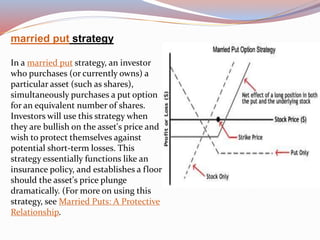
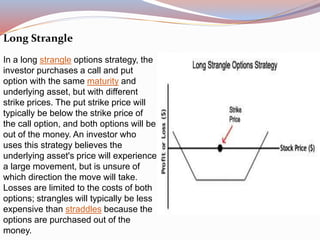
This document provides an overview of options and options strategies. It discusses that options can be used to protect investments, increase income, buy equities at lower prices, and benefit from price movements without owning the underlying asset. The benefits of options include orderly markets, flexibility, leverage, and limited risk for buyers. Several strategies are then described in detail, including covered calls, married puts, bull/bear call/put spreads, protective collars, long straddles/strangles, butterfly spreads, iron condors, and iron butterflies. Each strategy is outlined in 1-2 sentences.