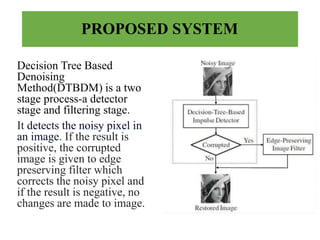
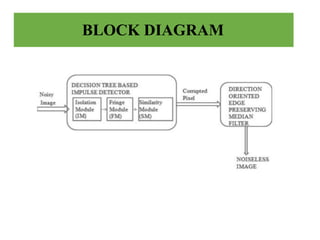
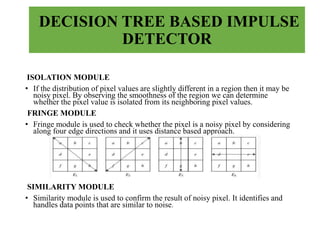
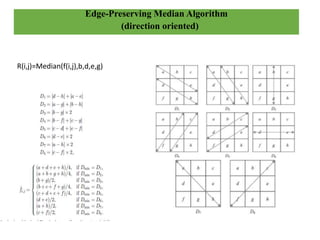
This document presents an efficient edge-preserving algorithm to remove impulse noise for Internet of Things (IoT) applications. It proposes a Decision Tree Based Denoising Method (DTBDM) with two stages: an impulse noise detector using isolation, fringe, and similarity modules to identify noisy pixels, and then an edge-preserving median filter to reconstruct the intensity values of noisy pixels while preserving edges. The DTBDM technique aims to effectively reduce impulse noise and obtain a better reconstructed image suitable for real-time IoT applications by identifying and correcting pixel values corrupted by impulse noise without blurring the overall image structure.