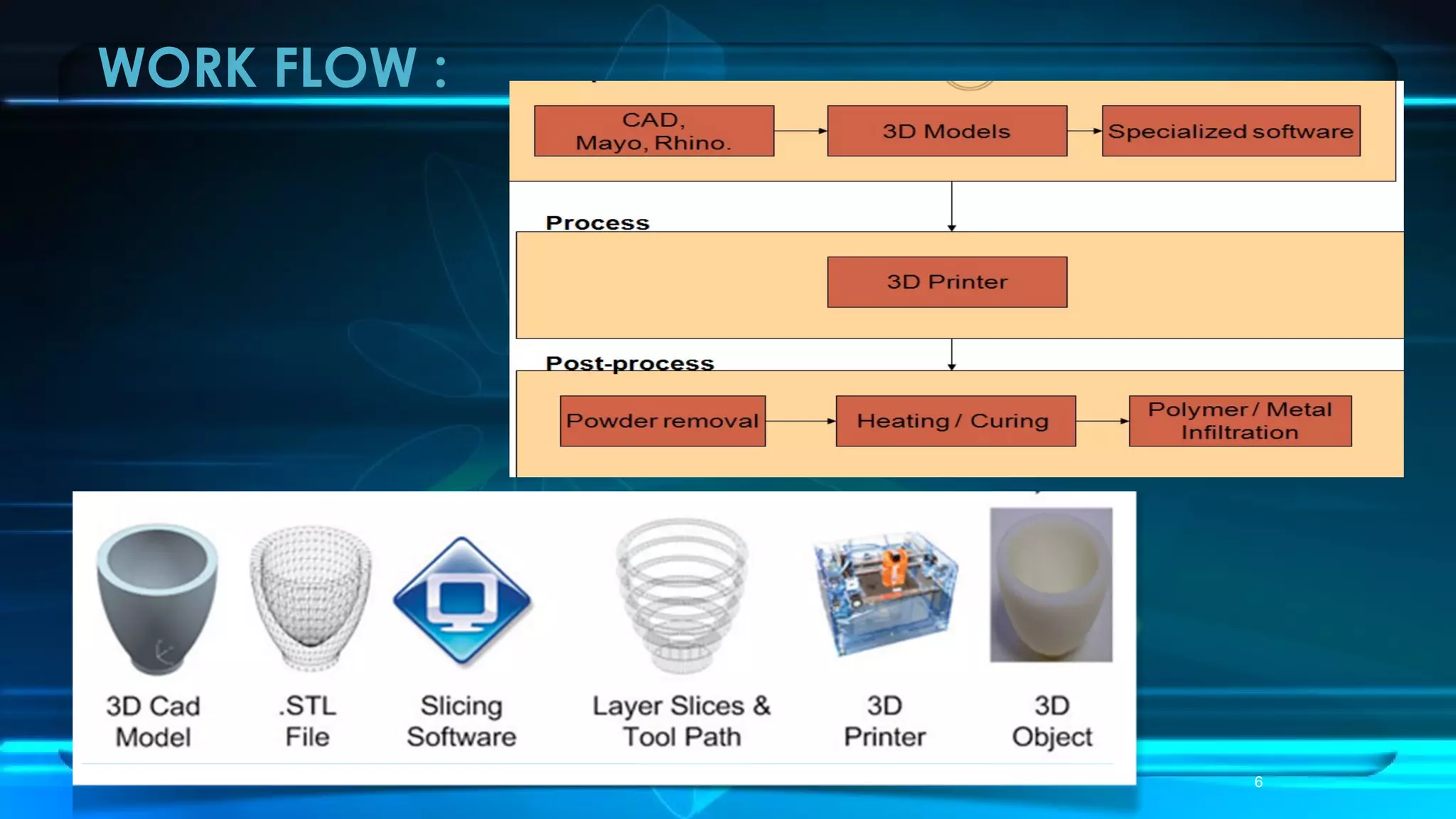
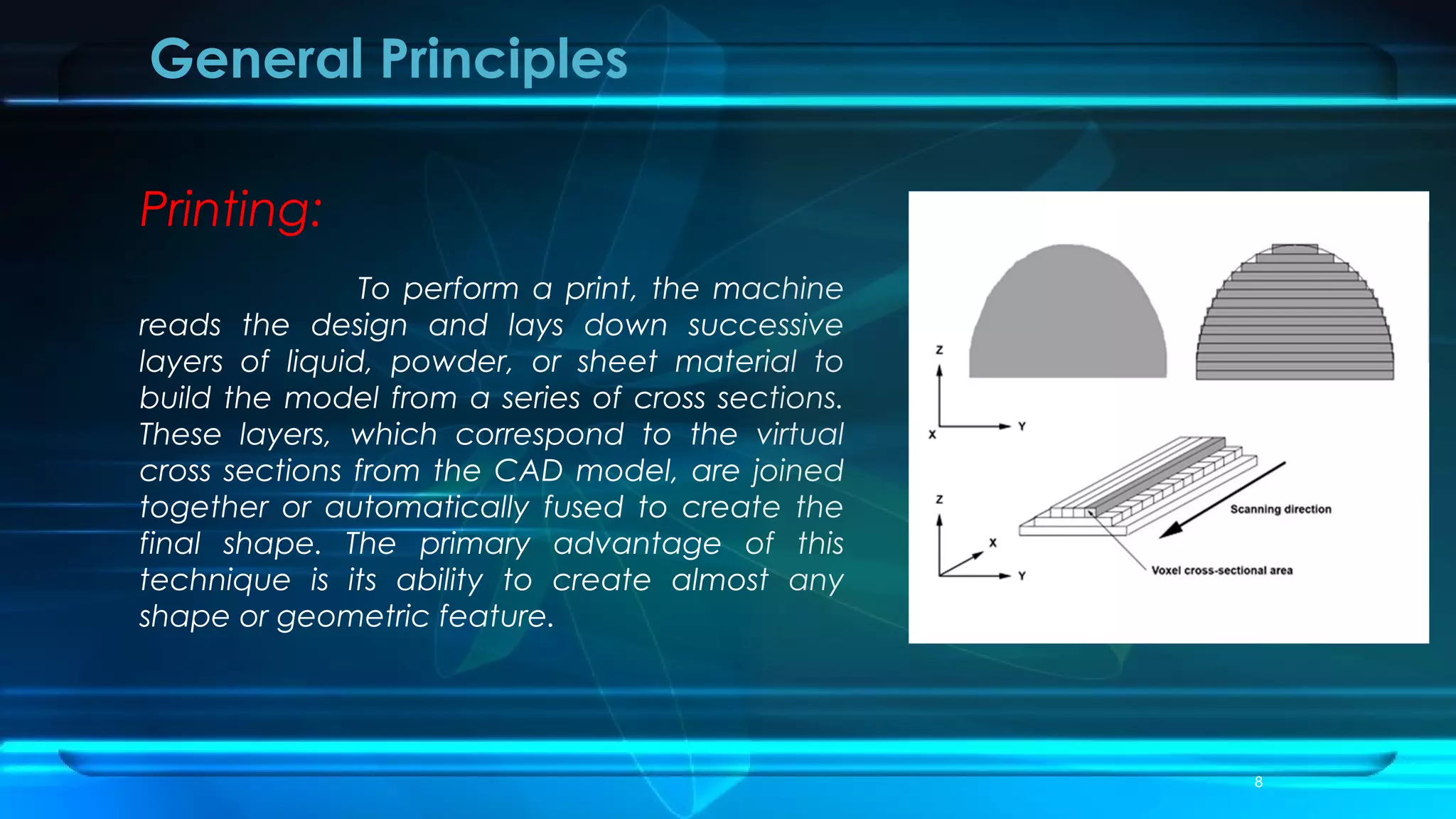
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process of making 3D objects from a digital file by successively adding material layer by layer under computer control. It works by slicing a virtual 3D model into thin horizontal layers and then producing the object by depositing one layer at a time. Applications of 3D printing include producing design prototypes, models for education, and customized medical implants and prosthetics. While the technology offers advantages like customization, there remain challenges to address such as cost, speed, and intellectual property issues.