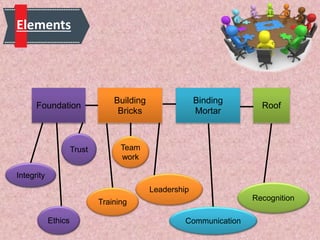
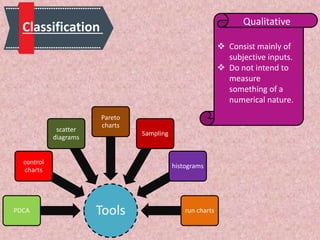
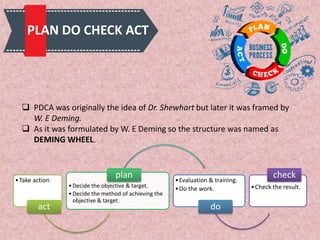
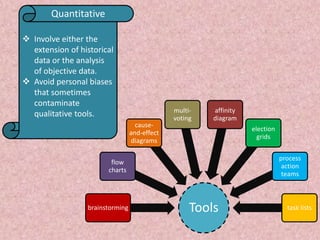
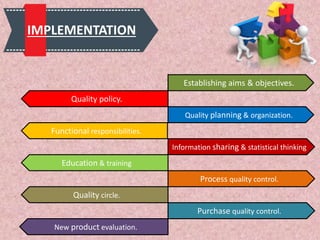
Total Quality Management (TQM) is a methodology derived from Japanese industry that focuses on continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. It involves organizing the entire organization around quality principles from top management down. Some key aspects of TQM include participative management, following Deming's 14 principles, using tools like PDCA cycles, and implementing aspects like training, teamwork, and leadership. Companies like Apple, Xerox, and Ford have benefited from implementing TQM through improved quality, productivity, and profitability.