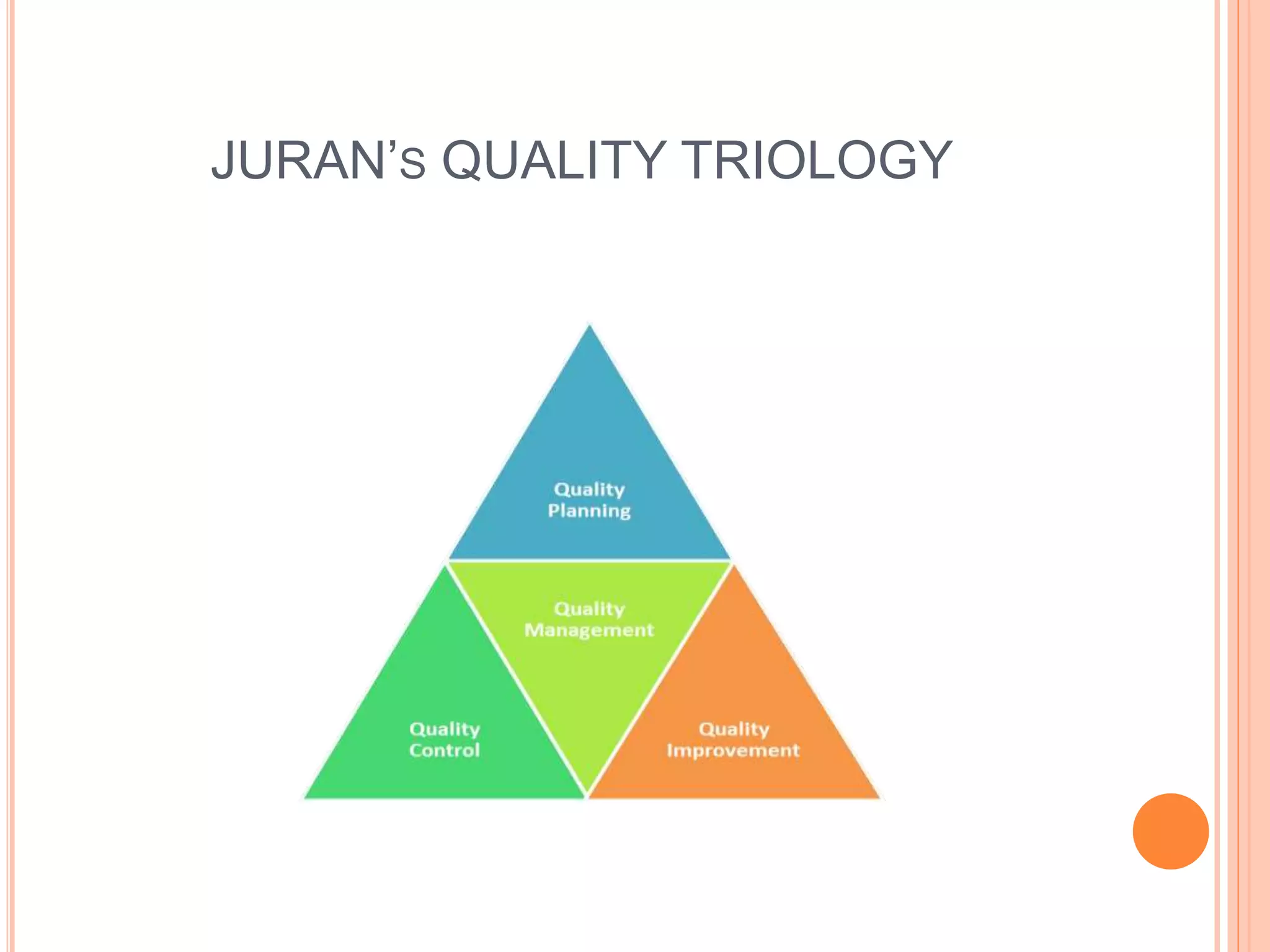
The document outlines key quality management principles proposed by Deming, Crosby, and Juran, aiming to enhance organizational effectiveness and product quality. Deming's 14 principles emphasize the need for a purpose-driven, quality-focused culture, while Crosby's steps for quality improvement stress commitment, measurement, and zero defects. Juran's trilogy presents a structured approach to quality management through awareness, goal setting, and continuous improvement processes.