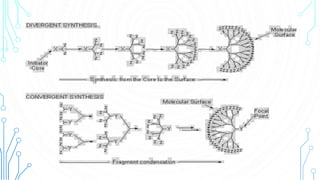
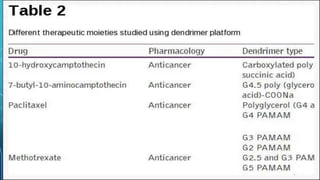
Dendrimers are nanosized, highly branched, three-dimensional molecules that were discovered in 1980. They have an interior core and interior layers made of repeating units attached to the core. Exterior layers are attached to the interior generations. Dendrimers are monodisperse, monoscale, highly soluble in water and non-polar solutions. They are synthesized using either a divergent method where the dendrimer grows from the core outwards, or a convergent method where small molecules come together and react inward to attach to the core. Dendrimers can be used to load and deliver drugs through encapsulation, electrostatic interactions, or covalent conjugation, and release drugs in response to changes in