Embed presentation
Download to read offline
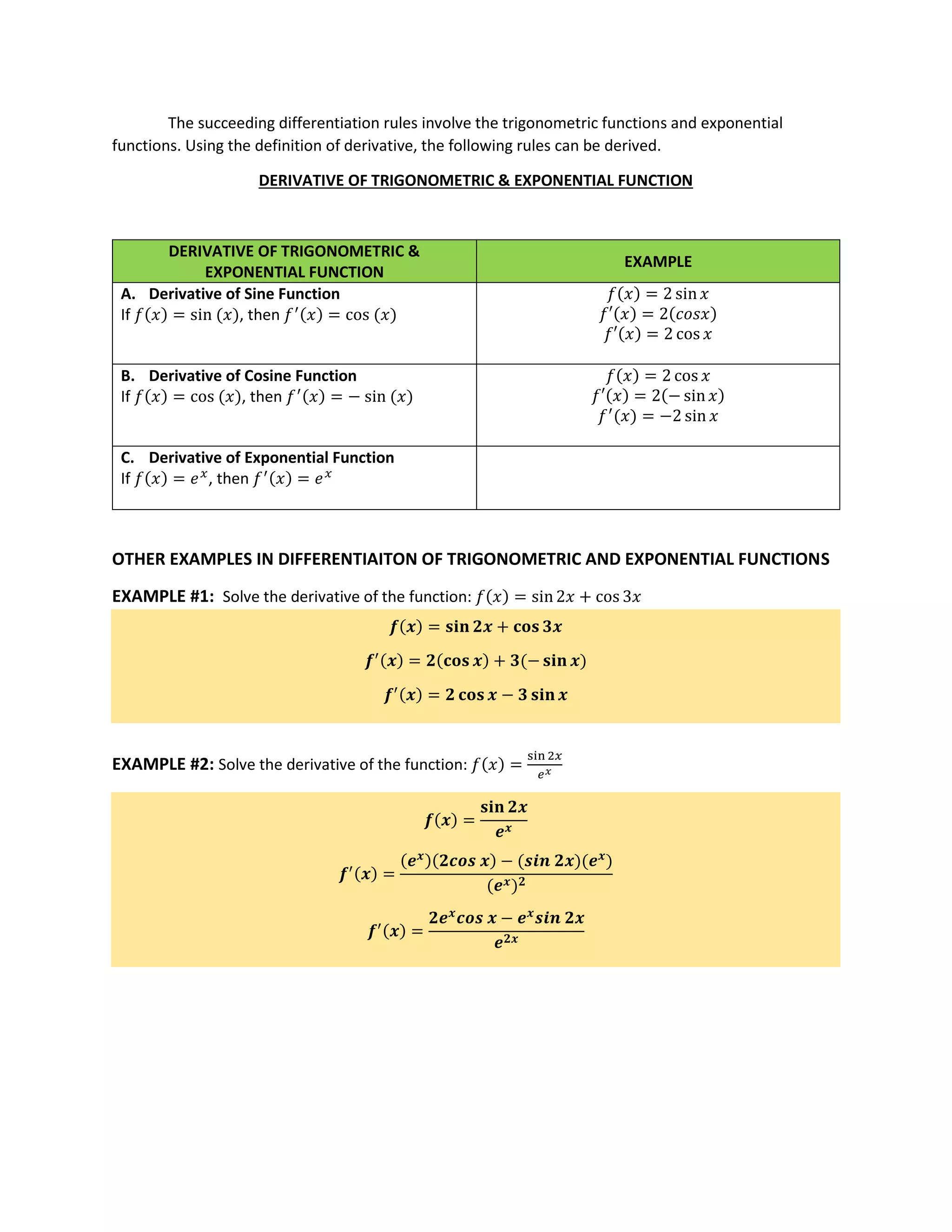
The document discusses rules for taking derivatives of trigonometric and exponential functions. It provides the derivatives of sine, cosine, and exponential functions, as well as examples of using these rules to find the derivatives of more complex functions that include trigonometric and exponential terms. Specifically, it states that the derivative of sine is cosine, the derivative of cosine is negative sine, and the derivative of an exponential function is itself. It then shows examples of finding the derivatives of f(x) = sin2x + cos 3x and f(x) = sin 2x/ex.
