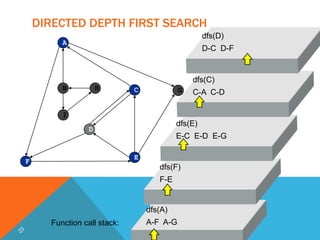
The document describes depth-first search (DFS), an algorithm for traversing or searching trees or graphs. It defines DFS, explains the process as visiting nodes by going deeper until reaching the end and then backtracking, provides pseudocode for the algorithm, gives an example on a directed graph, and discusses time complexity (O(V+E)), advantages like linear memory usage, and disadvantages like possible infinite traversal without a cutoff depth.