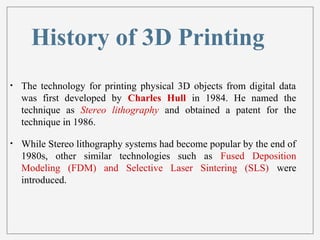
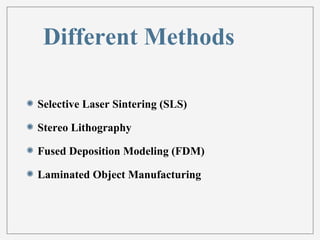
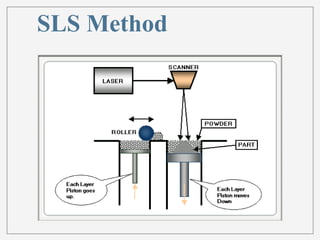
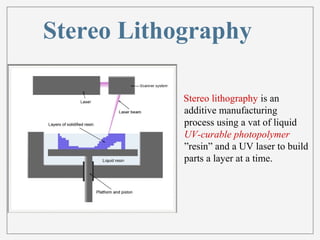
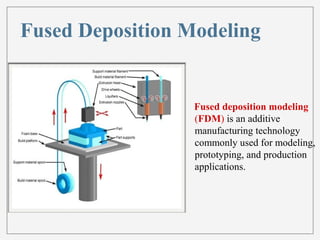
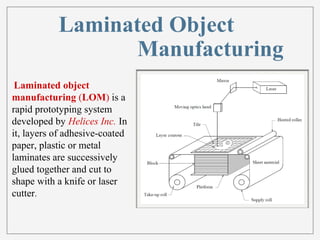
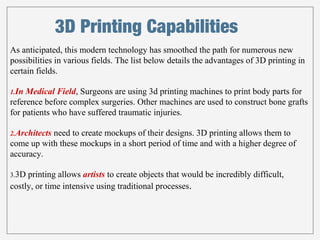
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is a technology that creates three-dimensional objects by layering materials, with its history dating back to Charles Hull's creation of stereo lithography in 1984. Various methods, such as selective laser sintering and fused deposition modeling, have emerged, enabling applications in fields like medicine, architecture, and art. Despite its advantages, including reduced product development times and costs, the full impact of 3D printing on business and society remains uncertain.